A Comprehensive Guide to Mapping Africa: Understanding its Importance and Benefits
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Mapping Africa: Understanding its Importance and Benefits
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Mapping Africa: Understanding its Importance and Benefits. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Mapping Africa: Understanding its Importance and Benefits

The African continent, a vast and diverse landmass, is often depicted on maps as a monolithic entity. However, a closer examination reveals a tapestry of distinct landscapes, cultures, and histories. Understanding the geography of Africa is crucial for comprehending its complexities and appreciating its unique characteristics.
Delving into the Continent’s Geographic Features:
Africa’s map is defined by its striking physical features, each contributing to the continent’s diverse ecosystems and rich cultural heritage.
1. Topography and Landforms:
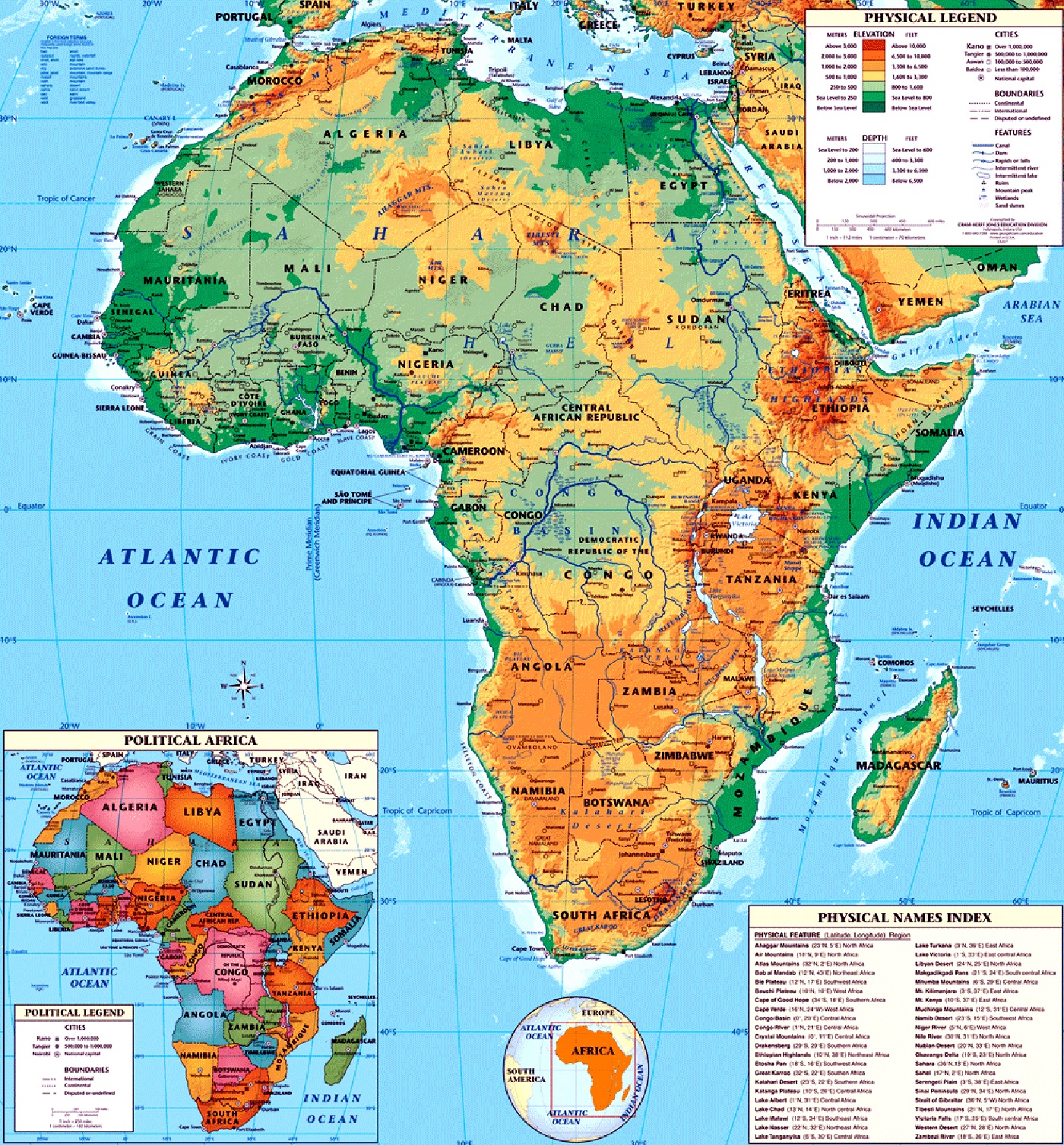
- The Great Rift Valley: This geological marvel, stretching over 6,000 kilometers, is a testament to the Earth’s tectonic activity. It creates a dramatic landscape with towering cliffs, volcanic peaks, and fertile valleys, shaping the lives of millions across the continent.
- Mount Kilimanjaro: The highest mountain in Africa, reaching over 5,895 meters, is a magnificent sight, attracting climbers and adventurers alike. Its snow-capped peak stands in stark contrast to the surrounding savannas, a symbol of Africa’s dramatic landscape.
- The Sahara Desert: The largest hot desert in the world, the Sahara stretches across vast swathes of North Africa. Its unforgiving environment presents unique challenges and opportunities, influencing human settlements and shaping traditional cultures.
- The Congo Basin: Home to the second-largest rainforest in the world, the Congo Basin is a biodiversity hotspot, teeming with diverse flora and fauna. Its dense vegetation and intricate river systems contribute significantly to the global climate.
- The Nile River: The longest river in the world, the Nile flows through eleven countries, providing life-sustaining water for millions. Its historical significance is immense, playing a crucial role in the development of ancient civilizations and shaping the cultural identity of the region.
2. Climate and Weather Patterns:
Africa’s diverse climate zones are influenced by factors like latitude, altitude, and proximity to oceans.
- Tropical Climates: Dominating the equatorial regions, tropical climates are characterized by high temperatures and significant rainfall, supporting lush rainforests and diverse ecosystems.
- Arid Climates: The Sahara and other desert regions experience extreme temperatures, with limited rainfall and harsh conditions.
- Mediterranean Climates: Coastal regions in North Africa experience mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers, fostering unique flora and fauna.
- Subtropical Climates: These regions, found in South Africa and parts of the east coast, experience warm temperatures year-round with distinct wet and dry seasons.
3. Natural Resources:
Africa is rich in natural resources, ranging from minerals and fossil fuels to fertile land and abundant water resources.
- Mineral Resources: The continent boasts significant reserves of gold, diamonds, platinum, copper, and iron ore, playing a crucial role in global trade and economies.
- Fossil Fuels: Africa possesses substantial oil and natural gas reserves, contributing significantly to global energy production.
- Agricultural Resources: Vast tracts of fertile land, coupled with favorable climates, support a diverse range of agricultural activities, including coffee, cocoa, cotton, and grains.
- Water Resources: The continent’s extensive river systems, lakes, and groundwater resources provide vital water for human consumption, agriculture, and industry.
Understanding the Importance of Mapping Africa:
Mapping Africa is not merely an academic exercise; it holds immense practical and societal value.
1. Spatial Planning and Development:
Accurate maps are essential for planning and managing infrastructure development, resource allocation, and urban expansion. By understanding the distribution of resources, topography, and population density, policymakers can make informed decisions about infrastructure projects, housing development, and sustainable land use.
2. Environmental Management and Conservation:
Mapping Africa’s ecosystems, biodiversity hotspots, and protected areas is crucial for environmental management and conservation efforts. It allows for the identification of vulnerable areas, the monitoring of deforestation and habitat loss, and the development of effective conservation strategies.
3. Disaster Response and Humanitarian Aid:
In the face of natural disasters, accurate maps are vital for coordinating rescue efforts, delivering aid to affected populations, and planning evacuation routes. They provide crucial information about terrain, infrastructure, and population distribution, enabling efficient and effective response.
4. Health and Disease Control:
Mapping disease prevalence, population density, and access to healthcare facilities is essential for public health initiatives. It enables the identification of vulnerable communities, the targeting of disease prevention programs, and the efficient distribution of healthcare resources.
5. Tourism and Recreation:
Maps play a vital role in promoting tourism and recreation, providing information about attractions, routes, and accommodation. Detailed maps encourage exploration, enhance travel experiences, and contribute to the economic development of tourism-dependent communities.
6. Education and Awareness:
Mapping Africa fosters a deeper understanding of the continent’s diverse cultures, landscapes, and challenges. It provides a visual representation of the continent’s interconnectedness and highlights the importance of cross-cultural exchange and cooperation.
FAQs about Mapping Africa:
1. What are the challenges associated with mapping Africa?
Mapping Africa presents several challenges, including:
- Data scarcity: Limited access to accurate and comprehensive data, especially in remote areas, can hinder the development of detailed and reliable maps.
- Political instability: Conflict and political unrest can disrupt mapping projects and restrict access to certain regions.
- Lack of infrastructure: Limited infrastructure, such as roads and communication networks, can make mapping expeditions difficult and costly.
- Technological limitations: Traditional mapping techniques may not be suitable for capturing the complexities of Africa’s terrain and diverse ecosystems.
2. What are the latest advancements in mapping Africa?
Recent advancements in technology, such as remote sensing, satellite imagery, and geographic information systems (GIS), have revolutionized mapping Africa. These technologies enable:
- High-resolution mapping: Detailed and accurate maps capturing the intricate details of landscapes and infrastructure.
- Real-time data acquisition: Continuous monitoring of changes in land use, environmental conditions, and population distribution.
- 3D modeling: Creating immersive virtual representations of African landscapes, enhancing understanding and visualization.
- Data sharing and collaboration: Facilitating the exchange of information and collaboration between researchers, policymakers, and organizations.
3. How can I contribute to mapping Africa?
Individuals can contribute to mapping Africa in various ways:
- Support organizations involved in mapping projects.
- Participate in citizen science initiatives.
- Use and promote accurate maps of Africa.
- Advocate for increased investment in mapping infrastructure and research.
- Share information and resources about Africa’s geography.
Tips for Drawing the Map of Africa:
- Start with a basic outline: Use a compass and ruler to create a rough outline of the continent’s shape.
- Focus on key features: Highlight major geographical features like the Great Rift Valley, the Sahara Desert, the Nile River, and Mount Kilimanjaro.
- Incorporate color and detail: Use different colors to represent different regions, ecosystems, and landforms.
- Include important cities and landmarks: Mark major cities, historical sites, and national parks.
- Add a scale and compass: Ensure the map is accurate and easy to navigate.
- Consider using digital tools: Utilize online mapping software or GIS platforms for more detailed and interactive maps.
Conclusion:
Mapping Africa is a crucial undertaking, offering invaluable insights into the continent’s geography, resources, and complexities. By understanding its diverse landscapes, ecosystems, and cultural heritage, we can foster a deeper appreciation for Africa’s unique characteristics and contribute to its sustainable development. Through continued advancements in mapping technology and collaborative efforts, we can create a more accurate and comprehensive representation of this vast and vibrant continent, paving the way for a brighter future for all.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Mapping Africa: Understanding its Importance and Benefits. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!