A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of China: Understanding the Land of the Rising Sun
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of China: Understanding the Land of the Rising Sun
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of China: Understanding the Land of the Rising Sun. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of China: Understanding the Land of the Rising Sun
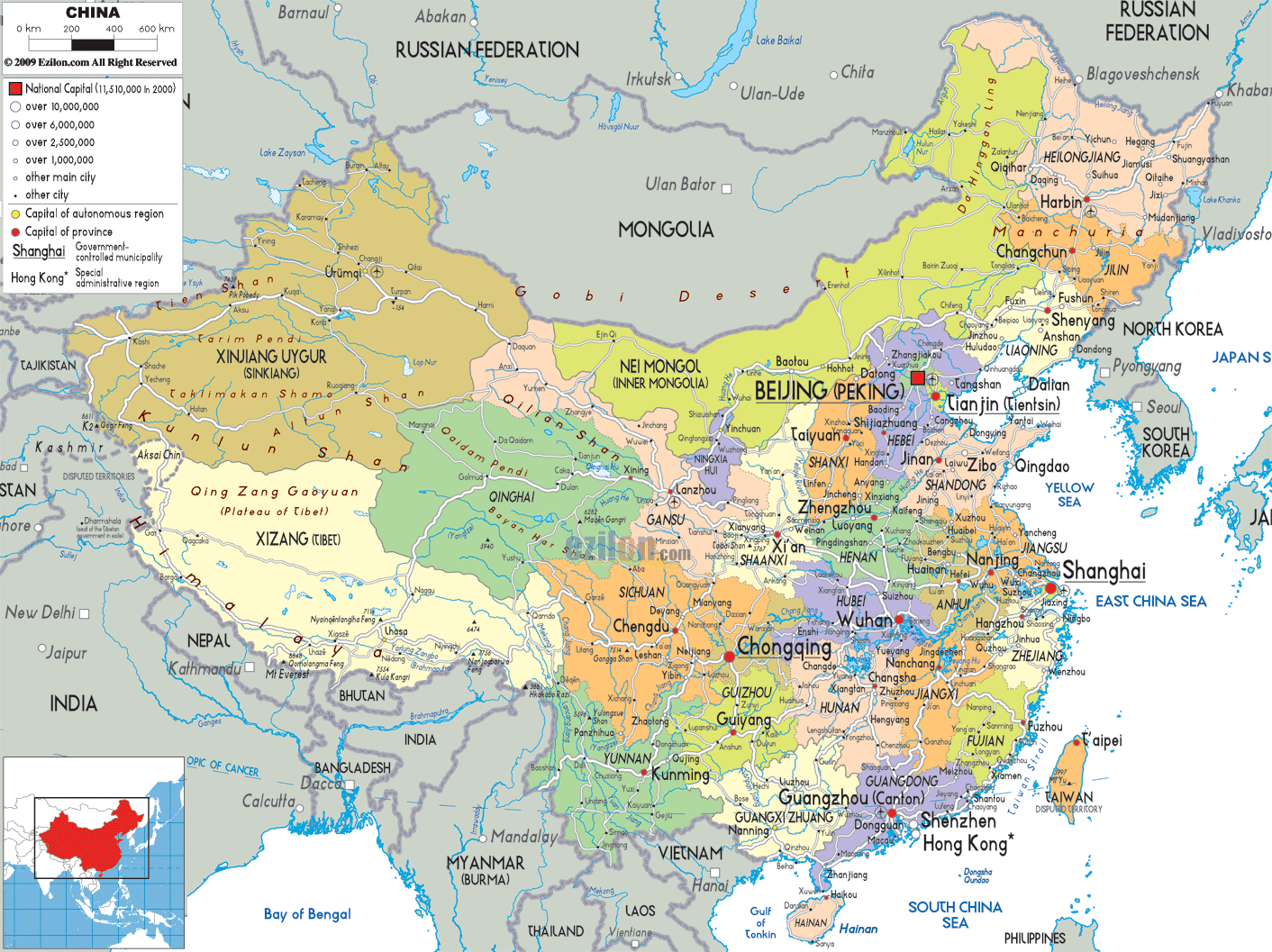
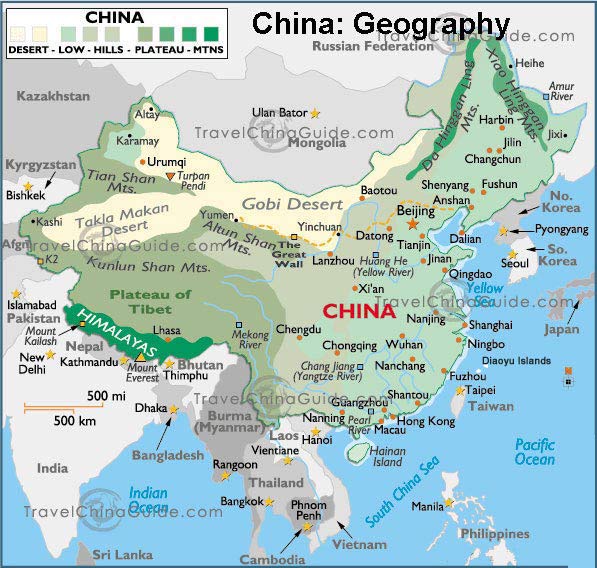
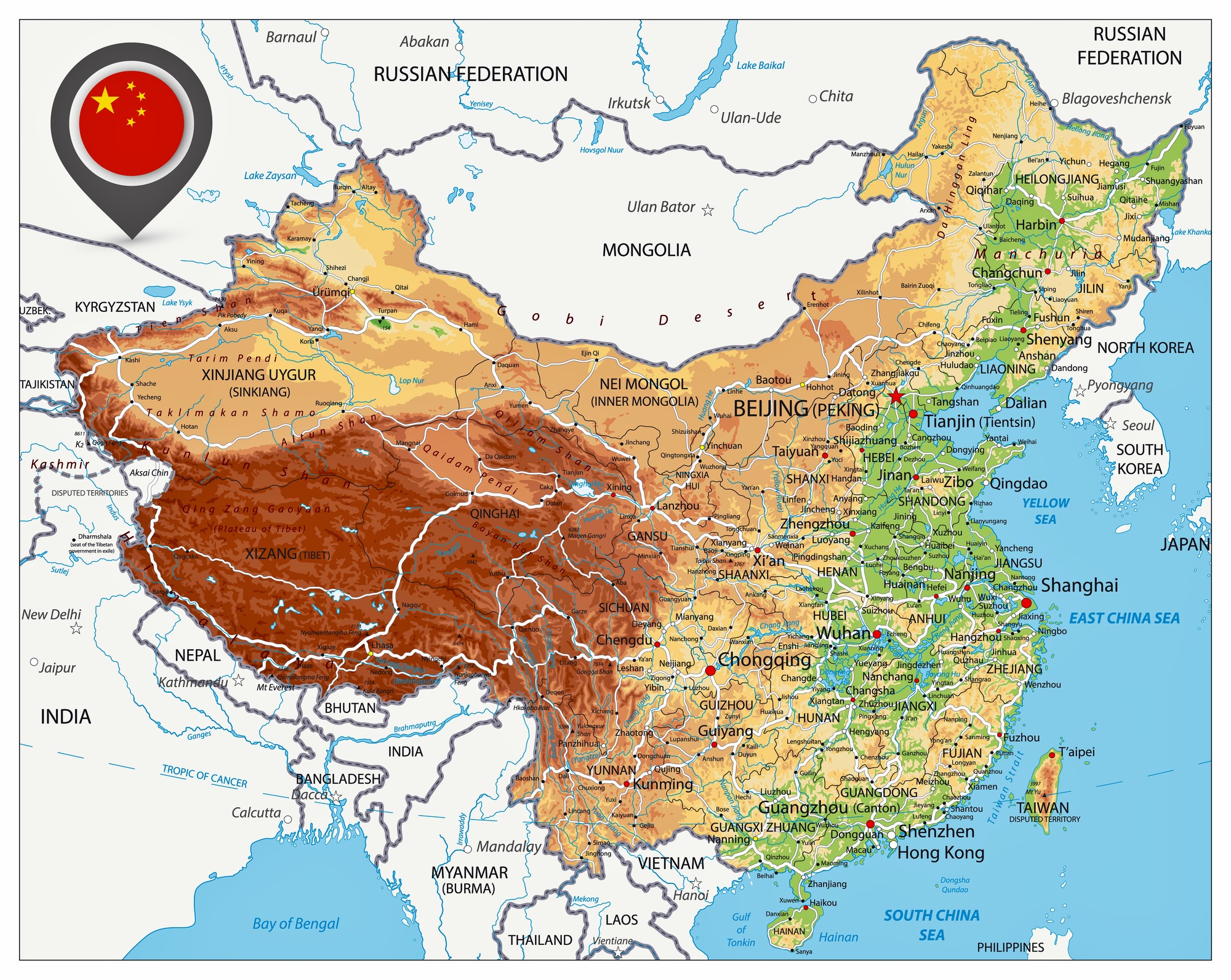
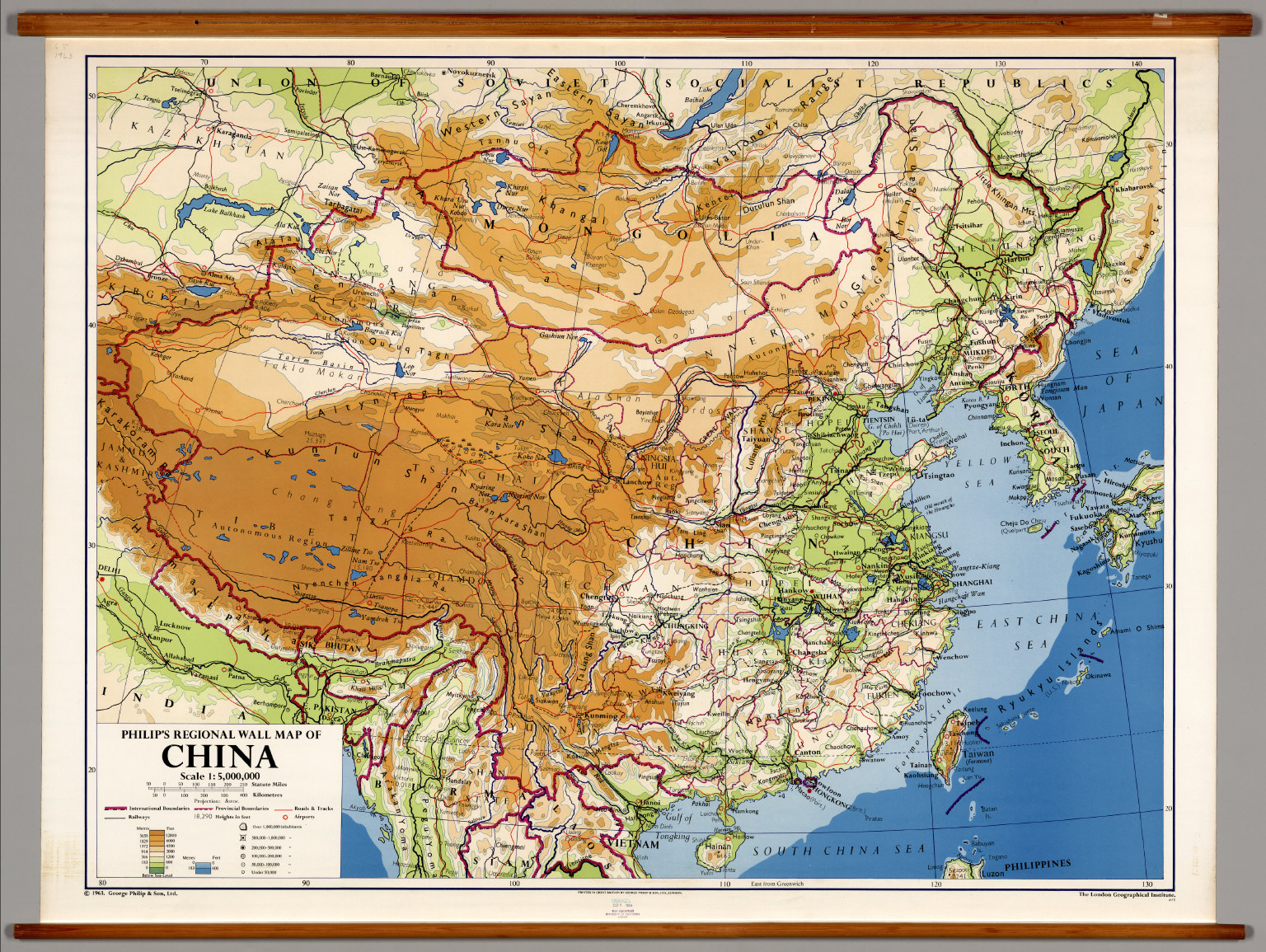
China, the world’s most populous nation, boasts a vast and diverse landscape that stretches across continents. Its intricate geography, encompassing towering mountains, sprawling plains, and fertile river valleys, has shaped its history, culture, and economic development. Understanding the map of China is crucial for grasping its complexities and appreciating its significance on the global stage.
A Geographical Overview:
China’s geographical expanse is immense, covering an area of approximately 9.597 million square kilometers. It is the world’s third-largest country by land area, trailing only Russia and Canada. Its diverse topography encompasses a wide range of geographical features, each contributing to its unique character:
-
The Eastern Coastal Region: This region, facing the East China Sea and the Pacific Ocean, is characterized by fertile plains, abundant rivers, and major cities like Shanghai, Beijing, and Guangzhou. It is the heart of China’s economic activity, home to major industries and ports.
-
The Western Plateau: This vast plateau, encompassing the Tibetan Plateau and the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, is characterized by high altitudes, rugged terrain, and sparse population. It is the source of many major rivers, including the Yangtze and the Yellow River, and holds immense ecological importance.
-
The Southwestern Mountains: This region, encompassing the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau and the Sichuan Basin, is characterized by mountainous terrain, abundant rainfall, and diverse ethnic groups. It is known for its rich biodiversity and unique cultural heritage.
-
The Northern Plains: This region, encompassing the North China Plain and the Northeast China Plain, is characterized by flat terrain, fertile soil, and a temperate climate. It is a major agricultural region, producing significant amounts of grain and other crops.
Historical Significance:
The map of China reflects its long and complex history, marked by periods of both unity and fragmentation. Its geographical features have played a crucial role in shaping its political and cultural development:
-
The Great Wall: Built over centuries, the Great Wall of China is a testament to the country’s historical struggles against nomadic invaders. It stretches for thousands of kilometers, marking the boundary between the settled agricultural regions of the north and the vast steppes of the north.
-
The Silk Road: This ancient trade route, connecting China to the West, traversed vast distances, passing through deserts, mountains, and fertile valleys. It facilitated cultural exchange and economic prosperity, linking China to the world.
-
The Yangtze River: This major waterway, the third-longest in the world, has served as a vital artery for trade and communication throughout Chinese history. It flows through fertile plains, connecting different regions and fostering cultural exchange.
-
The Yellow River: This river, known as the "Cradle of Chinese Civilization," has played a pivotal role in the development of Chinese agriculture and society. Its fertile valley has been a major center of population and economic activity for centuries.
Economic Importance:
The map of China highlights its economic dynamism and its increasing influence on the global stage. Its vast resources, skilled workforce, and strategic location have propelled its economic growth:
-
Manufacturing Hub: China is the world’s largest manufacturer, producing a wide range of goods from electronics to textiles. Its coastal cities, with access to major ports, have become global manufacturing centers.
-
Energy Resources: China possesses abundant energy resources, including coal, oil, and natural gas. Its energy production and consumption are crucial for its economic growth and development.
-
Agricultural Powerhouse: China is the world’s largest producer of agricultural products, including rice, wheat, and vegetables. Its fertile plains and advanced agricultural techniques contribute significantly to global food security.
-
Infrastructure Development: China has invested heavily in infrastructure development, including roads, railways, and airports. This has facilitated trade, transportation, and communication, connecting its vast territory and fostering economic growth.
International Relations:
The map of China also reveals its strategic importance in international relations. Its geographical location, bordering numerous countries, has made it a key player in regional and global affairs:
-
Regional Power: China is a major regional power, with significant influence in East Asia and the Pacific. It has been actively involved in promoting regional cooperation and development.
-
Global Partner: China is a key player in the global economy, with strong trade relations with countries around the world. It has been a major investor in infrastructure projects, contributing to global development.
-
Challenges and Opportunities: China faces challenges in maintaining its economic growth and addressing environmental concerns. Its expanding influence has also raised concerns about its ambitions and its role in international affairs.
Understanding the Map of China: Key Takeaways:
The map of China offers a window into its rich history, diverse geography, and dynamic economy. Its vast size, diverse landscapes, and strategic location have shaped its development and its role in the world. Understanding the map of China is essential for comprehending its complexities and appreciating its significance on the global stage.
FAQs about the Map of China:
1. What are the major geographical features of China?
China’s major geographical features include the Eastern Coastal Region, the Western Plateau, the Southwestern Mountains, and the Northern Plains. These diverse regions contribute to China’s unique character and influence its development.
2. How has the map of China influenced its history?
The map of China has played a crucial role in shaping its history, influencing its political development, cultural exchange, and economic prosperity. Features like the Great Wall, the Silk Road, and major rivers like the Yangtze and Yellow River have left an indelible mark on Chinese history.
3. What is the economic significance of China’s map?
China’s map highlights its economic dynamism, with its vast resources, skilled workforce, and strategic location driving its growth. It is a manufacturing hub, an energy powerhouse, an agricultural leader, and a major investor in infrastructure development.
4. What is China’s role in international relations?
China’s map reveals its strategic importance in international relations. It is a regional power, a global partner, and a key player in shaping global affairs. Its expanding influence presents both challenges and opportunities for the world.
Tips for Understanding the Map of China:
- Explore different maps: Utilize various maps, including physical, political, and thematic maps, to gain a comprehensive understanding of China’s geography, political boundaries, and key features.
- Focus on key regions: Pay attention to the major regions of China, such as the Eastern Coastal Region, the Western Plateau, and the Northern Plains, to understand their unique characteristics and contributions to the country’s development.
- Study historical landmarks: Explore historical landmarks like the Great Wall and the Silk Road to understand their significance in shaping China’s history and culture.
- Research economic centers: Identify major economic centers, including coastal cities like Shanghai and Guangzhou, to understand their role in China’s economic growth and global influence.
- Analyze international relations: Examine China’s relationship with neighboring countries and its role in global affairs to grasp its strategic importance and its impact on the world.
Conclusion:
The map of China is a powerful tool for understanding its complex history, diverse geography, and dynamic economy. It reveals the country’s vast size, its rich cultural heritage, and its increasing influence on the global stage. By studying the map of China, we gain a deeper appreciation for its unique character and its significance in the world.

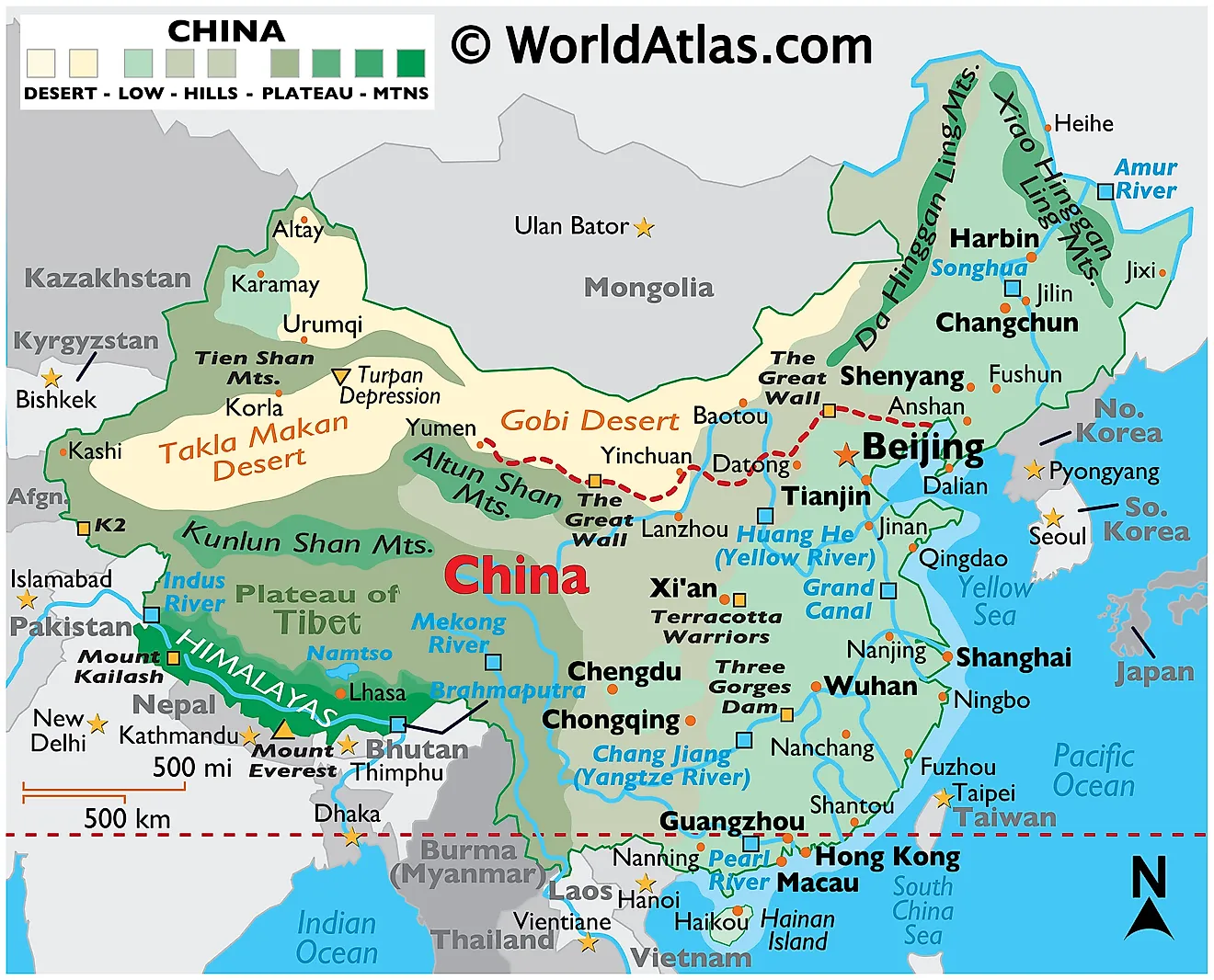
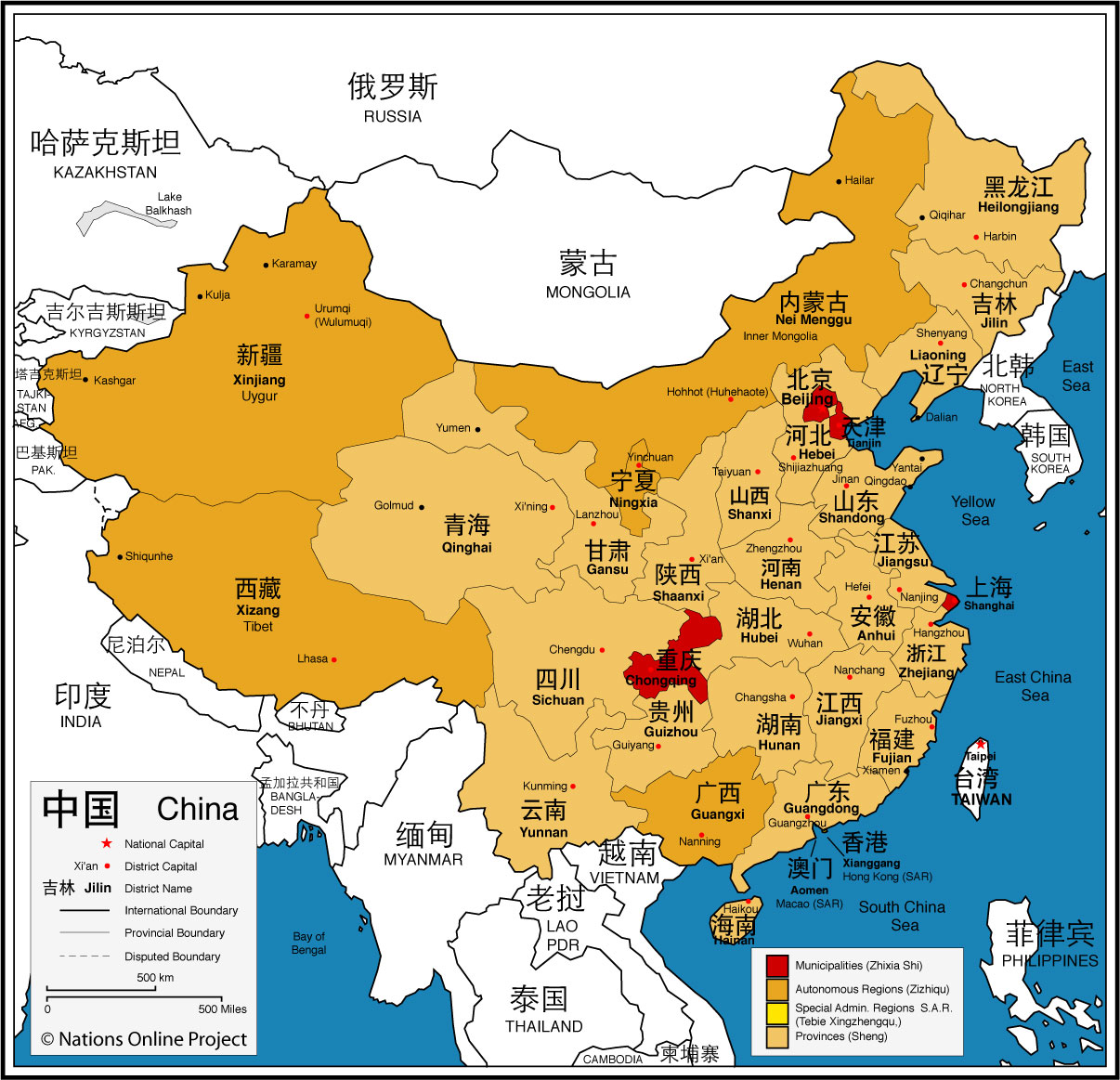
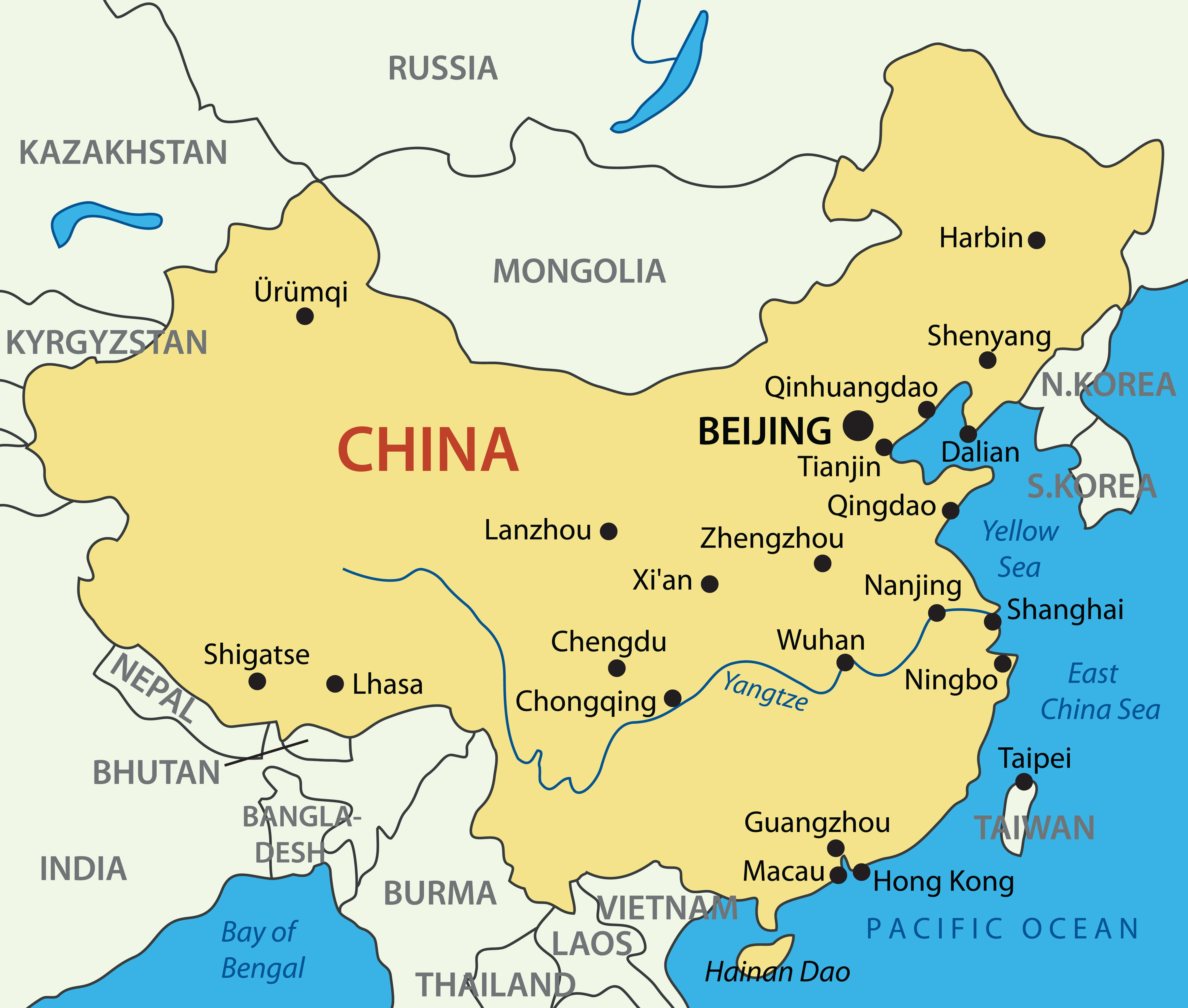

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of China: Understanding the Land of the Rising Sun. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!