Exploring the French Influence on the Map of Africa: A Historical and Cultural Journey
Related Articles: Exploring the French Influence on the Map of Africa: A Historical and Cultural Journey
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Exploring the French Influence on the Map of Africa: A Historical and Cultural Journey. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Exploring the French Influence on the Map of Africa: A Historical and Cultural Journey

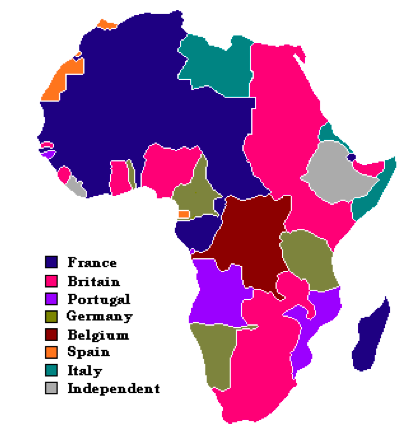
Africa, the second-largest continent, boasts a diverse tapestry of cultures, languages, and histories. One of the most significant influences on this tapestry is the legacy of French colonialism, which shaped the political and geographical landscape of the continent for centuries. Understanding the French influence on the map of Africa offers valuable insights into the continent’s present and future.
French Colonialism: A Legacy Etched on the Map
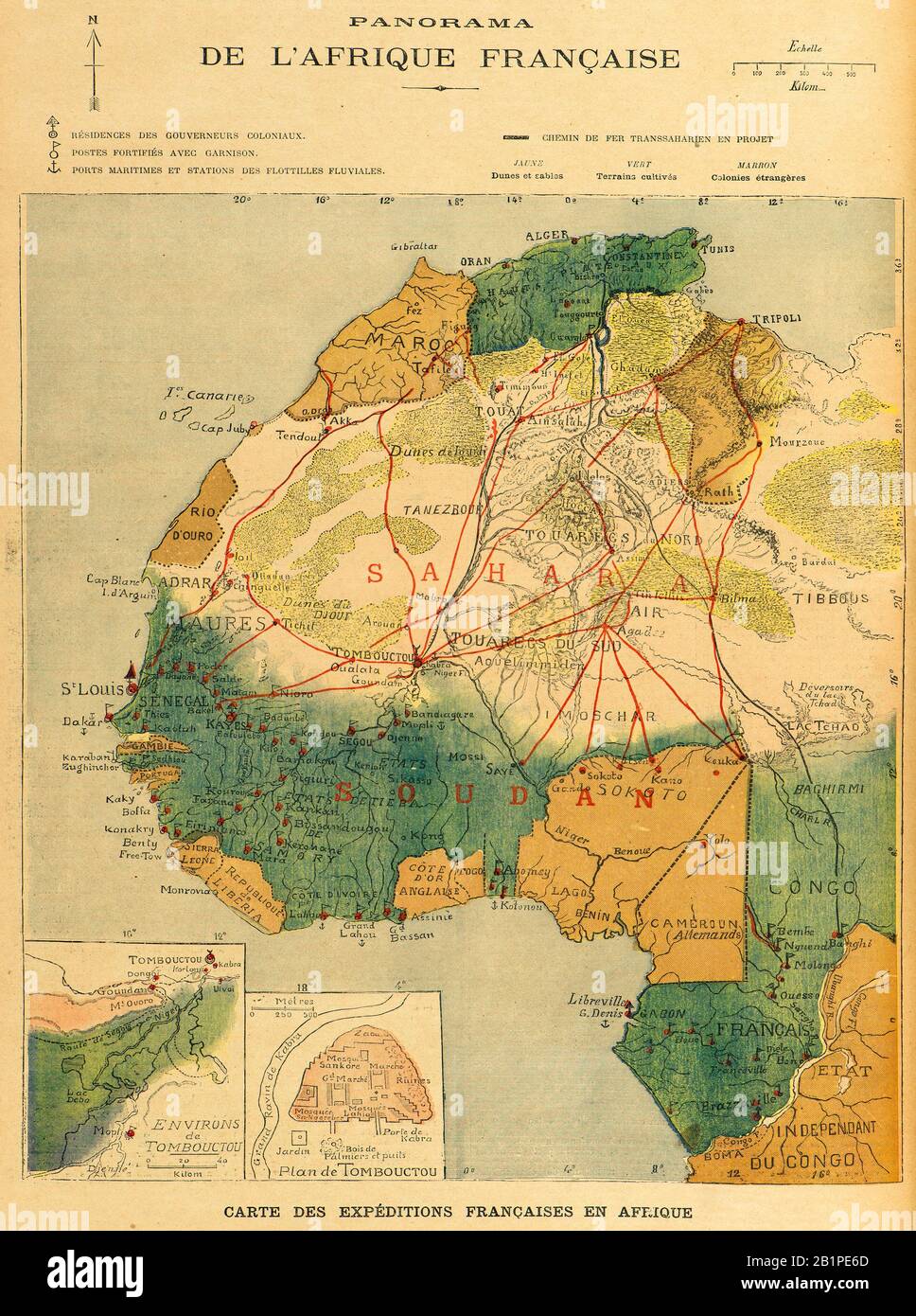
French colonialism in Africa began in the 17th century and reached its peak in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Through conquest, treaties, and diplomatic maneuvers, France established vast colonial territories across the continent, encompassing a diverse range of regions and populations. These territories were often grouped under the umbrella term "French Africa," reflecting the unifying administrative and cultural influence of the French colonial administration.
The French Empire in Africa: A Geographical Overview
The French empire in Africa was geographically extensive, encompassing diverse regions with unique characteristics.
- West Africa: France’s presence in West Africa was particularly significant. From Senegal in the west to Chad in the east, French colonies included present-day countries like Mali, Niger, Burkina Faso, and Benin. These regions played a vital role in the French colonial economy, contributing to the production of commodities like peanuts, cotton, and palm oil.
- Central Africa: In Central Africa, France established colonies in Gabon, Congo (Brazzaville), and the Central African Republic. These territories were rich in natural resources, particularly timber and minerals, which contributed to the colonial economy.
- North Africa: In North Africa, France’s influence was concentrated in Algeria, Morocco, and Tunisia. These regions were strategically important due to their proximity to Europe and their agricultural potential.
- East Africa: France’s presence in East Africa was more limited, primarily focused on Djibouti and parts of Madagascar. These territories served as strategic ports and naval bases.
The Impact of French Colonialism on the Map of Africa:
The legacy of French colonialism on the map of Africa is multifaceted.
- Political Boundaries: The French colonial administration established administrative boundaries that often disregarded existing ethnic and cultural divisions. This led to the creation of artificial states with diverse populations, sometimes contributing to political instability and conflict after independence.
- Language and Culture: French became the official language in many of the French colonies, influencing education, administration, and cultural practices. While French remains an important language in many former French colonies, its dominance has been challenged by the rise of local languages and cultures.
- Infrastructure and Development: The French colonial administration developed infrastructure in its colonies, including roads, railways, and ports. While these investments contributed to economic development, they were often geared towards serving the needs of the colonial economy rather than the local population.
- Political and Economic Dependence: French colonial policies created a system of economic dependence on France, with many colonies exporting raw materials and importing finished goods. This system continued to influence the economies of former French colonies after independence.
The French Influence on the Map of Africa: A Lasting Legacy
The French influence on the map of Africa is a complex and contested legacy. While colonialism brought about significant changes, including the creation of new political boundaries and the introduction of French language and culture, it also left behind challenges related to political instability, economic dependence, and the suppression of local cultures.
Understanding the French Influence on the Map of Africa: Key Considerations
- The Impact on Political Boundaries: The artificial nature of many post-colonial borders has contributed to conflicts and political instability in some regions.
- The Role of French Language and Culture: French remains an important language in many former French colonies, but its dominance is being challenged by the rise of local languages and cultures.
- Economic Dependence on France: The legacy of colonial economic dependence continues to influence the economies of many former French colonies.
- The Importance of Local Cultures: Recognizing and celebrating the diversity of African cultures is crucial for understanding the continent’s history and present.
Exploring the French Influence on the Map of Africa: A Path Forward
Understanding the French influence on the map of Africa is essential for comprehending the continent’s present and future. It is important to acknowledge both the positive and negative aspects of this legacy, recognizing the challenges and opportunities it presents for the future development of Africa.
FAQs about the French Influence on the Map of Africa:
Q: What are the major countries in Africa that were once French colonies?
A: Major countries in Africa that were once French colonies include: Algeria, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Congo (Brazzaville), Côte d’Ivoire, Djibouti, Gabon, Guinea, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, Togo, Tunisia, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Q: How did French colonialism impact the languages spoken in Africa?
A: French became the official language in many of the French colonies. While French remains an important language in many former French colonies, its dominance has been challenged by the rise of local languages and cultures.
Q: What are some of the lasting economic effects of French colonialism in Africa?
A: French colonial policies created a system of economic dependence on France, with many colonies exporting raw materials and importing finished goods. This system continued to influence the economies of former French colonies after independence.
Q: How did French colonialism impact the political landscape of Africa?
A: The French colonial administration established administrative boundaries that often disregarded existing ethnic and cultural divisions. This led to the creation of artificial states with diverse populations, sometimes contributing to political instability and conflict after independence.
Tips for Further Exploration:
- Explore the history of French colonialism in Africa: Research the major events, key figures, and policies that shaped the French colonial experience in Africa.
- Study the languages and cultures of former French colonies: Learn about the diverse languages and cultures that exist within former French colonies.
- Investigate the economic relationships between France and former French colonies: Analyze the economic ties that continue to exist between France and its former colonies.
- Consider the impact of French colonialism on contemporary African politics: Examine how the legacy of colonialism continues to influence political processes and structures in Africa.
Conclusion:
The French influence on the map of Africa is a complex and multi-layered legacy. While colonialism brought about significant changes, including the creation of new political boundaries and the introduction of French language and culture, it also left behind challenges related to political instability, economic dependence, and the suppression of local cultures. Understanding this legacy is crucial for comprehending the contemporary realities of Africa and for shaping a future that embraces the continent’s rich cultural diversity and fosters sustainable development.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the French Influence on the Map of Africa: A Historical and Cultural Journey. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!