Mapping the Conflict: Understanding Germany During World War II
Related Articles: Mapping the Conflict: Understanding Germany During World War II
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Conflict: Understanding Germany During World War II. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Conflict: Understanding Germany During World War II

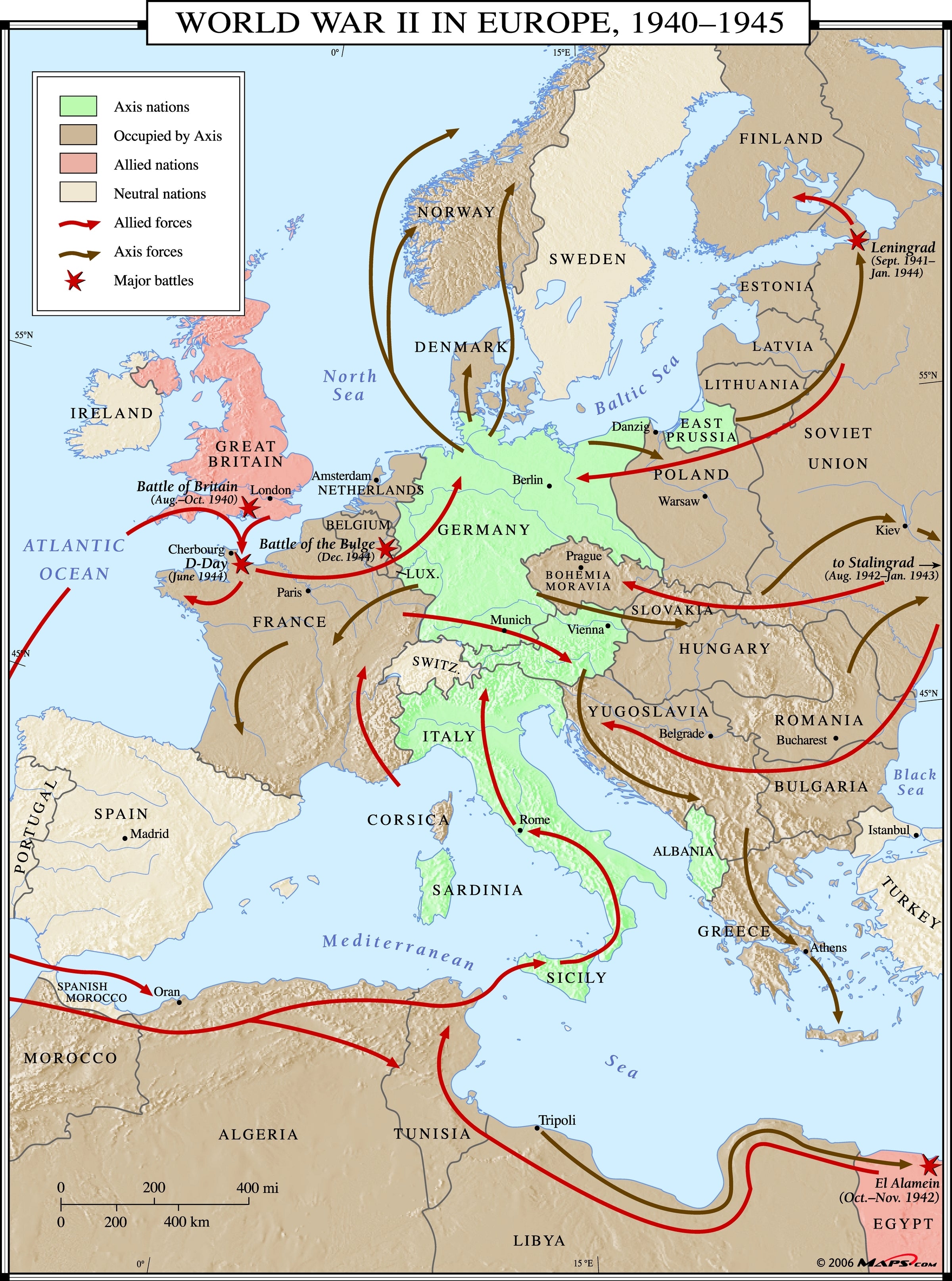
The Second World War, a global conflict of unprecedented scale and devastation, left an indelible mark on the world. Germany, at the heart of this conflict, underwent dramatic transformations both geographically and politically. Understanding the map of Germany during World War II is crucial for grasping the complexities of the war and its lasting consequences.
The Shifting Boundaries of War:
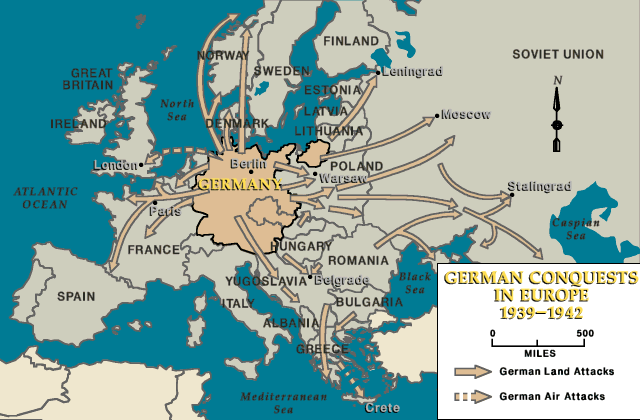
The map of Germany during World War II was a dynamic entity, reflecting the shifting tides of the conflict. The war’s initial stages saw Germany’s expansionist ambitions fueled by Nazi ideology. In 1938, the annexation of Austria and the Sudetenland in Czechoslovakia marked the beginning of Germany’s aggressive territorial expansion. The invasion of Poland in 1939 triggered the full-scale outbreak of the war.
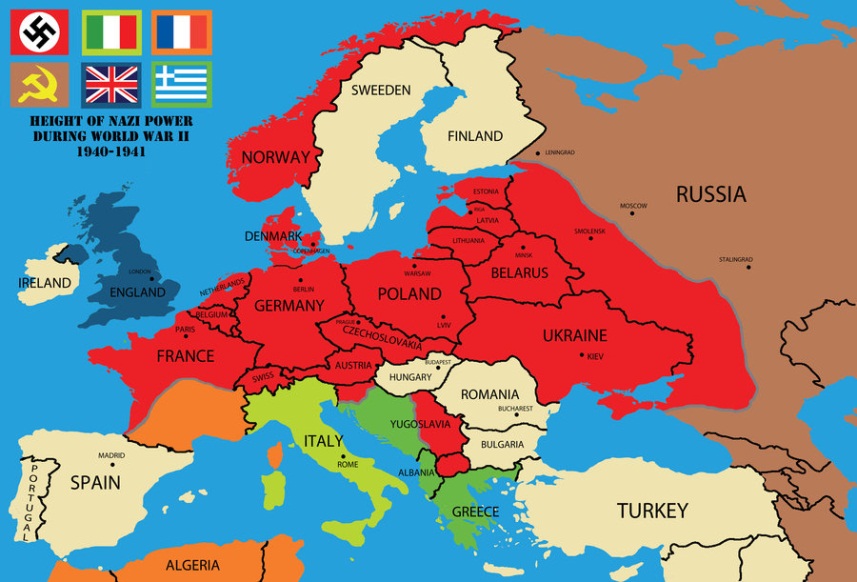
The Reich’s Expansion:
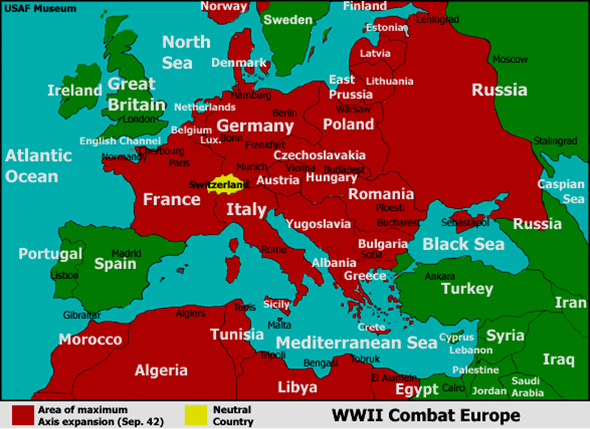
Germany’s territorial gains during the war were significant. The annexation of Czechoslovakia in 1939, followed by the conquest of Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France, created a vast empire under Nazi control. This expansion extended eastward, incorporating large swathes of Poland, the Soviet Union, and even parts of Yugoslavia and Greece.
The Rise of the Greater German Reich:
The map of Germany during World War II evolved into a complex tapestry of conquered territories and occupied zones. The German Reich, under the Nazi regime, aimed to establish a "Greater German Reich" encompassing all Germanic-speaking peoples and surrounding territories. This ambition, driven by racial ideology and territorial expansion, shaped the war’s course and the fate of millions.
The Impact of Occupation:
The occupied territories faced brutal subjugation under Nazi rule. Systematic exploitation, forced labor, and mass deportations became tools of oppression. The Holocaust, the systematic extermination of Jews and other minorities, was carried out across occupied territories, marking one of the darkest chapters in human history.
The Changing Map:
The tide of war eventually turned, and the map of Germany began to change dramatically. The Allied invasion of Normandy in 1944 marked a turning point, leading to the liberation of France and the gradual pushing back of German forces. By 1945, the Allied forces had liberated much of occupied Europe, and the German Reich was collapsing.
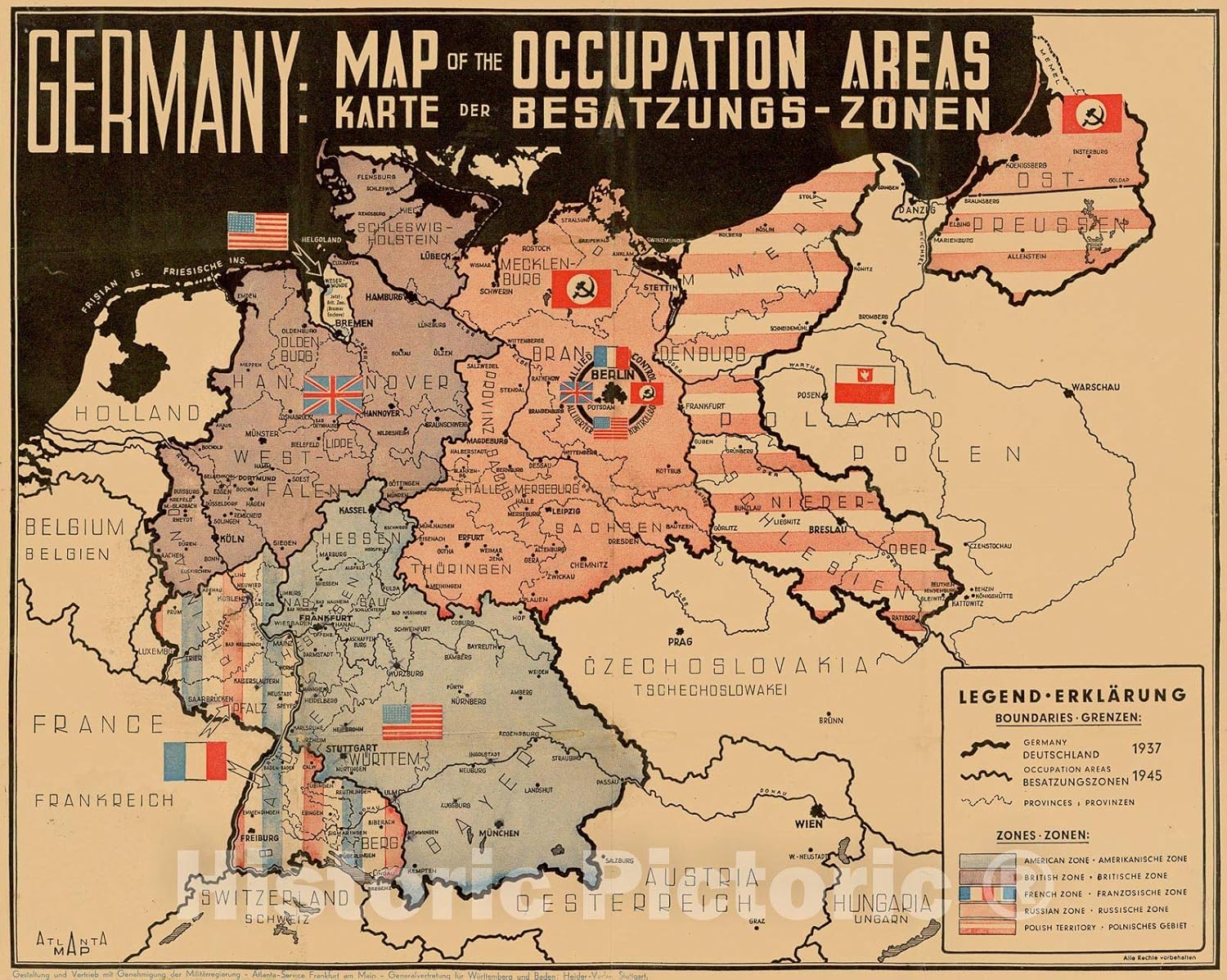
The Post-War Partition:
The end of the war brought about the division of Germany into four zones of occupation, controlled by the Allied powers: the United States, the Soviet Union, Great Britain, and France. This division, a consequence of the Cold War tensions, led to the creation of two German states: West Germany, a democratic republic, and East Germany, a communist state.
The Legacy of the Map:
The map of Germany during World War II remains a powerful symbol of the war’s devastation and its enduring impact on the world. It serves as a reminder of the human cost of conflict, the dangers of unchecked ambition, and the importance of safeguarding peace and understanding.
FAQs
1. What was the extent of Germany’s territorial expansion during World War II?
Germany’s territorial expansion during World War II was vast, encompassing countries in Western and Eastern Europe. They annexed Austria, Czechoslovakia, Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium, France, and large parts of Poland, the Soviet Union, Yugoslavia, and Greece.
2. How did the map of Germany change during the war?
The map of Germany during World War II was constantly changing as Germany conquered new territories and lost ground to Allied forces. The initial expansion of the Reich was followed by the gradual shrinking of its territory as the war progressed.
3. What was the impact of the occupation of territories by Germany?
The occupation of territories by Germany was marked by brutal subjugation, exploitation, forced labor, and mass deportations. The Holocaust, the systematic extermination of Jews and other minorities, was a direct consequence of Nazi ideology and the occupation.
4. What happened to Germany after the war?
After the war, Germany was divided into four zones of occupation, controlled by the Allied powers. This division led to the creation of two German states: West Germany and East Germany, which remained separated until the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989.
5. Why is the map of Germany during World War II important?
The map of Germany during World War II is important because it provides a visual representation of the war’s scale, the extent of Germany’s territorial ambitions, and the devastation it caused. It serves as a reminder of the human cost of conflict and the importance of preventing such tragedies from recurring.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Germany During World War II:
- Focus on the key events: The annexation of Austria, the invasion of Poland, the Battle of Stalingrad, and the Normandy landings are crucial turning points in the war.
- Study the borders: Pay attention to the shifting borders of Germany and the occupied territories. Understanding the boundaries of the Reich and its expansion is essential.
- Research the occupation: Explore the impact of Nazi rule on the occupied territories, focusing on the exploitation, forced labor, and the Holocaust.
- Consider the post-war division: The division of Germany into West and East Germany was a direct consequence of the war and the Cold War.
Conclusion:
The map of Germany during World War II is a complex and multifaceted representation of a tumultuous period in history. It highlights the expansionist ambitions of the Nazi regime, the brutal realities of occupation, and the lasting consequences of the conflict. Understanding the map helps us grasp the war’s scale, its impact on Europe and the world, and the importance of preserving peace and promoting understanding. It serves as a reminder of the human cost of conflict and the need to learn from history to prevent such tragedies from repeating.
![[Map] Map depicting the Allied campaign toward Germany, 26 Aug-14 Sep](http://ww2db.com/images/battle_liberationofbelgium6.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Conflict: Understanding Germany During World War II. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!