Navigating Namibia: A Comprehensive Guide to the Country’s Geographic Landscape
Related Articles: Navigating Namibia: A Comprehensive Guide to the Country’s Geographic Landscape
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating Namibia: A Comprehensive Guide to the Country’s Geographic Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Namibia: A Comprehensive Guide to the Country’s Geographic Landscape

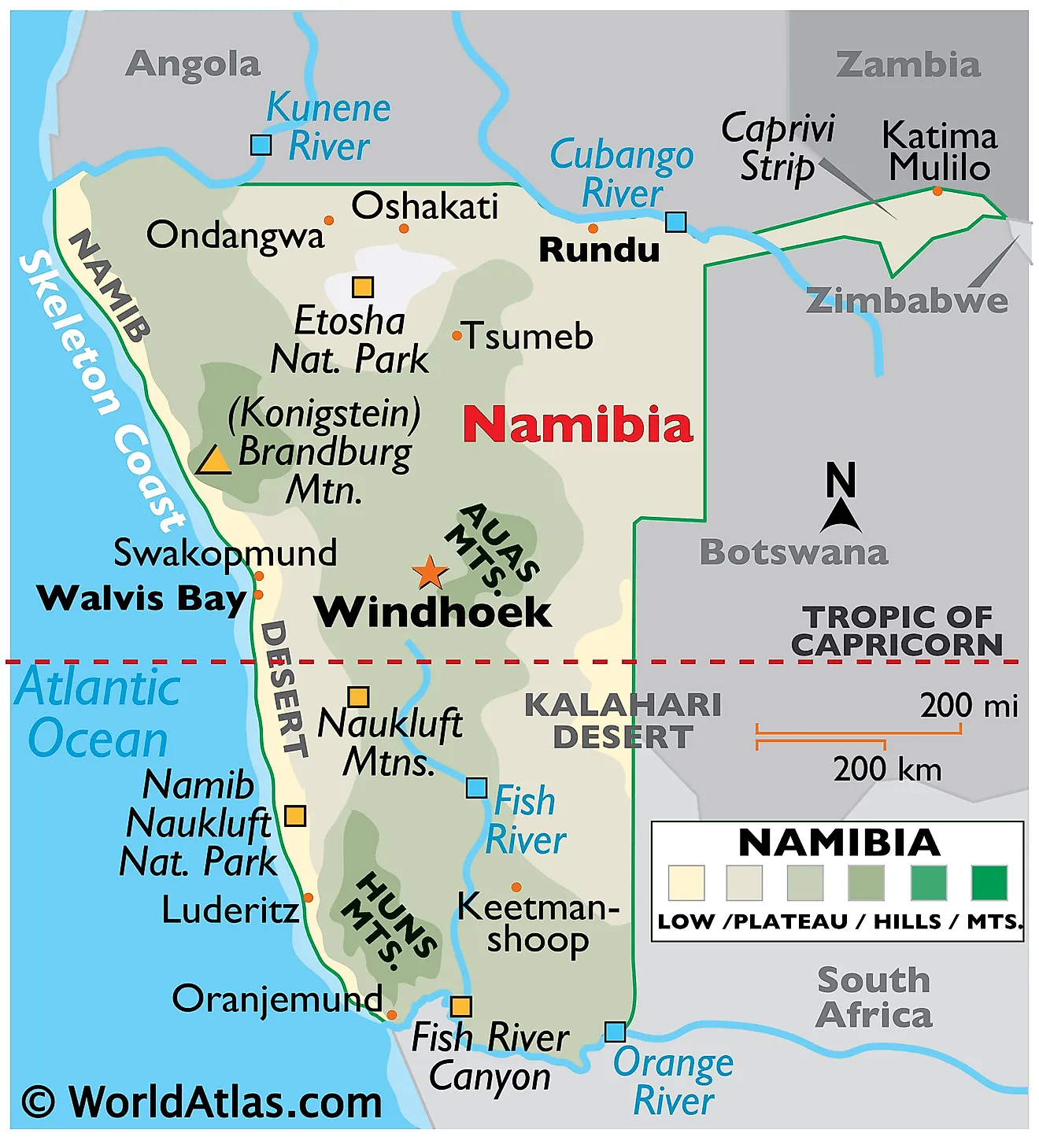
Namibia, a nation nestled in the southwestern corner of Africa, boasts a unique and diverse landscape that captivates travelers and geographers alike. Its geographic position, encompassing vast deserts, towering mountains, and a rugged coastline, presents a fascinating tapestry of natural wonders. Understanding the country’s geography through the lens of a map is crucial for appreciating its rich biodiversity, cultural heritage, and economic potential.
Namibia on the World Map: A Glimpse into its Location and Significance
Namibia’s location on the world map is a testament to its strategic importance. Situated on the Atlantic coast of Southern Africa, it shares borders with Angola, Botswana, South Africa, and Zambia. This strategic position has historically influenced its cultural and economic development, serving as a crossroads for trade and cultural exchange.
A Detailed Look at Namibia’s Geographic Features:
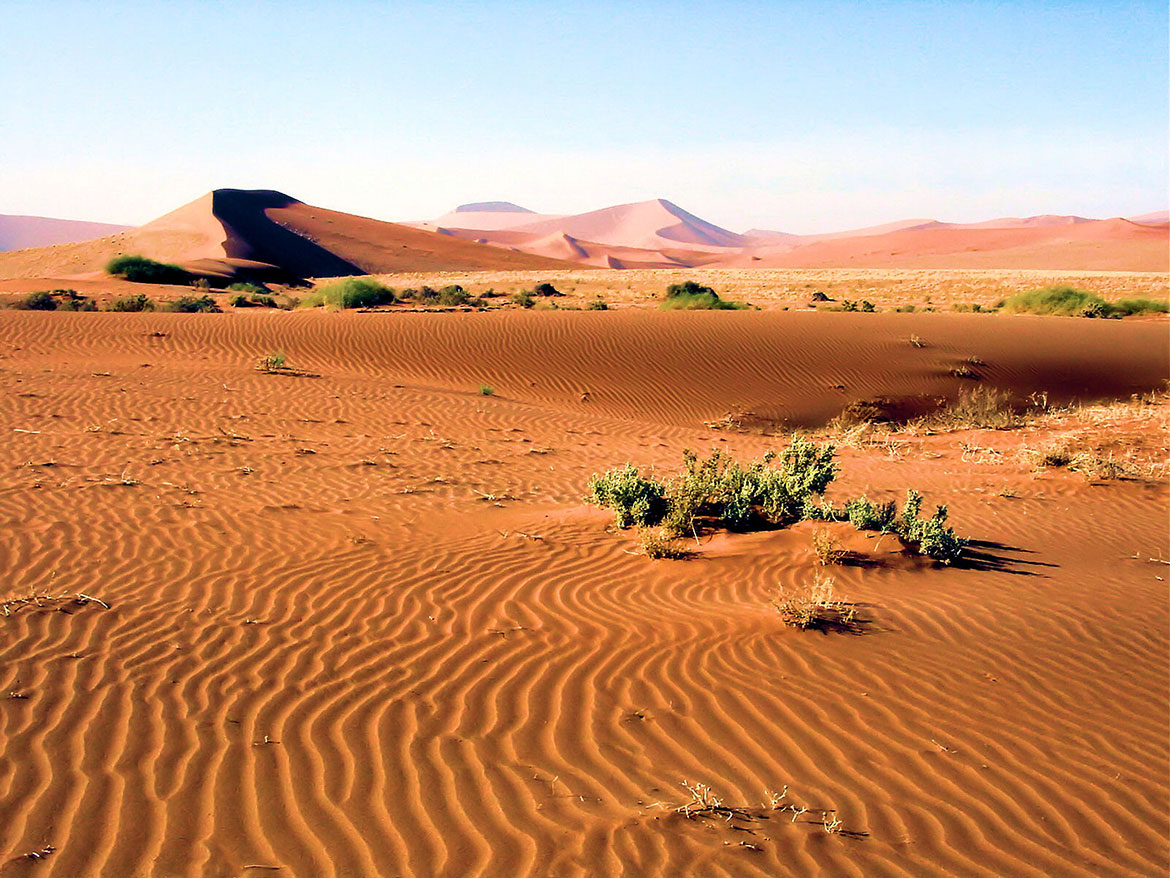
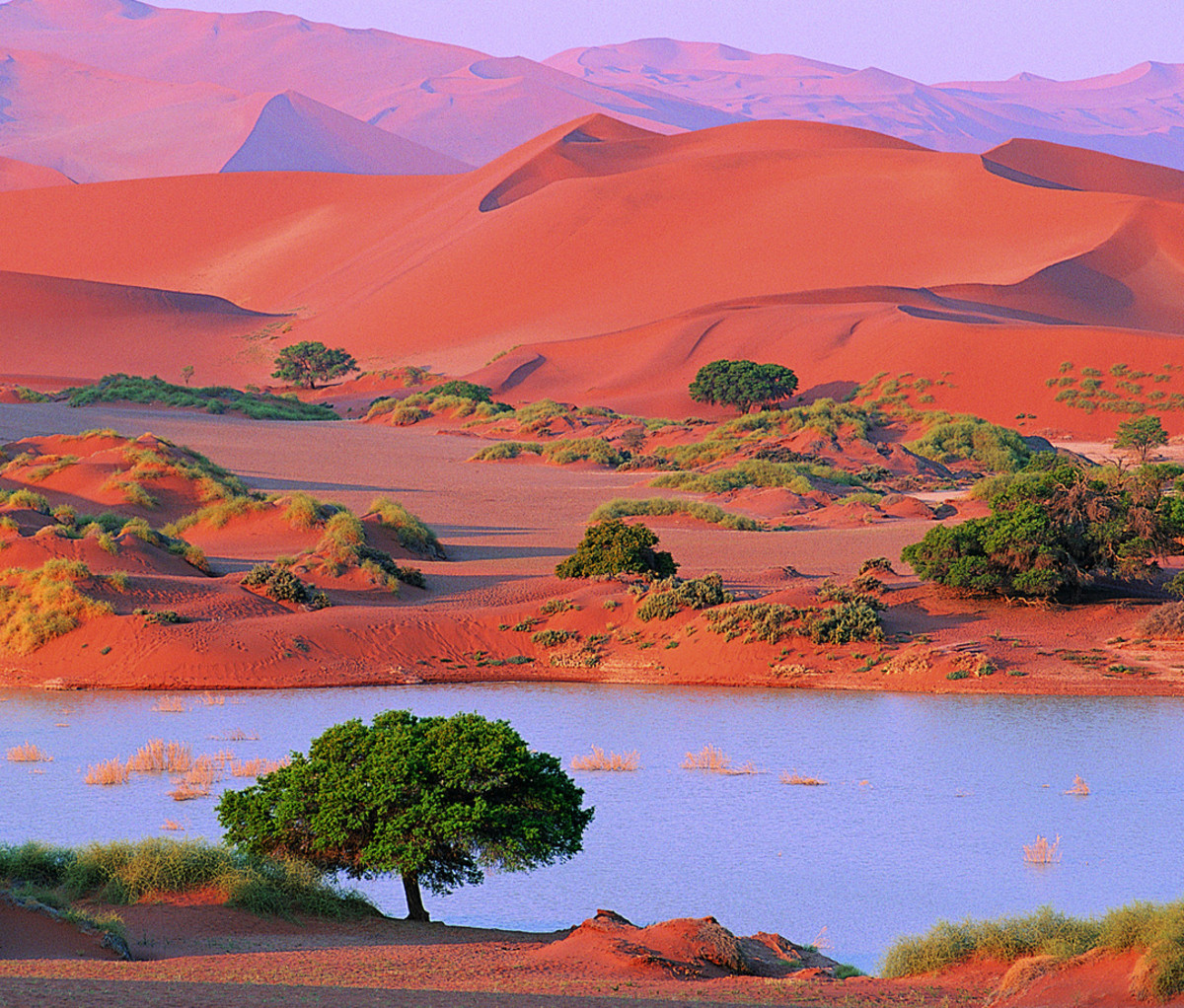
1. The Namib Desert: A Vast and Ancient Landscape
The Namib Desert, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, dominates the western portion of the country, stretching for over 2,000 kilometers along the Atlantic coast. This ancient desert, estimated to be over 80 million years old, is characterized by towering sand dunes, starkly contrasting with the blue expanse of the ocean. The Namib Desert is a testament to the resilience of life in extreme environments, hosting a variety of unique plant and animal species adapted to its harsh conditions.
2. The Skeleton Coast: A Rugged and Remote Shoreline
The Skeleton Coast, a notorious stretch of coastline bordering the Namib Desert, is a stark reminder of the unforgiving nature of the Atlantic Ocean. Its name derives from the numerous shipwrecks that have occurred along its shores, a consequence of treacherous currents, fog, and shallow waters. The Skeleton Coast is a captivating mix of dramatic rock formations, ancient shipwrecks, and a diverse array of marine life, making it a popular destination for adventurous travelers.
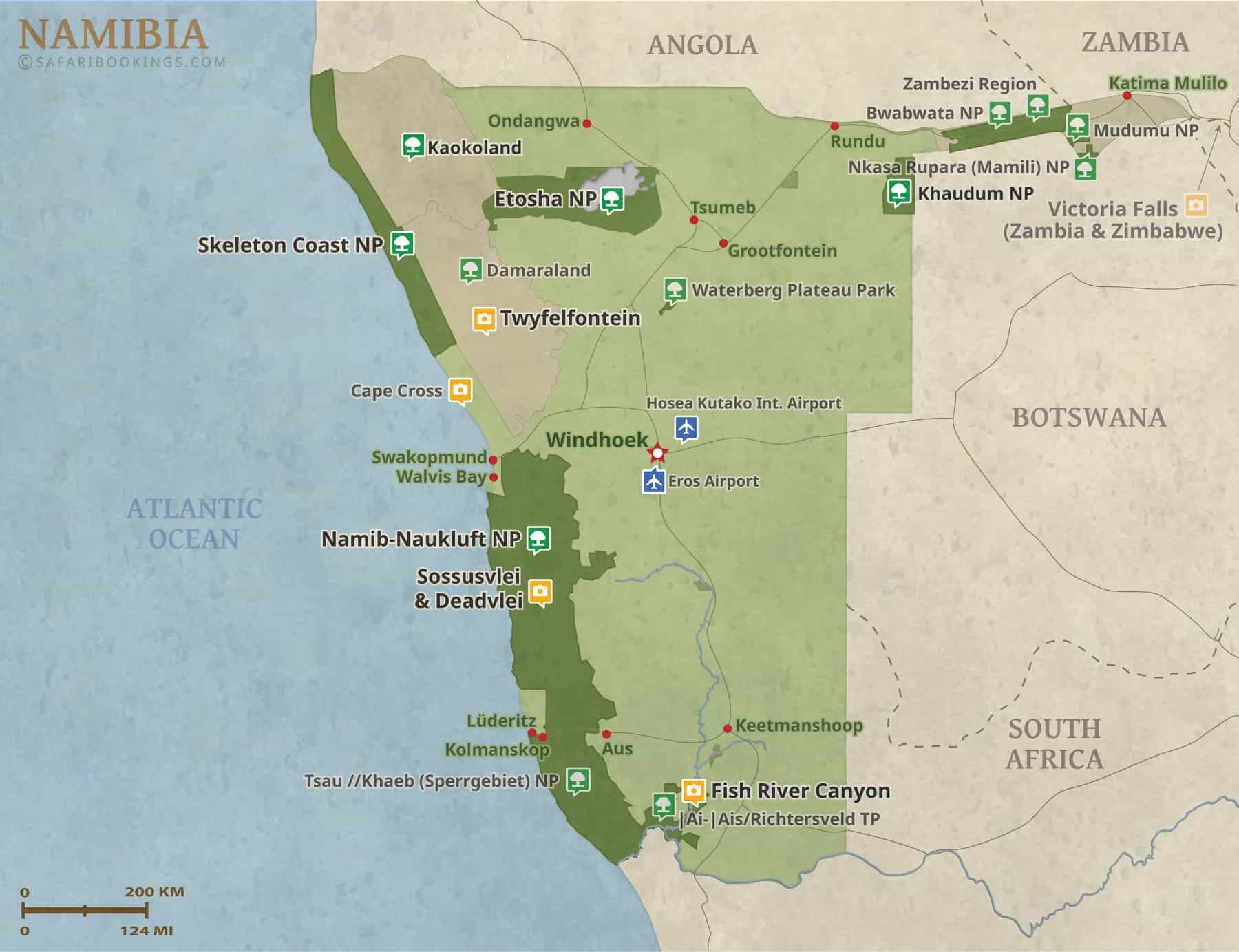
3. The Etosha National Park: A Wildlife Haven
Etosha National Park, located in the northeastern part of the country, is a wildlife sanctuary renowned for its abundance of diverse animal species. Its vast salt pan, Etosha Pan, acts as a natural water source, attracting a plethora of animals, including elephants, lions, giraffes, zebras, and numerous bird species. The park’s diverse ecosystems, ranging from open grasslands to dense woodlands, provide a sanctuary for a wide array of wildlife, making it a prime destination for wildlife enthusiasts and nature lovers.
4. The Damaraland: A Region of Rugged Beauty and Cultural Significance
Damaraland, situated in the northwestern part of Namibia, is characterized by rugged mountains, ancient rock formations, and a rich cultural heritage. The region is home to the Damara people, whose traditional way of life is deeply intertwined with the land. Damaraland is also known for its unique geological formations, including the Twyfelfontein rock engravings, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, which provide a glimpse into the ancient history of the region.
5. The Fish River Canyon: A Grand Canyon of Southern Africa
The Fish River Canyon, located in the south of the country, is the largest canyon in Africa and one of the largest in the world. The canyon, carved by the Fish River over millions of years, is a breathtaking spectacle of natural grandeur. Its sheer cliffs, winding river, and diverse flora and fauna make it a popular destination for hiking and exploring the wonders of nature.
6. The Caprivi Strip: A Gateway to the Okavango Delta
The Caprivi Strip, a narrow strip of land in the northeastern part of Namibia, is a geographically diverse region with a unique cultural heritage. The strip, known for its abundant wildlife, serves as a gateway to the Okavango Delta in Botswana, one of the world’s largest inland deltas. Its diverse ecosystems, ranging from floodplains to woodlands, support a rich array of wildlife, making it a popular destination for wildlife safaris and nature enthusiasts.
Understanding the Importance of Namibia’s Geographic Landscape:
1. Biodiversity and Conservation:
Namibia’s diverse geographic landscape is a haven for a remarkable array of plant and animal species, many of which are endemic to the region. The country’s vast deserts, rugged coastlines, and diverse ecosystems support a rich biodiversity, making it a key area for conservation efforts. Protecting these ecosystems is crucial for preserving the unique biodiversity of Namibia and ensuring the sustainability of its natural resources.
2. Tourism and Economic Development:
Namibia’s stunning natural beauty and diverse cultural heritage make it a popular destination for tourists from around the world. Tourism is a significant contributor to the country’s economy, providing employment opportunities and generating revenue for conservation efforts. By promoting responsible tourism practices, Namibia can ensure that its natural resources are sustainably managed for the benefit of both present and future generations.
3. Cultural Heritage and Indigenous Knowledge:
The geographic landscape of Namibia has shaped the culture and traditions of its indigenous communities for centuries. The land provides essential resources, inspires art and storytelling, and serves as a source of identity for these communities. Preserving and promoting the cultural heritage of these communities is crucial for maintaining the rich tapestry of Namibian culture.
4. Water Resources and Sustainability:
Water resources are scarce in Namibia, particularly in the arid regions. The country’s geographic landscape, characterized by low rainfall and high evaporation rates, poses challenges for water management. Sustainable water management practices are essential for ensuring the availability of water for human consumption, agriculture, and industry, particularly in the face of climate change.
5. Mineral Resources and Economic Potential:
Namibia is rich in mineral resources, including diamonds, uranium, and copper. The country’s geographic landscape has played a crucial role in the discovery and exploitation of these resources, contributing to its economic development. However, responsible mining practices are essential for ensuring the sustainable use of these resources and minimizing environmental impact.
FAQs about Namibia’s Geography:
1. What is the highest point in Namibia?
The highest point in Namibia is Brandberg Mountain, which reaches a height of 2,573 meters (8,442 feet) above sea level.
2. What is the largest city in Namibia?
The largest city in Namibia is Windhoek, the capital of the country.
3. What is the climate like in Namibia?
Namibia has a predominantly arid climate, with low rainfall and high temperatures, particularly in the desert regions. The coastal areas experience a more temperate climate due to the influence of the Atlantic Ocean.
4. What are the main languages spoken in Namibia?
The official languages of Namibia are English and Afrikaans. However, numerous indigenous languages are also spoken throughout the country, including Damara/Nama, Herero, and Kavango.
5. What are some of the most popular tourist destinations in Namibia?
Some of the most popular tourist destinations in Namibia include Etosha National Park, Sossusvlei, the Skeleton Coast, Fish River Canyon, and the Namib Desert.
Tips for Exploring Namibia’s Geographic Landscape:
1. Plan Your Itinerary Carefully:
Namibia’s vast and diverse landscape requires careful planning to make the most of your trip. Consider your interests, time constraints, and budget when planning your itinerary.
2. Choose the Right Mode of Transportation:
Namibia’s vast distances can be best explored by car, allowing you to travel at your own pace and access remote areas. However, for certain destinations, such as the Skeleton Coast, guided tours may be necessary.
3. Respect the Environment:
Namibia’s fragile ecosystems require responsible tourism practices. Avoid littering, stay on designated trails, and respect the wildlife.
4. Learn About the Local Culture:
Namibia’s rich cultural heritage is an integral part of its identity. Engage with local communities, learn about their traditions, and appreciate their unique perspectives.
5. Be Prepared for Extreme Conditions:
Namibia’s climate can be extreme, with hot temperatures and limited water resources. Pack accordingly, including sunscreen, hats, and plenty of water.
Conclusion:
Namibia’s geographic landscape is a tapestry of natural wonders, from the vastness of the Namib Desert to the rugged beauty of the Skeleton Coast. Understanding the country’s geography is crucial for appreciating its rich biodiversity, cultural heritage, and economic potential. By embracing responsible tourism practices and respecting the environment, we can ensure that this unique and fascinating country continues to thrive for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Namibia: A Comprehensive Guide to the Country’s Geographic Landscape. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!