Navigating the Healthcare Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Healthcare
Related Articles: Navigating the Healthcare Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Healthcare
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Healthcare Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Healthcare. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Healthcare Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Healthcare
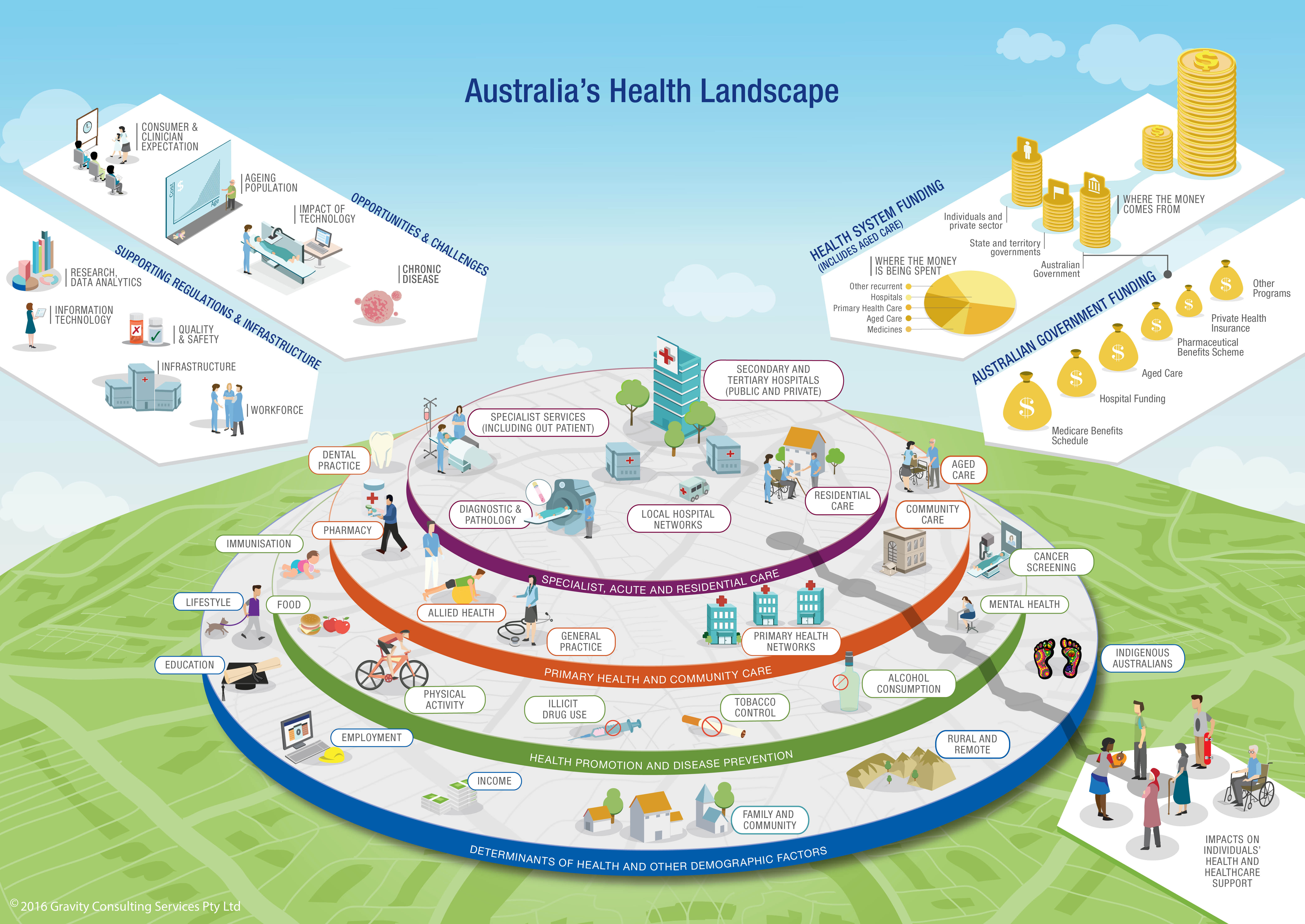
The healthcare landscape is a complex and constantly evolving terrain. Navigating this landscape effectively requires clear direction, accurate information, and a reliable guide. This is where map healthcare emerges as an indispensable tool, offering a comprehensive framework to understand, manage, and optimize the intricate network of healthcare services.
Defining Map Healthcare: A Framework for Understanding
Map healthcare, also known as healthcare mapping, is a multi-faceted approach that utilizes data analysis, visualization, and spatial technologies to create a detailed representation of healthcare systems and their interactions. This representation, often visualized as a map, provides a powerful tool for understanding:
- Healthcare Resource Distribution: Map healthcare reveals the geographical distribution of healthcare facilities, including hospitals, clinics, pharmacies, and other essential healthcare providers. This information highlights areas with access gaps, enabling targeted interventions to improve healthcare equity.
- Patient Flow and Referral Patterns: By mapping patient journeys, healthcare systems can analyze referral patterns, identify bottlenecks in the system, and optimize patient flow for smoother transitions between different healthcare providers.
- Disease Prevalence and Risk Factors: Integrating health data with geographic information systems (GIS) allows for the mapping of disease prevalence and risk factors, enabling public health officials to identify high-risk areas and implement targeted prevention programs.
- Healthcare Workforce Distribution: Map healthcare can visualize the distribution of healthcare professionals, such as physicians, nurses, and specialists, highlighting areas with shortages and informing workforce planning initiatives.
- Health Outcomes and Disparities: Mapping health outcomes, such as mortality rates, morbidity rates, and access to care, helps identify disparities in healthcare access and quality, driving efforts to address inequities.
Benefits of Map Healthcare: A Compass for Improvement
The application of map healthcare offers a multitude of benefits across various healthcare stakeholders:
For Healthcare Providers:
- Improved Patient Care: By understanding patient flow patterns and identifying bottlenecks, healthcare providers can streamline care pathways, reduce waiting times, and enhance overall patient experience.
- Enhanced Resource Allocation: Visualizing the distribution of healthcare resources allows for more efficient allocation of staff, equipment, and services, ensuring that resources are directed to areas with the highest need.
- Targeted Interventions: Identifying geographic areas with high disease prevalence or health disparities allows for the development and implementation of targeted interventions to improve health outcomes.
For Public Health Officials:
- Effective Disease Surveillance: Mapping disease prevalence and risk factors provides valuable insights for public health officials to monitor outbreaks, track disease trends, and implement targeted interventions.
- Improved Health Equity: By identifying disparities in healthcare access and quality, map healthcare empowers public health officials to address inequities and ensure equal access to healthcare for all.
- Strategic Planning: Understanding the geographic distribution of healthcare resources and populations allows for more effective planning of public health programs and initiatives.
For Healthcare Policymakers:
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Map healthcare provides policymakers with comprehensive data and visualizations to support evidence-based decision making on healthcare policy, resource allocation, and infrastructure development.
- Health System Optimization: By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of healthcare systems, policymakers can develop strategies to improve efficiency, effectiveness, and accessibility.
- Transparency and Accountability: Mapping healthcare data fosters transparency and accountability by providing a clear picture of healthcare resource allocation, access, and performance.
Key Technologies Driving Map Healthcare
The power of map healthcare lies in the convergence of several key technologies:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS provides the foundation for mapping healthcare data, allowing for the visualization and analysis of spatial relationships.
- Big Data Analytics: Healthcare data is vast and complex. Big data analytics tools are essential for processing and analyzing large datasets to extract meaningful insights.
- Remote Sensing: Satellite imagery and aerial photography provide valuable data on the geographic landscape, population density, and infrastructure, enriching map healthcare applications.
- Mobile Technologies: Mobile devices with GPS capabilities enable real-time data collection and location tracking, enhancing the accuracy and relevance of map healthcare information.
Challenges and Considerations in Map Healthcare
While map healthcare offers significant potential, it is not without its challenges:
- Data Quality and Availability: The accuracy and completeness of healthcare data are crucial for effective map healthcare applications. Ensuring data quality and accessibility remains a significant challenge.
- Privacy and Security: Protecting patient privacy and ensuring the security of sensitive healthcare data is paramount. Robust data governance and anonymization techniques are essential.
- Interoperability and Standardization: Interoperability between different healthcare systems and data standards is crucial for seamless data sharing and analysis.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of map healthcare raises ethical considerations regarding potential bias, discrimination, and the equitable distribution of resources.
FAQs on Map Healthcare
Q: What are some real-world examples of map healthcare in action?
A:
- Disease Surveillance: Public health agencies utilize map healthcare to track the spread of infectious diseases, identify high-risk areas, and target interventions.
- Resource Allocation: Hospitals use map healthcare to visualize the distribution of beds, staff, and equipment, optimizing resource allocation and ensuring efficient use of resources.
- Health Equity Initiatives: Map healthcare helps identify disparities in healthcare access and quality, enabling the development of targeted programs to address inequities.
Q: How can I access map healthcare resources and tools?
A:
- Public Health Agencies: Many public health agencies offer map healthcare resources and data visualization tools.
- Research Institutions: Universities and research institutions often develop and disseminate map healthcare tools and applications.
- Commercial Software Providers: Several commercial software providers offer GIS and data analysis tools specifically designed for healthcare applications.
Q: What are some tips for implementing map healthcare effectively?
A:
- Define clear goals and objectives: Clearly define the purpose and intended outcomes of map healthcare initiatives.
- Ensure data quality and accuracy: Prioritize data quality and validation to ensure the reliability of map healthcare insights.
- Engage stakeholders: Involve healthcare providers, public health officials, and policymakers in the planning and implementation of map healthcare initiatives.
- Address ethical considerations: Ensure responsible and ethical use of map healthcare data, respecting patient privacy and promoting equity.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future with Map Healthcare
Map healthcare is a transformative force in the healthcare landscape, offering a powerful framework for understanding, managing, and optimizing complex healthcare systems. By harnessing the power of data visualization, spatial technologies, and big data analytics, map healthcare empowers healthcare providers, public health officials, and policymakers to make informed decisions, improve patient care, and address health disparities. As technology continues to evolve, map healthcare will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of healthcare, ensuring that healthcare systems are more efficient, effective, and equitable for all.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Healthcare Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Healthcare. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!