Navigating the Oracle Cloud: A Comprehensive Guide to Oracle AZs
Related Articles: Navigating the Oracle Cloud: A Comprehensive Guide to Oracle AZs
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Oracle Cloud: A Comprehensive Guide to Oracle AZs. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Oracle Cloud: A Comprehensive Guide to Oracle AZs

Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) provides a robust and scalable platform for businesses of all sizes. Central to this platform are Oracle Availability Domains (AZs), which play a critical role in ensuring high availability, fault tolerance, and disaster recovery capabilities. Understanding the concept of Oracle AZs is crucial for optimizing cloud deployments and maximizing the benefits of OCI.
What are Oracle Availability Domains?
Oracle AZs are physically isolated and independent data centers within a specific region. Each AZ houses its own power, cooling, and networking infrastructure, ensuring that failures in one AZ do not impact the others. This inherent isolation is fundamental to achieving high availability and resilience in OCI.
Key Features and Benefits of Oracle AZs:
- High Availability: By deploying applications across multiple AZs, businesses can ensure continuous operation even in the event of a failure within a single AZ. This redundancy minimizes downtime and maximizes service uptime.
- Fault Tolerance: The physical separation of AZs within a region makes them inherently fault-tolerant. If one AZ experiences an outage, applications deployed in other AZs within the same region remain unaffected.
- Disaster Recovery: By deploying applications across different regions, which consist of multiple AZs, businesses can achieve disaster recovery capabilities. In the event of a regional disaster, applications in a different region can seamlessly take over, minimizing disruption.
- Performance Optimization: By deploying applications within the same AZ, businesses can benefit from lower latency and improved network performance. This is particularly advantageous for applications requiring real-time data processing or high-performance computing.
- Scalability and Flexibility: AZs provide a scalable and flexible environment for cloud deployments. Businesses can easily add or remove resources based on changing needs without impacting application availability.
Understanding the Map of Oracle AZs:
The map of Oracle AZs provides a visual representation of OCI’s global footprint and the availability of services within each region. Each region comprises multiple AZs, offering redundancy and fault tolerance. The map is a valuable tool for:
- Planning Cloud Deployments: Businesses can use the map to identify regions and AZs best suited for their specific needs, considering factors such as location, latency, and available services.
- Understanding Service Availability: The map highlights the availability of different OCI services within each region and AZ. This information is crucial for selecting the appropriate services and deployment strategies.
- Optimizing Performance: By understanding the location of AZs and their proximity to users, businesses can optimize application performance and minimize latency.
Frequently Asked Questions about Oracle AZs:
Q: How many AZs are there in each Oracle region?
A: The number of AZs within a region varies depending on the specific location. Typically, regions have at least three AZs, providing redundancy and fault tolerance.
Q: Can I deploy applications across multiple regions?
A: Yes, deploying applications across multiple regions is possible and highly recommended for achieving disaster recovery capabilities. This ensures that applications remain operational even in the event of a regional disaster.
Q: What are the differences between Oracle AZs and Availability Zones in other cloud providers?
A: While the concept of AZs is similar across different cloud providers, the specific implementation and features may vary. It is important to consult the documentation of each provider to understand the nuances of their AZs.
Tips for Using Oracle AZs Effectively:
- Plan for Redundancy: Design applications with redundancy in mind, deploying critical components across multiple AZs within a region or even across different regions for enhanced disaster recovery.
- Utilize Availability Zones for High Availability: Leverage the isolation and redundancy of AZs to ensure continuous operation of applications even in the event of failures within a single AZ.
- Consider Regional Availability: When deploying applications, carefully consider the availability of services within different regions and choose the most suitable region based on your specific requirements.
- Optimize Performance with Proximity: Deploy applications within AZs closest to your users to minimize latency and improve application performance.
- Utilize OCI’s Monitoring and Management Tools: Utilize OCI’s monitoring and management tools to track the health and performance of applications deployed across multiple AZs.
Conclusion:
Oracle AZs are a fundamental component of OCI, providing a robust and resilient platform for cloud deployments. By understanding the concept of AZs, businesses can leverage the benefits of high availability, fault tolerance, disaster recovery, and performance optimization. The map of Oracle AZs is a valuable tool for navigating the global footprint of OCI and making informed decisions regarding cloud deployment strategies. By utilizing AZs effectively, businesses can build highly available and resilient applications, maximizing the potential of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.


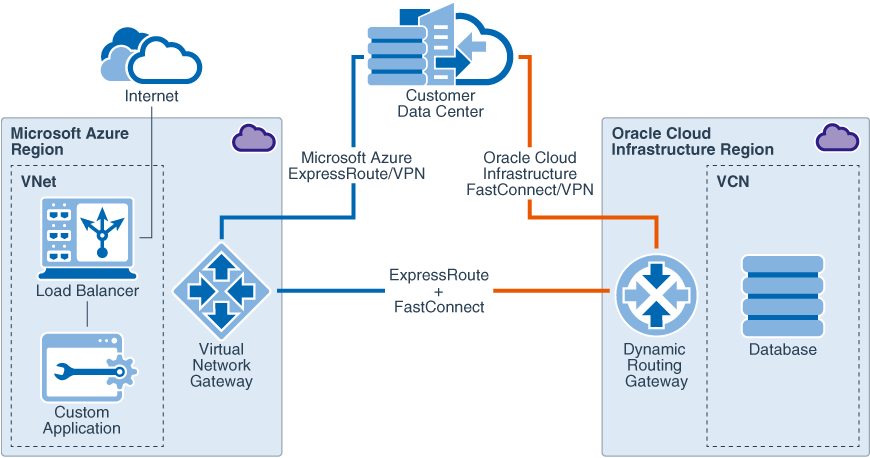


![[Video 2 of 5] 3 Ways to Connect To The Oracle Cloud](https://k21academy.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/OCI_Step123_2.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Oracle Cloud: A Comprehensive Guide to Oracle AZs. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!