Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Look at the United States Railroad Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Look at the United States Railroad Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Look at the United States Railroad Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Look at the United States Railroad Map
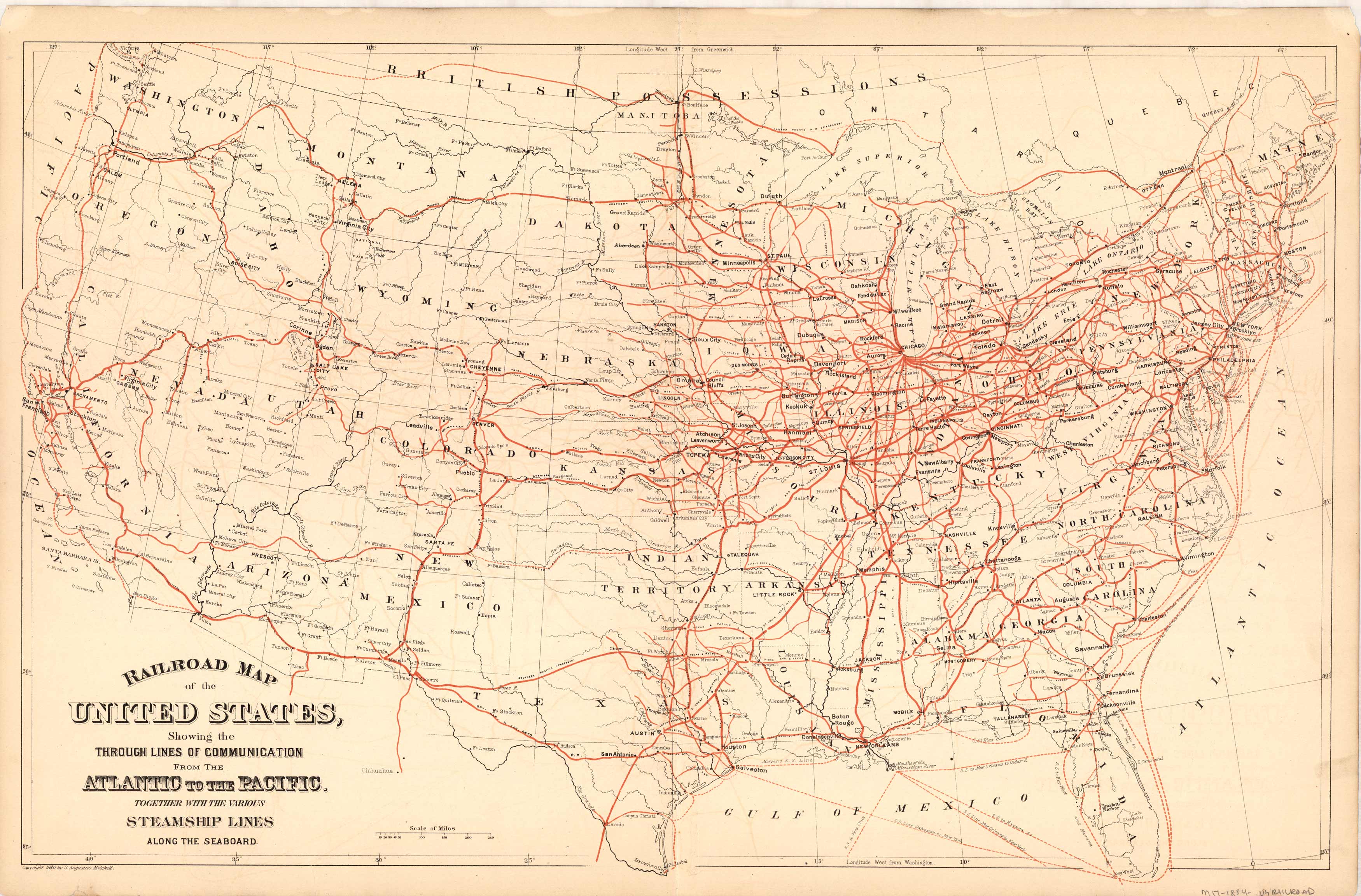
The United States railroad map, a complex web of steel arteries crisscrossing the nation, represents more than just lines on a page. It embodies the history, industry, and economic backbone of the country. Understanding this intricate network provides insights into the nation’s development, its transportation infrastructure, and its future potential.
A Historical Journey: From Transcontinental Rails to Modern Networks
The story of the United States railroad map begins in the 19th century with the ambitious dream of connecting the Atlantic and Pacific coasts. The transcontinental railroad, completed in 1869, marked a pivotal moment, transforming the nation’s landscape and paving the way for westward expansion. This monumental feat not only facilitated the movement of people and goods but also spurred the growth of cities, industries, and economies.
The early 20th century saw a rapid expansion of the rail network, with numerous lines connecting major cities and industrial centers. This period witnessed the rise of powerful railroad companies, shaping the economic and political landscape of the nation. The map, once a symbol of progress, also reflected the challenges of competition and consolidation within the industry.
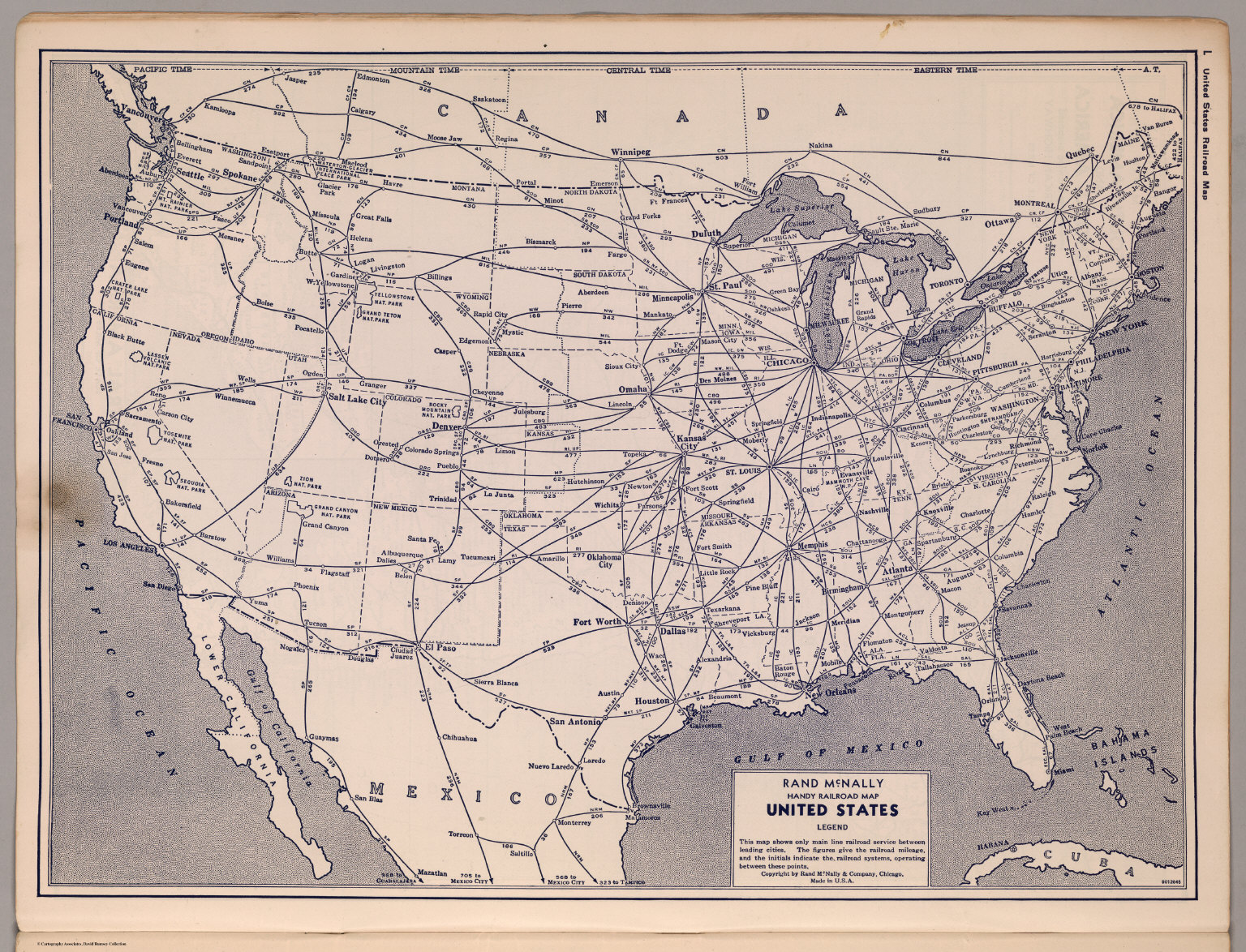
Modern Networks: Evolution and Adaptation
Today, the United States railroad map reflects a dynamic and evolving system. Technological advancements, economic shifts, and environmental concerns have influenced its evolution. While passenger rail remains a vital part of the network, freight transportation dominates the scene.
Understanding the Network: Key Components and Players
The United States railroad map comprises several key components:
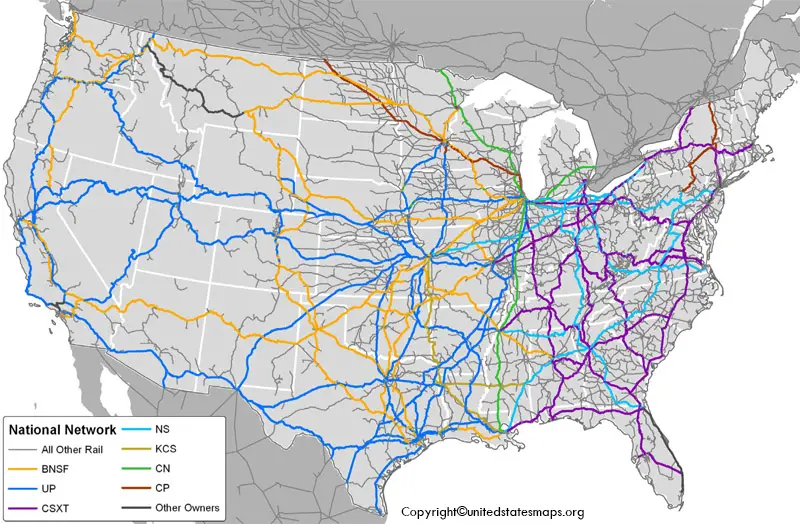
- Class I Railroads: These are the largest freight railroads, responsible for transporting vast quantities of goods across the country. Examples include Union Pacific, BNSF Railway, CSX Transportation, and Norfolk Southern Railway.
- Regional Railroads: These smaller railroads operate within specific regions, often connecting with Class I railroads for longer-distance transportation.
- Short-Line Railroads: These highly localized railroads serve specific industries or communities, playing a crucial role in regional economies.
- Passenger Rail: Amtrak, the national passenger railroad, operates a network of routes connecting major cities across the country.
The Importance of the United States Railroad Map
The United States railroad map plays a vital role in the nation’s economy and society:
- Economic Engine: Railroads are responsible for transporting a significant portion of the nation’s freight, including raw materials, manufactured goods, and agricultural products. This efficient transportation system supports industries, businesses, and jobs across the country.
- Infrastructure Backbone: The rail network serves as a critical component of the national infrastructure, connecting cities, towns, and industries. It provides a reliable and efficient mode of transportation for both passengers and freight.
- Environmental Impact: Railroads are a relatively environmentally friendly mode of transportation compared to trucking. They consume less fuel per ton-mile and generate fewer greenhouse gas emissions.
- National Security: The rail network plays a crucial role in national security, providing a vital transportation system for military equipment and supplies.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its importance, the United States railroad map faces several challenges:
- Aging Infrastructure: Many rail lines require significant investment to maintain and upgrade, ensuring safety and efficiency.
- Competition from Other Modes of Transportation: The rise of trucking and air cargo has led to increased competition for freight transportation.
- Environmental Concerns: The rail industry must continue to address environmental concerns related to noise pollution, land use, and emissions.
However, the United States railroad map also presents significant opportunities:
- Investment in Infrastructure: The government and private sector are investing in modernizing and expanding the rail network, improving efficiency and capacity.
- Focus on Intermodal Transportation: The integration of rail with other modes of transportation, such as trucking and shipping, is improving efficiency and reducing costs.
- Expansion of Passenger Rail: There is growing interest in expanding passenger rail service, providing a more sustainable and efficient mode of transportation.
Navigating the Future: Sustainability and Innovation
The future of the United States railroad map lies in its ability to adapt to changing needs and challenges. Sustainability and innovation will play a crucial role in shaping the network’s future.
- Adopting Green Technologies: The industry is exploring and implementing technologies that reduce environmental impact, such as electric locomotives and biofuels.
- Improving Efficiency: Optimizing operations, implementing advanced scheduling systems, and leveraging data analytics can enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
- Investing in Research and Development: Continued investment in research and development is essential to explore new technologies and solutions for the future of rail transportation.
FAQs about the United States Railroad Map
Q: What is the longest railroad line in the United States?
A: The longest railroad line in the United States is the Union Pacific Railroad’s main line, stretching over 3,200 miles from Council Bluffs, Iowa, to Portland, Oregon.
Q: How many railroads operate in the United States?
A: The United States has over 700 railroads, ranging from Class I railroads to short-line railroads.
Q: What are the main freight commodities transported by railroads?
A: Railroads transport a wide range of freight commodities, including agricultural products, chemicals, coal, construction materials, and manufactured goods.
Q: What are the major passenger rail routes in the United States?
A: Amtrak operates a network of passenger rail routes, including the Northeast Corridor, the California Zephyr, and the Coast Starlight.
Q: What are the environmental benefits of rail transportation?
A: Rail transportation is more fuel-efficient and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions than trucking. It also contributes to reduced traffic congestion and air pollution.
Tips for Understanding the United States Railroad Map
- Explore Online Resources: Several websites and interactive maps provide detailed information about the United States railroad network.
- Read Industry Publications: Publications such as Railway Age and Trains Magazine offer insights into the industry’s trends and developments.
- Visit Railroad Museums: Railroad museums provide a fascinating glimpse into the history and evolution of rail transportation.
- Travel by Train: Experiencing passenger rail firsthand can provide a unique perspective on the network’s role in connecting communities.
Conclusion
The United States railroad map is a testament to the nation’s history, industry, and economic growth. This intricate network continues to evolve, adapting to changing needs and challenges. By understanding its importance, challenges, and opportunities, we can appreciate its role in shaping the nation’s future. As technology advances and the demand for sustainable transportation solutions grows, the United States railroad map will continue to play a vital role in connecting communities, supporting industries, and driving economic progress.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Look at the United States Railroad Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!