Pataliputra: A City That Shaped Ancient India
Related Articles: Pataliputra: A City That Shaped Ancient India
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Pataliputra: A City That Shaped Ancient India. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Pataliputra: A City That Shaped Ancient India

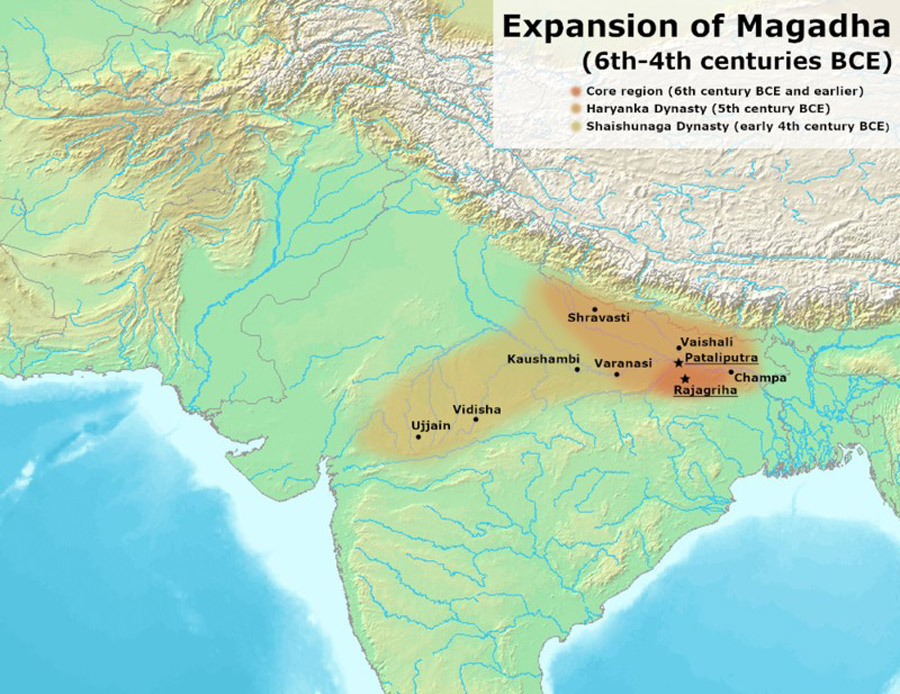
Pataliputra, a city synonymous with grandeur and power, stands as a testament to the brilliance of ancient Indian civilization. Its strategic location on the banks of the Ganges River, coupled with its sophisticated urban planning and rich cultural heritage, propelled it to become the capital of the mighty Magadha Empire, shaping the course of Indian history for centuries.
A Glimpse into History:
Pataliputra’s origins can be traced back to the 5th century BCE, when it was founded by the legendary King Ajatashatru of the Magadha Empire. The city’s strategic location, nestled amidst fertile plains and near the confluence of the Ganges and Son rivers, made it a natural hub for trade and commerce. This strategic advantage, combined with the empire’s military prowess, allowed Pataliputra to flourish and become a major political and economic center.
Pataliputra on the Map:
Pataliputra, located in present-day Patna, Bihar, was a meticulously planned city. Ancient texts like the Arthashastra and the Buddhist Jataka tales provide valuable insights into its layout. The city was divided into distinct sectors, each with its specific function.
- The Royal Palace (Rajagriha): This majestic structure was the seat of the king and housed the administrative offices.
- The City Walls: Constructed with brick and wood, the city walls served as a formidable defense system, protecting Pataliputra from external threats.
- The Market (Nagara): This bustling commercial center was the heart of Pataliputra’s economy, where goods from across the empire and beyond were traded.
- The Residential Areas: The city was home to a diverse population, including artisans, merchants, farmers, and government officials, who resided in well-organized residential areas.
- The Parks and Gardens: Pataliputra was renowned for its lush gardens and parks, offering respite from the bustling city life.
A Flourishing Metropolis:
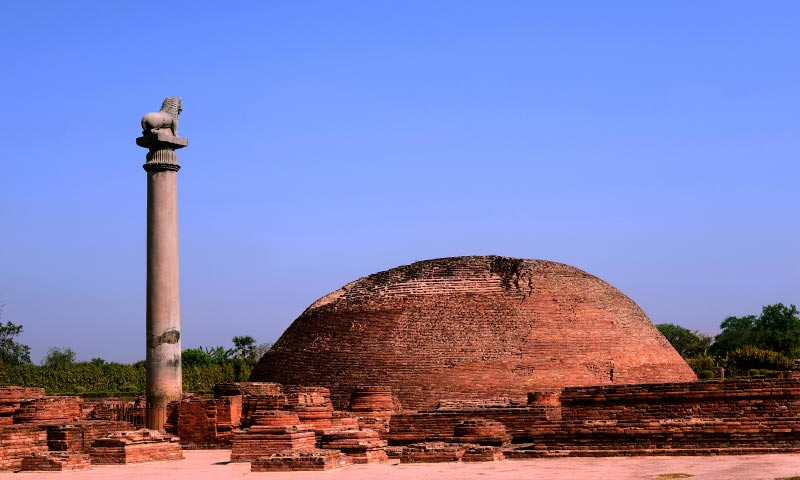
Under the rule of the Mauryan Empire, Pataliputra reached its zenith. Emperor Ashoka, who adopted Buddhism and embarked on a peaceful reign, further enhanced the city’s infrastructure and promoted its cultural development. The city was adorned with magnificent buildings, including the Ashoka Stambh (Ashoka’s Pillar), a testament to his legacy.
Pataliputra served as a crucial center for the dissemination of Buddhist teachings. The city was home to renowned scholars and monasteries, attracting pilgrims from across the ancient world. The city’s cosmopolitan nature fostered a vibrant exchange of ideas and knowledge, contributing to the growth of Indian philosophy and literature.
A Legacy of Grandeur:
While Pataliputra’s glory was eventually eclipsed by the rise of other empires, its legacy continues to resonate. The city’s architectural marvels, urban planning, and cultural contributions have left an indelible mark on Indian history. The ruins of Pataliputra, now part of Patna, offer a glimpse into the past and stand as a reminder of the grandeur and sophistication of ancient Indian civilization.
FAQs about Pataliputra:
1. What is the significance of Pataliputra’s location?
Pataliputra’s location on the banks of the Ganges River made it a strategic trade center and a natural hub for communication and transport.
2. How was Pataliputra planned and organized?
Pataliputra was meticulously planned with distinct sectors dedicated to different functions, including the royal palace, market, residential areas, and parks.
3. What was the role of Pataliputra in the spread of Buddhism?
Pataliputra was a major center for the spread of Buddhism, housing renowned scholars and monasteries that attracted pilgrims from across the ancient world.
4. What are some of the notable architectural features of Pataliputra?
Pataliputra was known for its magnificent buildings, including the Ashoka Stambh, the royal palace, and the city walls.
5. What is the significance of Pataliputra in Indian history?
Pataliputra played a pivotal role in shaping ancient Indian history as the capital of the Magadha Empire. Its cultural contributions and urban planning left a lasting legacy on Indian civilization.
Tips for Visiting Pataliputra:
- Explore the Archaeological Museum: This museum houses artifacts from the ancient city, providing insights into its history and culture.
- Visit the Ashoka Stambh: This pillar, erected by Emperor Ashoka, is a significant historical monument and a testament to Pataliputra’s past grandeur.
- Explore the ruins of the ancient city: The ruins of Pataliputra offer a glimpse into the city’s layout and architectural marvels.
- Attend the Patna Mahotsav: This annual festival celebrates the city’s rich cultural heritage and offers a vibrant cultural experience.
Conclusion:
Pataliputra stands as a testament to the ingenuity and cultural prowess of ancient India. Its strategic location, sophisticated urban planning, and rich cultural heritage propelled it to become a powerful center of learning, trade, and political influence. The city’s legacy continues to inspire, reminding us of the brilliance of ancient Indian civilization and its enduring impact on the world. While the city’s physical presence may have faded with time, its spirit lives on, inspiring future generations to learn from its history and strive for similar achievements.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Pataliputra: A City That Shaped Ancient India. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!