The Global Landscape of Oil: Understanding the Distribution and Significance of a Vital Resource
Related Articles: The Global Landscape of Oil: Understanding the Distribution and Significance of a Vital Resource
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Global Landscape of Oil: Understanding the Distribution and Significance of a Vital Resource. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Global Landscape of Oil: Understanding the Distribution and Significance of a Vital Resource
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Global Landscape of Oil: Understanding the Distribution and Significance of a Vital Resource
- 3.1 Unveiling the Geographic Distribution of Oil Reserves
- 3.2 Mapping Global Oil Production
- 3.3 The Flow of Oil: Global Consumption Patterns
- 3.4 The Dynamics of Oil Prices: A Complex Interplay of Factors
- 3.5 The Importance of Oil: A Multifaceted Resource
- 3.6 The Challenges of Oil Dependence: Environmental and Economic Concerns
- 3.7 The Transition to a Sustainable Energy Future
- 3.8 FAQs:
- 3.9 Tips:
- 3.10 Conclusion:
- 4 Closure
The Global Landscape of Oil: Understanding the Distribution and Significance of a Vital Resource

Oil, a ubiquitous energy source, plays a pivotal role in modern society, fueling transportation, manufacturing, and numerous other industries. Understanding the global distribution of this critical resource is crucial for policymakers, economists, and individuals alike. A map of oil reserves, production, and consumption provides a visual representation of the intricate network of energy flows that shape our world.
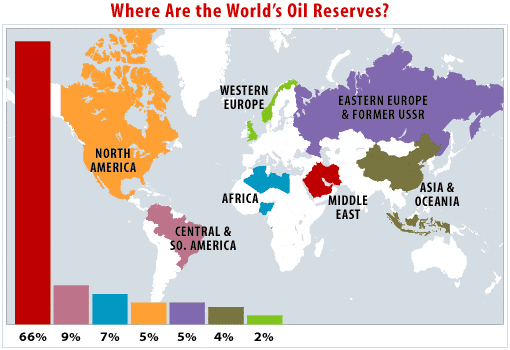
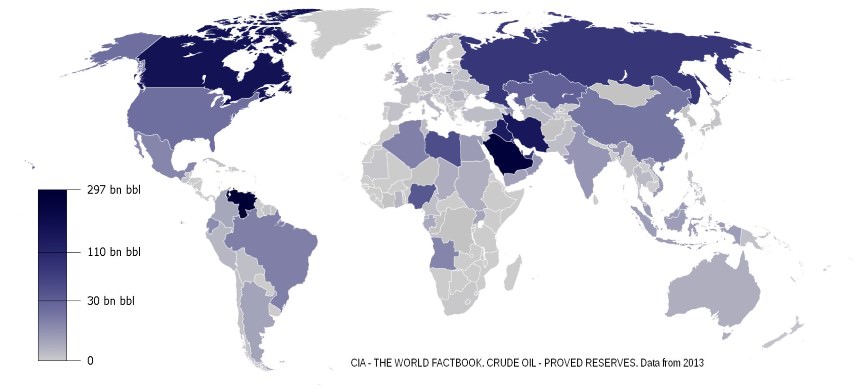
Unveiling the Geographic Distribution of Oil Reserves
The earth’s oil reserves are not evenly distributed. The Middle East, particularly the Arabian Peninsula, holds the largest share, accounting for approximately 48% of global reserves. This region’s vast oil fields, notably in Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Kuwait, and the United Arab Emirates, have historically been the cornerstone of global oil supply.
Beyond the Middle East, other significant oil reserves are found in:
- Latin America: Venezuela, Brazil, and Mexico boast considerable reserves, contributing to the region’s economic importance.
- Africa: Nigeria, Libya, and Algeria possess substantial oil resources, playing a key role in the continent’s energy landscape.
- North America: The United States, Canada, and Mexico hold significant reserves, with recent technological advancements unlocking previously inaccessible shale oil deposits in the United States.
- Russia: As a major oil producer and exporter, Russia holds substantial reserves, contributing significantly to global energy markets.
- Asia: China, with its rapidly growing economy, has been actively expanding its oil reserves through exploration and strategic partnerships.
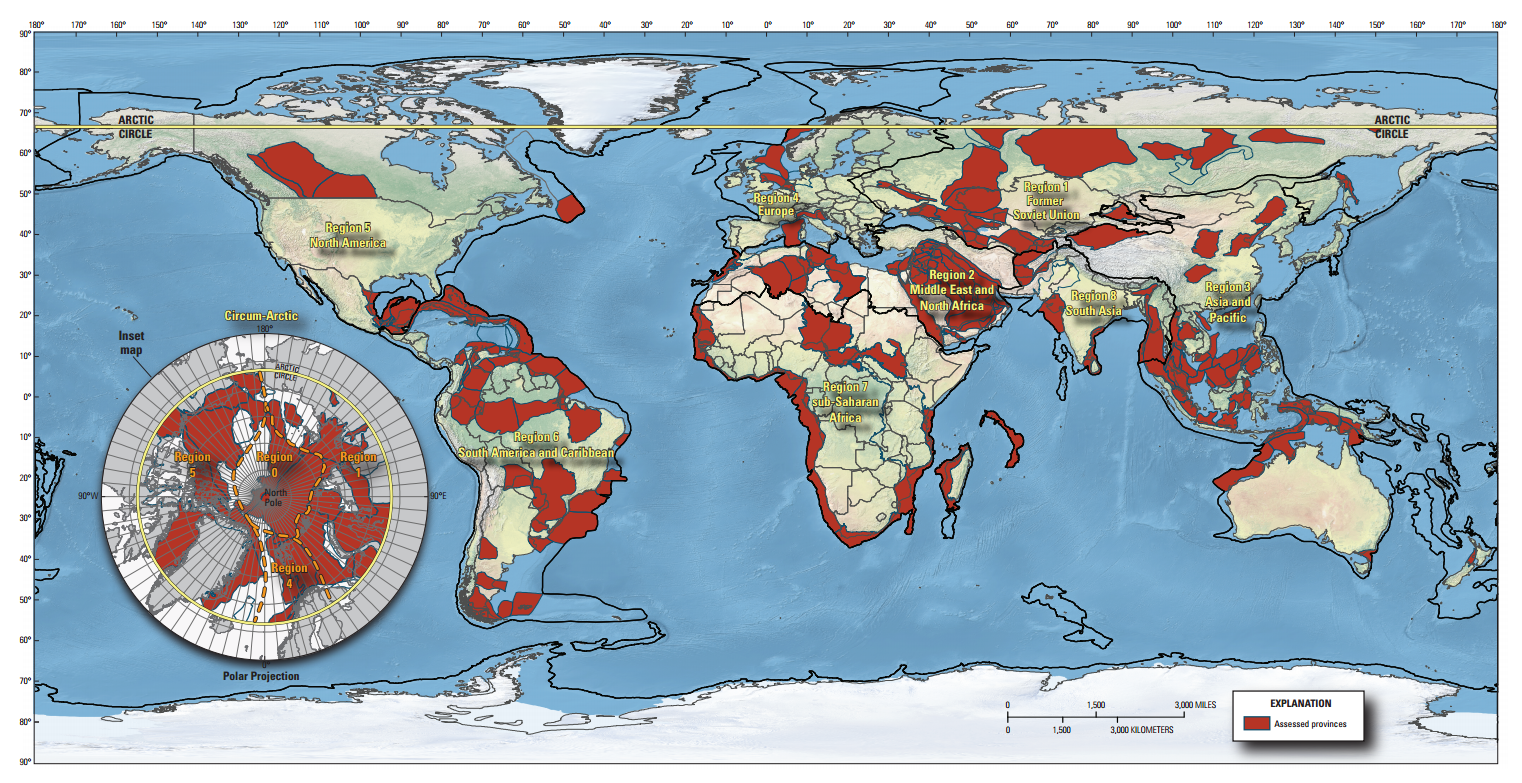
Mapping Global Oil Production
The map of oil production reflects the global distribution of reserves but also incorporates the complexities of extraction, refining, and transportation. While the Middle East remains the dominant producer, other regions have emerged as significant players, including:
- North America: The United States, fueled by shale oil production, has become a major oil producer, significantly impacting global markets.
- Russia: Russia’s vast oil fields and robust production infrastructure make it a leading oil producer, influencing global supply and pricing.
- China: China’s growing energy demand has led to increased domestic production and strategic investments in overseas oil fields.
- Africa: Several African countries, like Nigeria and Angola, are significant oil producers, contributing to global supply and economic growth.
The Flow of Oil: Global Consumption Patterns
The global map of oil consumption highlights the interconnectedness of nations and the dependence of industrialized economies on this resource. The largest consumers of oil are:
- United States: The United States, with its large population and reliance on automobiles, remains the world’s top oil consumer.
- China: China’s rapid industrialization and growing vehicle fleet have propelled it to become the second largest oil consumer globally.
- Japan: Japan’s dependence on imported oil for energy needs makes it a significant consumer.
- India: India’s growing economy and rising middle class are driving increased oil consumption.
- European Union: The European Union, as a collective, represents a substantial oil consumer, with varying levels of dependence on this resource across member states.
The Dynamics of Oil Prices: A Complex Interplay of Factors
The price of oil is a crucial factor in the global economy, influencing energy costs, inflation, and economic growth. The price is determined by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Supply and Demand: The balance between global oil supply and demand is the primary driver of price fluctuations.
- Geopolitical Events: Political instability in oil-producing regions, such as the Middle East, can disrupt supply chains and lead to price spikes.
- Economic Growth: Global economic growth often leads to increased oil demand, driving prices higher.
- Technological Advancements: New technologies, such as shale oil extraction, can impact supply and price dynamics.
- Currency Fluctuations: The value of the US dollar, the currency in which oil is traded, can influence oil prices.
The Importance of Oil: A Multifaceted Resource
Oil’s significance extends beyond its role as an energy source. It is a crucial input for numerous industries, including:
- Transportation: Oil fuels vehicles, airplanes, and ships, powering global transportation systems.
- Manufacturing: Oil-based products, such as plastics, fertilizers, and chemicals, are essential inputs for various industries.
- Agriculture: Oil-derived fertilizers and pesticides are critical for modern agricultural practices.
- Construction: Oil-based products, such as asphalt and building materials, are integral to infrastructure development.
The Challenges of Oil Dependence: Environmental and Economic Concerns
The reliance on oil presents significant challenges, including:
- Environmental Impact: Oil extraction and combustion contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change.
- Resource Depletion: Finite oil reserves raise concerns about future energy security and the need for alternative sources.
- Price Volatility: Fluctuations in oil prices can create economic instability, particularly for countries heavily reliant on oil imports.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Competition for oil resources can lead to geopolitical tensions and conflicts.
The Transition to a Sustainable Energy Future
The challenges posed by oil dependence have spurred efforts to transition to a more sustainable energy future. This transition involves:
- Developing Renewable Energy Sources: Investing in renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, is crucial for reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
- Improving Energy Efficiency: Improving energy efficiency in transportation, buildings, and industries can reduce overall energy consumption.
- Promoting Sustainable Transportation: Encouraging electric vehicles, public transportation, and cycling can reduce reliance on oil for transportation.
FAQs:
1. What are the largest oil reserves in the world?
The Middle East holds the largest share of global oil reserves, with Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Kuwait, and the United Arab Emirates possessing significant reserves.
2. How does the map of oil production differ from the map of oil reserves?
While the map of oil reserves shows the geographic distribution of oil deposits, the map of oil production reflects the actual extraction and output of oil, which can be influenced by factors like technology, infrastructure, and political stability.
3. What are the main factors influencing oil prices?
Oil prices are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including global supply and demand, geopolitical events, economic growth, technological advancements, and currency fluctuations.
4. What are the environmental consequences of oil dependence?
Oil extraction and combustion contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change. Oil spills and pollution also have devastating impacts on ecosystems.
5. What are some alternative energy sources that can reduce reliance on oil?
Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydropower, and geothermal energy, are promising alternatives to oil.
Tips:
- Stay informed about global oil market trends: Follow news and analysis related to oil production, consumption, and pricing.
- Consider the environmental impact of oil consumption: Make conscious choices to reduce your carbon footprint, such as choosing fuel-efficient vehicles or using public transportation.
- Support investments in renewable energy: Encourage policies and initiatives that promote the development and adoption of renewable energy sources.
- Promote energy efficiency: Adopt energy-saving practices at home and in your workplace to reduce energy consumption.
Conclusion:
The map of oil in the world provides a visual representation of a complex and interconnected energy system. Understanding the distribution of oil reserves, production, and consumption is essential for policymakers, businesses, and individuals alike. The challenges posed by oil dependence, including environmental impact, resource depletion, and price volatility, highlight the need for a transition to a more sustainable energy future. By embracing renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable transportation, we can move towards a future that is less reliant on fossil fuels and more resilient to the challenges of climate change.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Global Landscape of Oil: Understanding the Distribution and Significance of a Vital Resource. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!