The Gulag Archipelago: A Map of Soviet Repression
Related Articles: The Gulag Archipelago: A Map of Soviet Repression
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Gulag Archipelago: A Map of Soviet Repression. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Gulag Archipelago: A Map of Soviet Repression

The term "Gulag" refers to the vast network of forced labor camps established throughout the Soviet Union during the 20th century. These camps were a defining feature of the Soviet totalitarian state, serving as instruments of political repression and social control. While the term "Gulag" is often used to refer to the camps themselves, it more accurately encompasses the entire system of forced labor, including the camps, the administration, and the legal framework that enabled it.
Mapping the Gulag Archipelago:
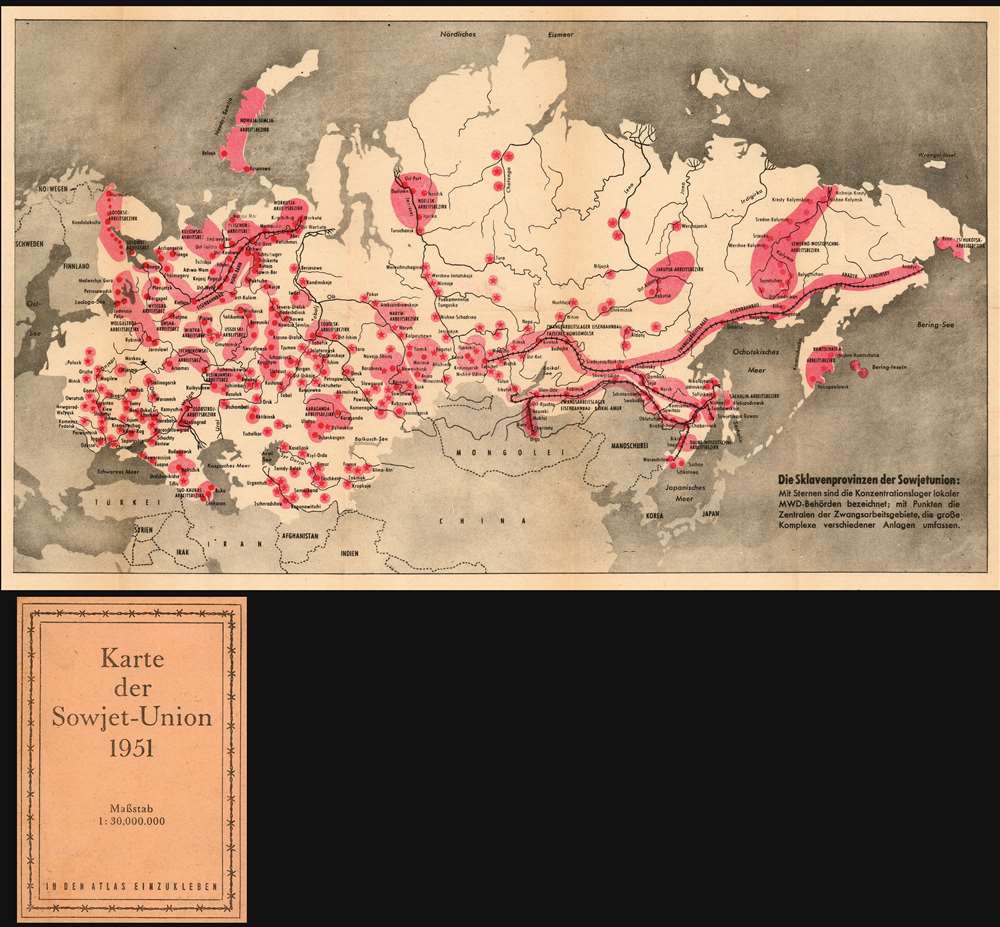
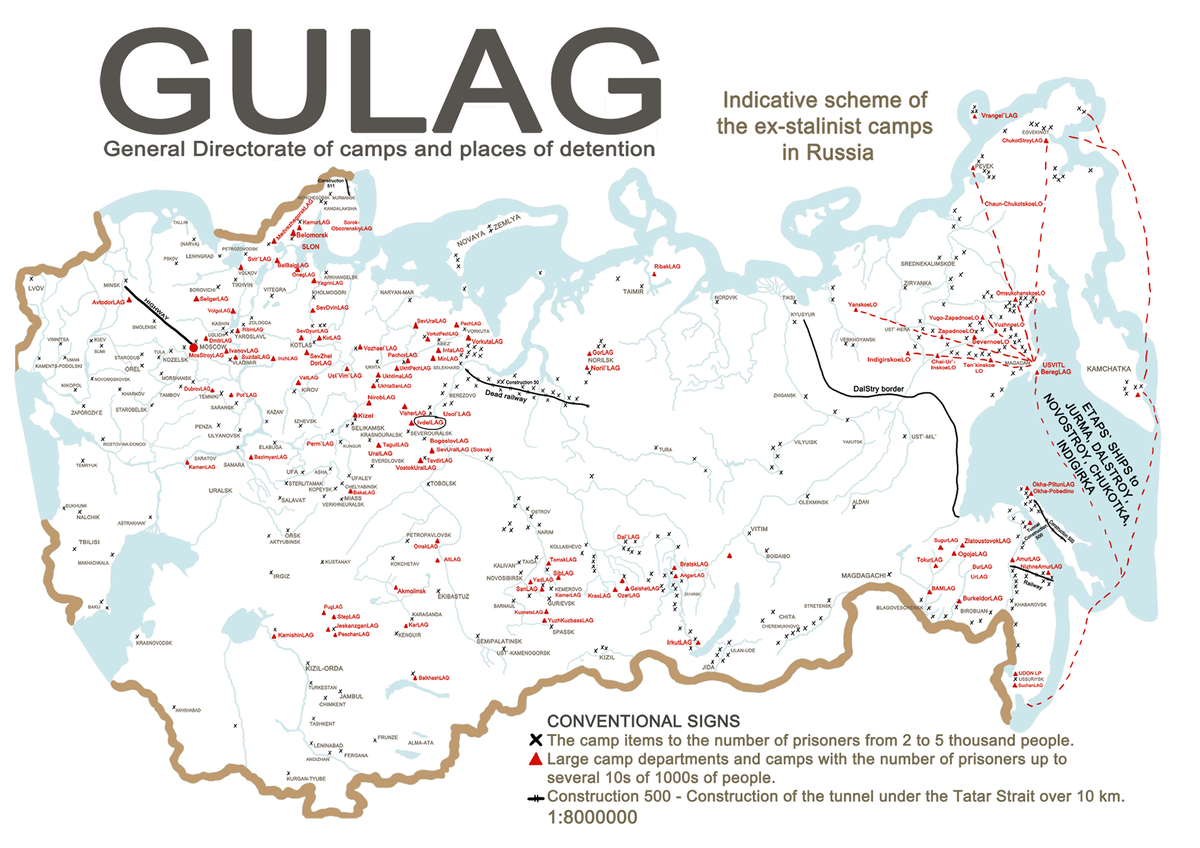
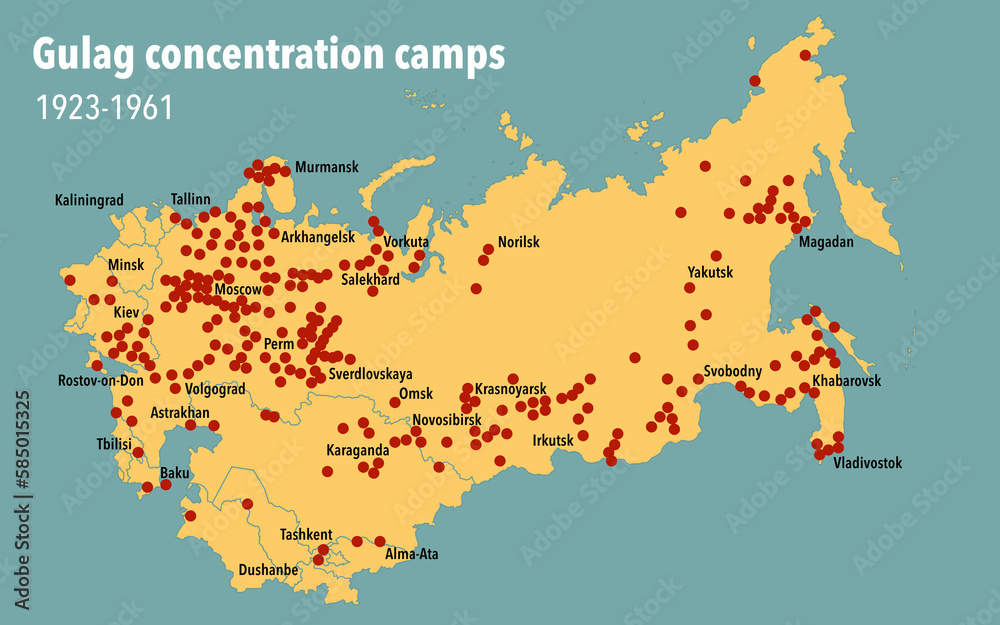
Understanding the Gulag system requires visualizing its geographical scope. The Gulag Archipelago, as it is often called, spanned the entire Soviet Union, from the Arctic Circle to the Caucasus Mountains. The camps were located in remote and harsh regions, often in areas with extreme climates and limited resources. This strategic placement aimed to isolate prisoners and make escape extremely difficult.
The Gulag Map: A Tool for Understanding Repression:
A map of the Gulag system is an invaluable tool for understanding the extent of Soviet repression. It reveals the vastness of the system, the diverse geographical locations of the camps, and the interconnectedness of the network. By studying a Gulag map, one can gain insights into:
- The geographical distribution of repression: The map highlights the regions where the camps were concentrated, revealing patterns of political persecution across different ethnic groups and social classes.
- The harsh conditions of the camps: The map provides context for the extreme climate conditions, remote locations, and lack of resources that prisoners endured.
- The scale of the system: The map visually demonstrates the sheer number of camps and the vast population of prisoners held within them, offering a tangible representation of the human cost of the Gulag.
- The political motivations behind the system: The map reveals the strategic placement of camps in relation to key industrial centers, transportation routes, and resource-rich areas, illustrating the economic and political goals of the Gulag.
Beyond the Physical Map: Understanding the Gulag’s Impact:
While a physical map offers a visual representation of the Gulag system, it is essential to understand the system’s broader impact on Soviet society and the world. The Gulag was not merely a system of imprisonment; it was a tool of terror and control that had profound social, economic, and political consequences.
Social Impact:
- The destruction of families and communities: The arbitrary arrests and forced labor of millions of people shattered families and communities, leaving behind a legacy of trauma and loss.
- The erosion of trust and social cohesion: The pervasive fear of being arrested and sent to the Gulag created an atmosphere of suspicion and mistrust within Soviet society.
- The suppression of dissent and intellectual freedom: The Gulag served as a powerful deterrent against any form of opposition to the Soviet regime, silencing critics and stifling intellectual and artistic expression.
Economic Impact:
- The exploitation of forced labor: The Gulag was a major source of cheap labor for the Soviet economy, utilizing prisoners for construction projects, resource extraction, and industrial production.
- The inefficiency and waste of resources: The harsh conditions and lack of incentives in the camps resulted in low productivity and widespread waste, ultimately hindering the development of the Soviet economy.
- The creation of a black market: The scarcity of goods and services within the camps led to the development of a thriving black market, further undermining the Soviet economic system.
Political Impact:
- The consolidation of totalitarian power: The Gulag served as a key tool for consolidating the power of the Soviet regime, eliminating political opposition and suppressing dissent.
- The creation of a climate of fear and repression: The threat of being sent to the Gulag created a climate of fear and silence, stifling any form of independent thought or action.
- The distortion of historical narratives: The Gulag system was a dark secret of the Soviet Union, and its history was systematically erased or distorted by the regime, perpetuating a culture of denial and misinformation.
The Legacy of the Gulag:
The Gulag system was a dark chapter in human history, leaving behind a legacy of trauma, loss, and injustice. Its impact on Soviet society and the world continues to be felt today, as the memories of the victims and the lessons of the system remain relevant.
FAQs about the Gulag:
Q: What was the purpose of the Gulag?
A: The Gulag was primarily a tool of political repression and social control. It served to eliminate political opposition, suppress dissent, and provide cheap labor for the Soviet economy.
Q: Who were the prisoners in the Gulag?
A: The Gulag held a diverse population of prisoners, including political opponents, religious figures, ethnic minorities, intellectuals, and ordinary citizens who were deemed "enemies of the state" for various reasons.
Q: What were the conditions like in the Gulag?
A: The conditions in the Gulag were brutal and inhumane. Prisoners were subjected to forced labor, malnutrition, disease, and violence. Mortality rates were extremely high, and many prisoners died from exhaustion, starvation, or exposure to the elements.
Q: How did the Gulag system end?
A: The Gulag system gradually declined in the late 1950s and early 1960s, following the death of Joseph Stalin and the rise of Nikita Khrushchev. While some camps were closed, the system was not fully dismantled, and forced labor continued in various forms until the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991.
Tips for Understanding the Gulag:
- Study historical maps and documents: Examining maps of the Gulag and reading firsthand accounts of prisoners can provide a deeper understanding of the system’s geography and the experiences of its victims.
- Explore the archives: Numerous archives and museums around the world hold valuable documents and artifacts related to the Gulag, offering insights into the system’s history and impact.
- Engage with academic literature: There is a wealth of scholarly research on the Gulag, providing in-depth analysis of the system’s origins, operation, and consequences.
- Attend lectures and workshops: Participating in events focused on the Gulag can provide valuable insights from experts and allow for discussions with others interested in the topic.
Conclusion:
The Gulag system was a dark stain on the history of the Soviet Union, a testament to the dangers of totalitarianism and the human cost of repression. Understanding the Gulag is crucial for understanding the 20th century and for preventing similar atrocities from occurring in the future. By studying the maps, archives, and literature related to the Gulag, we can honor the memory of the victims and ensure that their suffering is not forgotten.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Gulag Archipelago: A Map of Soviet Repression. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!