The Tarim Basin: A Geological and Ecological Tapestry
Related Articles: The Tarim Basin: A Geological and Ecological Tapestry
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Tarim Basin: A Geological and Ecological Tapestry. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Tarim Basin: A Geological and Ecological Tapestry

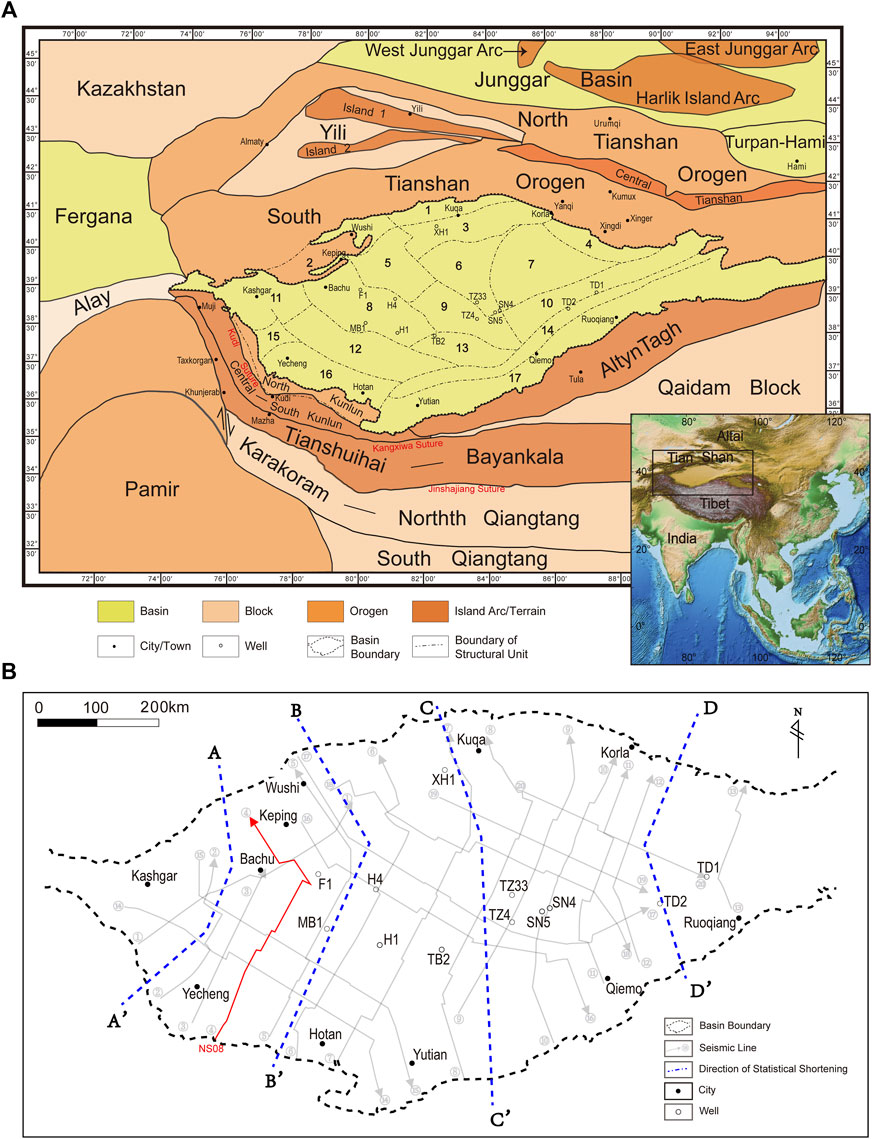
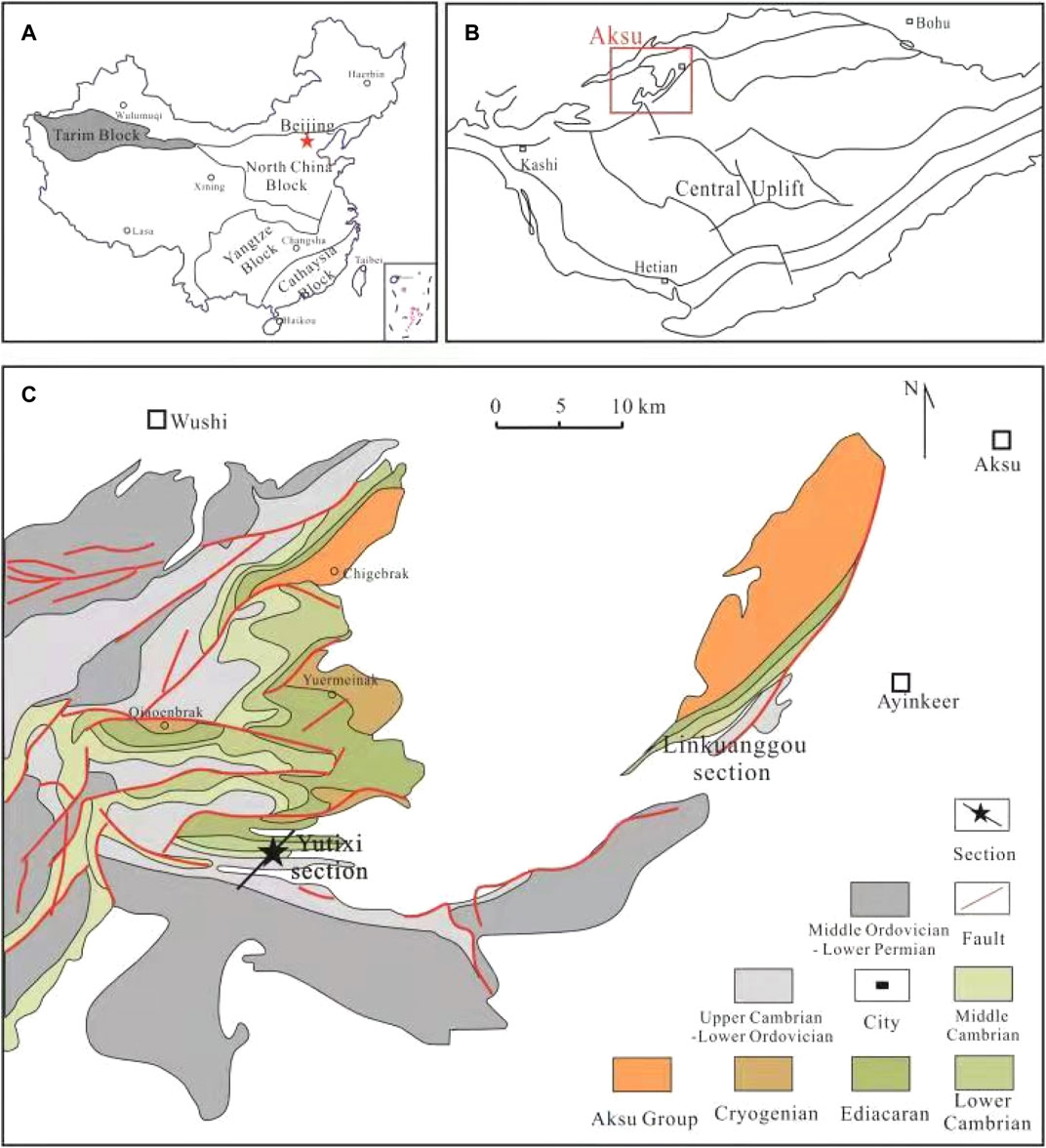
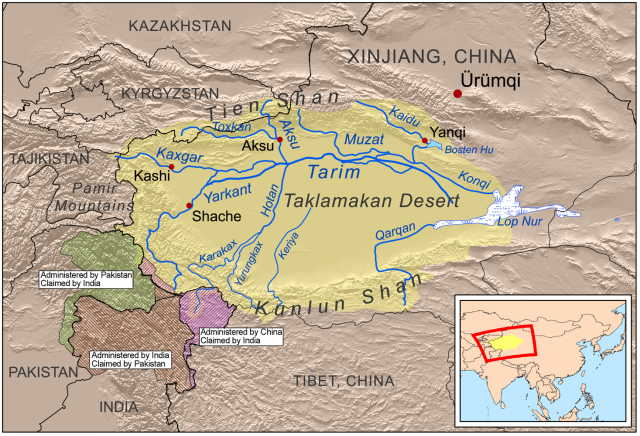
The Tarim Basin, a vast endorheic basin located in Northwest China, stands as a testament to the intricate interplay of geological forces and ecological processes. This arid expanse, encompassing an area of approximately 500,000 square kilometers, holds within its boundaries a rich history, a diverse ecosystem, and significant economic potential.
A Geological Legacy:
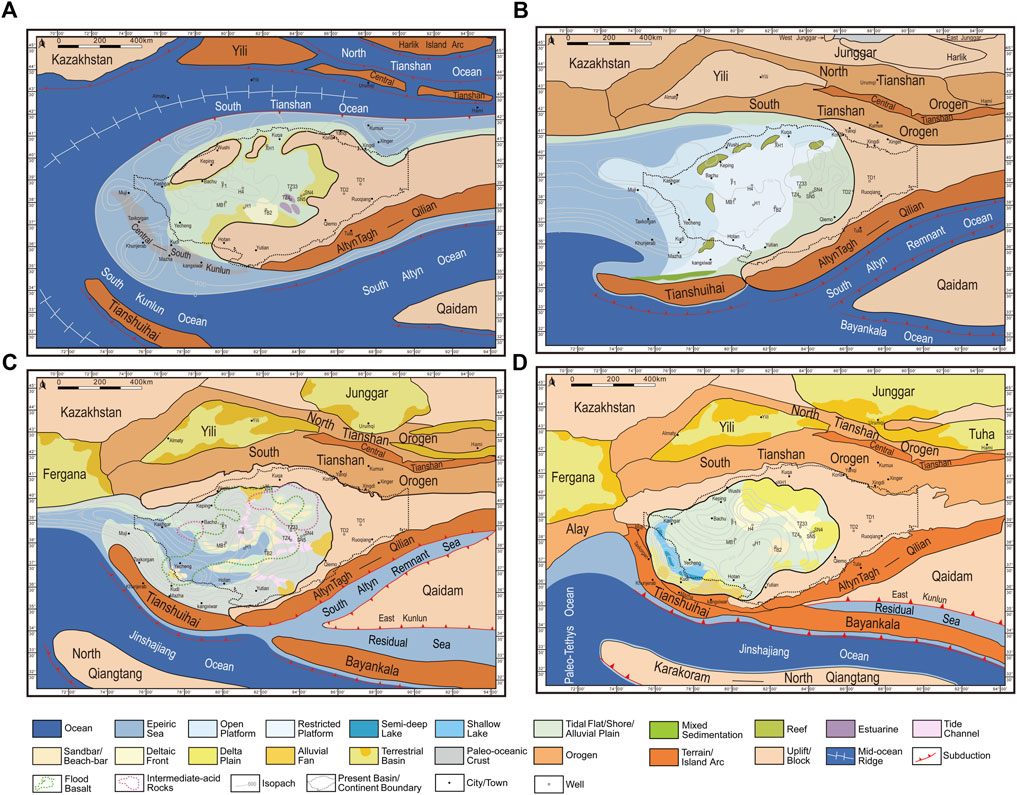
The Tarim Basin’s formation is a story etched in time, spanning millions of years. The basin’s origins lie in the collision of the Eurasian and Indian tectonic plates, which triggered the uplift of the surrounding mountains, including the Kunlun, Tian Shan, and Pamir ranges. These towering peaks act as natural barriers, trapping moisture and creating the characteristic aridity of the basin.
Over time, sediments eroded from these mountains accumulated in the basin, forming thick layers of alluvial deposits. This process, coupled with tectonic activity, led to the development of a complex geological structure, characterized by deep depressions, vast plains, and numerous salt lakes.
A Unique and Fragile Ecosystem:
The Tarim Basin, despite its harsh environment, harbors a remarkable array of life. The basin’s unique ecosystem has evolved to thrive in the face of extreme aridity, high salinity, and limited precipitation.
- The Taklamakan Desert: The heart of the Tarim Basin is dominated by the Taklamakan Desert, one of the largest and most arid deserts in the world. This vast expanse of sand dunes, covering an area of approximately 337,600 square kilometers, presents a formidable challenge to life. Yet, within this seemingly desolate landscape, specialized plants and animals have adapted to survive.
- Oases: Scattered across the basin are oases, verdant pockets of life sustained by groundwater sources. These oases, often home to ancient settlements, serve as critical habitats for a variety of plant and animal species.
- The Tarim River: The Tarim River, the basin’s lifeline, flows through the southern portion of the basin. It originates in the Kunlun Mountains and traverses the desert before finally emptying into the Lop Nur, a terminal lake. This river sustains a unique ecosystem, providing water for agriculture and supporting a diverse range of aquatic life.
Economic Significance:
The Tarim Basin holds considerable economic potential, driven by its rich natural resources.
- Oil and Gas: The basin is a major source of oil and natural gas, with vast reserves discovered beneath its arid plains. The development of these resources has played a crucial role in China’s energy security.
- Mineral Resources: The basin also contains significant deposits of minerals, including copper, gold, and potash. The exploitation of these resources has contributed to the region’s economic development.
- Agriculture: Though limited by aridity, agriculture plays a vital role in the basin’s economy. The oases, sustained by groundwater, support the cultivation of crops like cotton, dates, and grapes.
Challenges and Conservation:
Despite its economic potential, the Tarim Basin faces numerous challenges, primarily related to its fragile environment.
- Desertification: The basin is vulnerable to desertification, driven by climate change, overgrazing, and unsustainable agricultural practices. This process threatens the livelihoods of local communities and the unique biodiversity of the region.
- Water Scarcity: The Tarim Basin is characterized by water scarcity, with limited precipitation and a high rate of evaporation. This scarcity poses challenges to agriculture, industry, and the sustainability of the basin’s ecosystem.
- Pollution: Industrial activities, particularly the extraction of oil and gas, have led to pollution of water resources and soil contamination. This poses a threat to human health and the environment.
The Importance of the Tarim Basin:
The Tarim Basin stands as a crucial area for China’s economic development, ecological balance, and cultural heritage.
- Energy Security: The basin’s oil and gas reserves contribute significantly to China’s energy security, reducing reliance on external sources.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: The basin’s unique ecosystem, despite its aridity, harbors a remarkable array of plant and animal species, making it a biodiversity hotspot.
- Cultural Significance: The Tarim Basin is home to ancient settlements, including the Silk Road cities of Loulan and Niya, providing valuable insights into the history and culture of the region.
FAQs about the Tarim Basin:
1. What is the climate of the Tarim Basin?
The Tarim Basin has a hyper-arid climate, characterized by extremely low precipitation, high temperatures, and strong winds. The basin receives less than 50 millimeters of rainfall annually, making it one of the driest regions on Earth.
2. What are the major cities in the Tarim Basin?
The major cities in the Tarim Basin include Kashgar, Hotan, and Yarkand. These cities serve as important economic and cultural centers for the region.
3. What are the major threats to the Tarim Basin’s ecosystem?
The major threats to the Tarim Basin’s ecosystem include desertification, water scarcity, pollution, and habitat fragmentation.
4. What are some of the efforts to conserve the Tarim Basin’s environment?
Efforts to conserve the Tarim Basin’s environment include the establishment of protected areas, the implementation of sustainable agricultural practices, and the promotion of renewable energy sources.
5. What is the significance of the Tarim Basin in Chinese history?
The Tarim Basin has played a significant role in Chinese history, serving as a crossroads for trade and cultural exchange along the Silk Road. Ancient settlements, including Loulan and Niya, provide valuable insights into the region’s past.
Tips for Understanding the Tarim Basin:
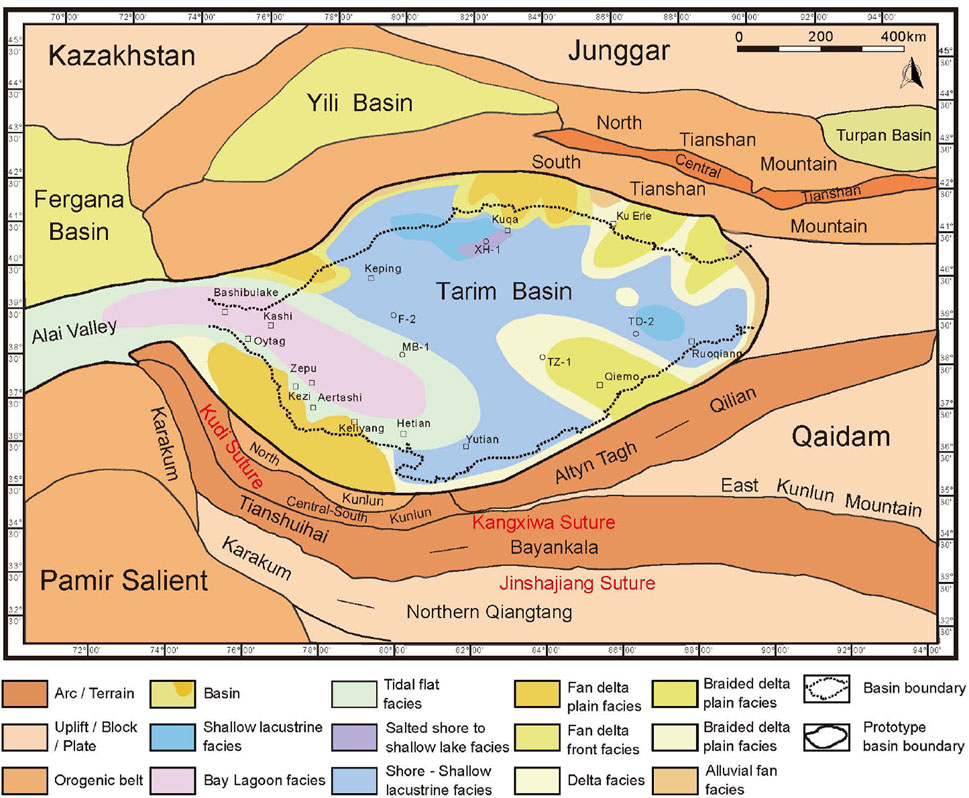
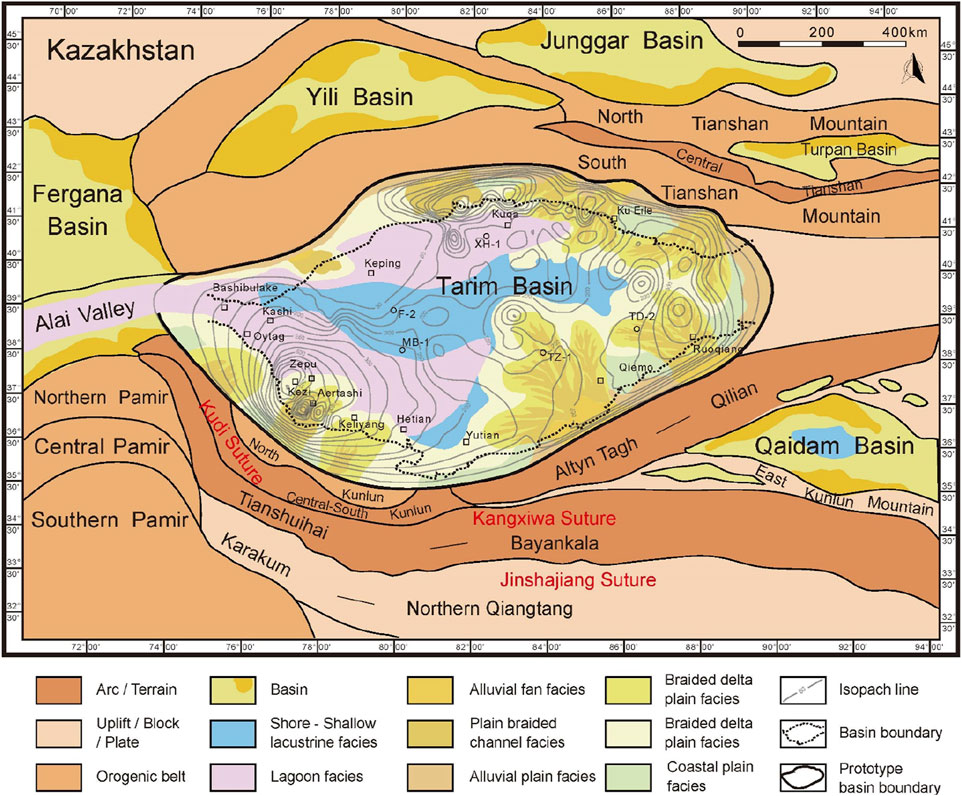
- Visualize the Map: Use a map of the Tarim Basin to understand its geographical location, surrounding mountains, and major rivers.
- Explore the Ecosystem: Research the unique plant and animal species that have adapted to the basin’s arid environment.
- Learn about the History: Explore the ancient civilizations that once thrived in the Tarim Basin, including the Silk Road cities.
- Consider the Economic Impact: Investigate the role of the Tarim Basin in China’s energy security and economic development.
- Be Aware of Environmental Challenges: Understand the threats facing the basin’s ecosystem and the efforts being made to conserve it.
Conclusion:
The Tarim Basin, a vast and arid expanse in Northwest China, stands as a testament to the enduring power of geological forces and the resilience of life. This unique ecosystem, characterized by extreme conditions and diverse inhabitants, holds significant economic potential while facing numerous environmental challenges. Understanding the Tarim Basin’s complex interplay of geology, ecology, and human activity is crucial for ensuring its sustainable future.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Tarim Basin: A Geological and Ecological Tapestry. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!