Understanding Flood Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to USGS Flood Maps
Related Articles: Understanding Flood Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to USGS Flood Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Flood Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to USGS Flood Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Flood Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to USGS Flood Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Flood Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to USGS Flood Maps
- 3.1 What are USGS Flood Maps?
- 3.2 The Importance of USGS Flood Maps
- 3.3 How to Access and Interpret USGS Flood Maps
- 3.4 FAQs about USGS Flood Maps
- 3.5 Tips for Using USGS Flood Maps
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding Flood Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to USGS Flood Maps

Flooding is a natural phenomenon that can cause significant damage to property, infrastructure, and lives. Recognizing and mitigating flood risks is crucial for communities and individuals alike. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) plays a vital role in this endeavor by providing valuable resources, including comprehensive flood maps. These maps serve as essential tools for understanding flood hazards, making informed decisions, and building resilience.
What are USGS Flood Maps?
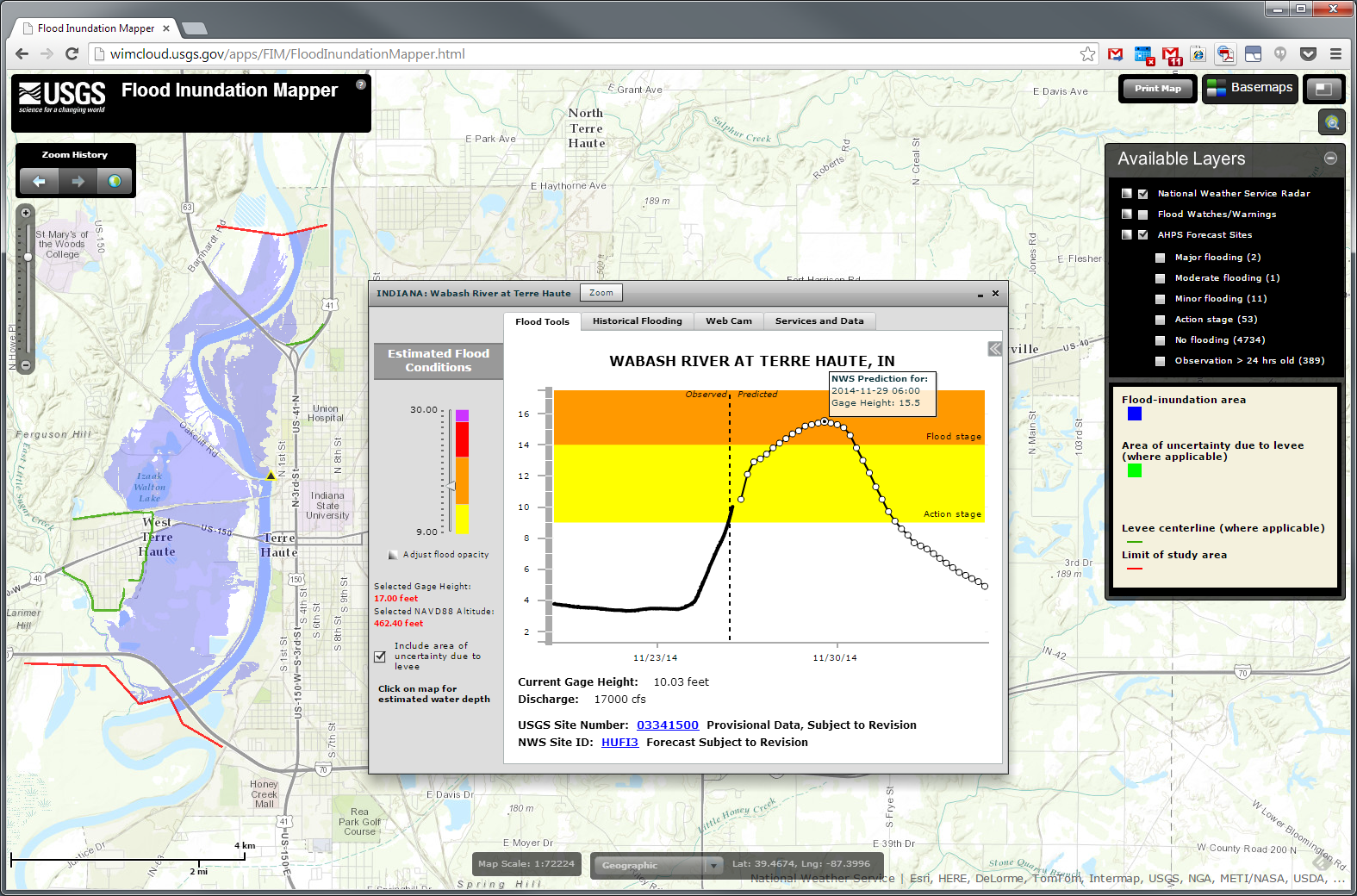
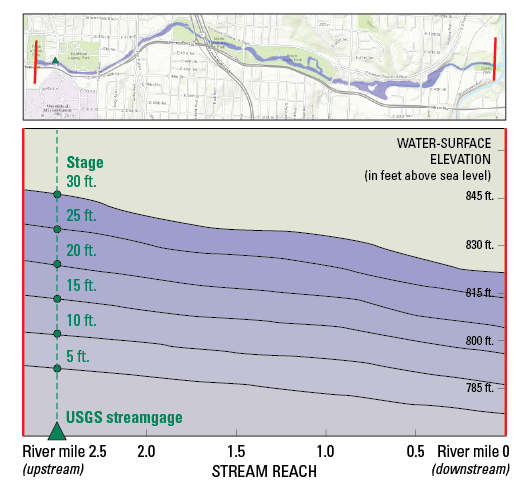
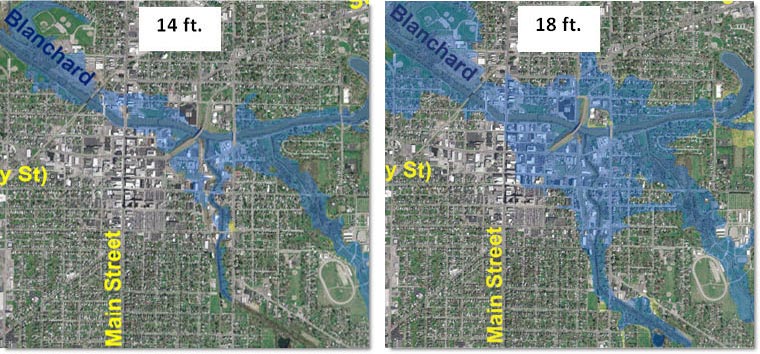
USGS flood maps, also known as Flood Insurance Rate Maps (FIRMs), are detailed representations of flood zones and their associated flood risks. They depict areas that have a 1% chance of experiencing a flood event in any given year, often referred to as the "100-year floodplain." These maps are developed based on extensive scientific data, including historical flood records, topographic surveys, and hydrological models.
The Importance of USGS Flood Maps
USGS flood maps are instrumental in numerous aspects of flood risk management:
- Understanding Flood Hazards: The maps clearly identify areas susceptible to flooding, allowing communities and individuals to assess their potential risks. This knowledge enables proactive planning and mitigation measures.
- Flood Insurance Requirements: Flood maps are used by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) to determine flood insurance requirements for properties within designated flood zones. Understanding these requirements ensures adequate financial protection in case of a flood event.
- Community Planning and Development: Local governments utilize flood maps to guide land use planning, zoning regulations, and infrastructure development, ensuring that new construction projects minimize flood risks and protect vulnerable areas.
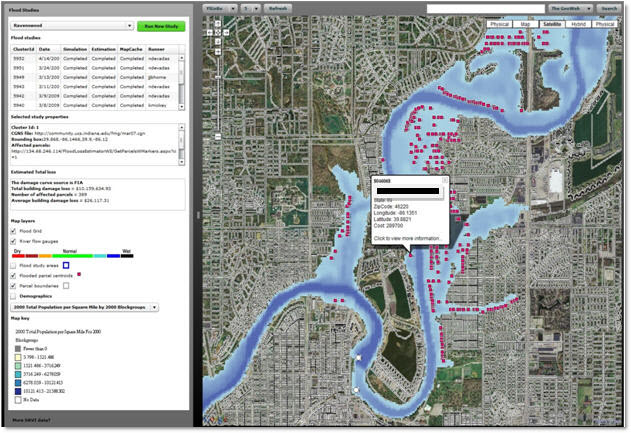
- Emergency Response and Recovery: Flood maps provide crucial information for emergency responders, enabling efficient resource allocation and evacuation strategies during flood events. They also facilitate post-flood recovery efforts by identifying areas most affected and guiding reconstruction plans.
- Individual Risk Assessment: Individuals can use flood maps to evaluate the flood risk of their property, understand potential damages, and explore mitigation options to reduce their vulnerability.
How to Access and Interpret USGS Flood Maps
USGS flood maps are readily accessible through various channels:
- FEMA’s Flood Map Service Center: This online platform offers comprehensive flood map information for the entire United States. Users can search by address, location, or map number.
- USGS Flood Hazard Portal: This portal provides access to a wide range of flood-related data and resources, including flood maps, flood frequency analysis, and flood risk assessments.
- Local Government Offices: Many local governments maintain copies of flood maps for their jurisdictions and can provide assistance in interpreting the information.
Interpreting flood maps requires understanding the different flood zone designations:
- Special Flood Hazard Area (SFHA): This zone represents the 100-year floodplain, with a 1% annual chance of flooding. Properties within this zone typically require flood insurance.
- Zone A: This zone indicates areas that are susceptible to flooding but lack sufficient data to determine the precise flood risk.
- Zone X: This zone represents areas with a minimal risk of flooding.
- Other Flood Zones: Flood maps may include additional zones, such as floodways, coastal flood zones, and areas with specific flood hazards.
FAQs about USGS Flood Maps
1. What is the difference between a flood map and a flood risk assessment?
Flood maps provide a visual representation of flood zones, while flood risk assessments offer a more detailed analysis of flood hazards, including potential flood depths, velocities, and inundation durations.
2. How often are flood maps updated?
Flood maps are typically updated every five years, but updates can occur more frequently based on significant flood events, new data availability, or changes in development patterns.
3. Can I appeal a flood zone designation on a USGS flood map?
Yes, property owners can appeal flood zone designations if they believe the map is inaccurate or outdated. FEMA provides a formal appeal process for such cases.
4. What are some examples of flood mitigation measures?
Common flood mitigation measures include elevating structures, installing floodproofing measures like flood walls or flood vents, and creating natural flood buffers like wetlands or green infrastructure.
5. What are the benefits of purchasing flood insurance?
Flood insurance provides financial protection against flood damages, helping individuals and communities recover from flood events more effectively.
Tips for Using USGS Flood Maps
- Consult with a qualified professional: For complex flood risk assessments or mitigation planning, seek advice from a licensed engineer or floodplain manager.
- Consider future development plans: When making property purchase or development decisions, factor in potential flood risks and the implications of flood zone designations.
- Stay informed about flood events: Monitor weather forecasts and flood warnings, and be prepared to evacuate if necessary.
- Participate in community flood mitigation efforts: Support local initiatives aimed at reducing flood risks and enhancing community resilience.
Conclusion
USGS flood maps are invaluable tools for understanding and managing flood risks. By providing comprehensive information about flood zones and associated hazards, they empower communities and individuals to make informed decisions, mitigate potential damages, and build resilience against the impacts of flooding. Understanding the information provided by USGS flood maps is essential for promoting public safety, safeguarding property, and fostering sustainable development in flood-prone areas.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Flood Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to USGS Flood Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!