Understanding the Tamarack Fire: A Comprehensive Guide to Fire Maps and Resources
Related Articles: Understanding the Tamarack Fire: A Comprehensive Guide to Fire Maps and Resources
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Tamarack Fire: A Comprehensive Guide to Fire Maps and Resources. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Tamarack Fire: A Comprehensive Guide to Fire Maps and Resources
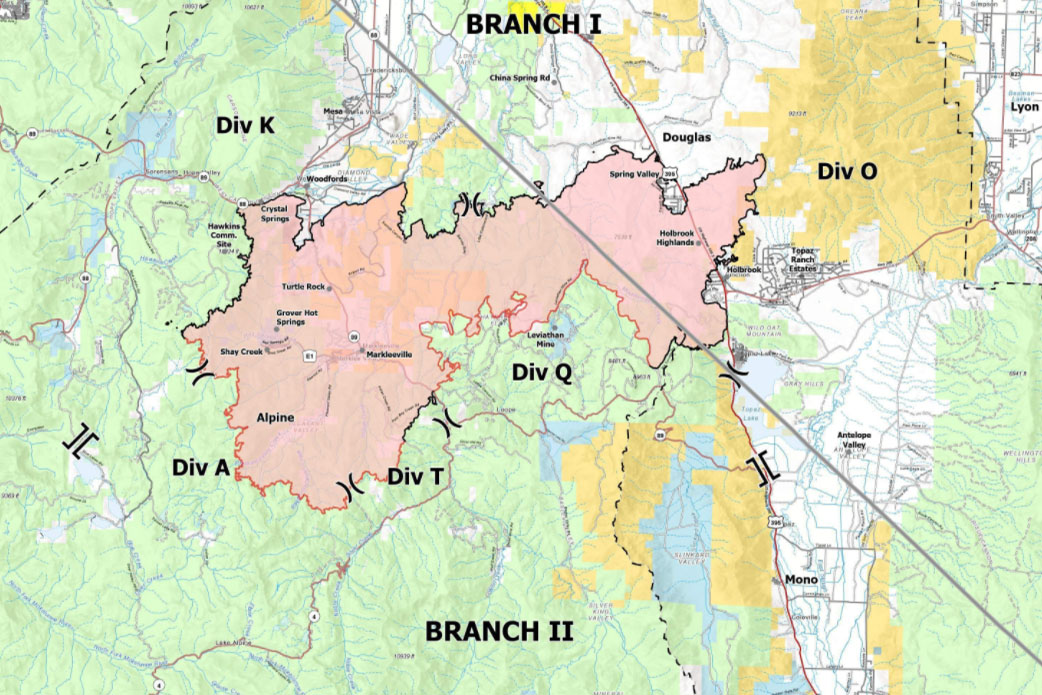
The Tamarack Fire, a significant wildfire that burned in California in 2021, serves as a stark reminder of the increasing threat of wildfires in a changing climate. Understanding fire maps and the resources available to track and manage these events is crucial for public safety, environmental protection, and informed decision-making. This article provides a detailed overview of Tamarack Fire maps, their significance, and the tools available to access and interpret this valuable information.
What is a Fire Map?
A fire map is a visual representation of a wildfire’s location, perimeter, and spread over time. These maps utilize various data sources, including satellite imagery, aerial reconnaissance, and ground observations, to provide a comprehensive picture of the fire’s progression. Fire maps are essential for firefighters, emergency responders, and the public to:
- Track the fire’s movement: Fire maps help visualize the fire’s path, allowing authorities to predict its potential spread and take proactive measures to protect lives and property.
- Identify areas of active fire: Maps highlight areas of intense burning, enabling firefighters to prioritize resources and focus their efforts on the most critical zones.
- Assess fire behavior: Fire maps provide insights into the fire’s intensity, rate of spread, and potential for growth, aiding in developing effective suppression strategies.
- Communicate with the public: Fire maps serve as a vital tool for informing the public about the fire’s location, potential impact, and evacuation orders, facilitating informed decision-making.
Tamarack Fire Maps: A Case Study
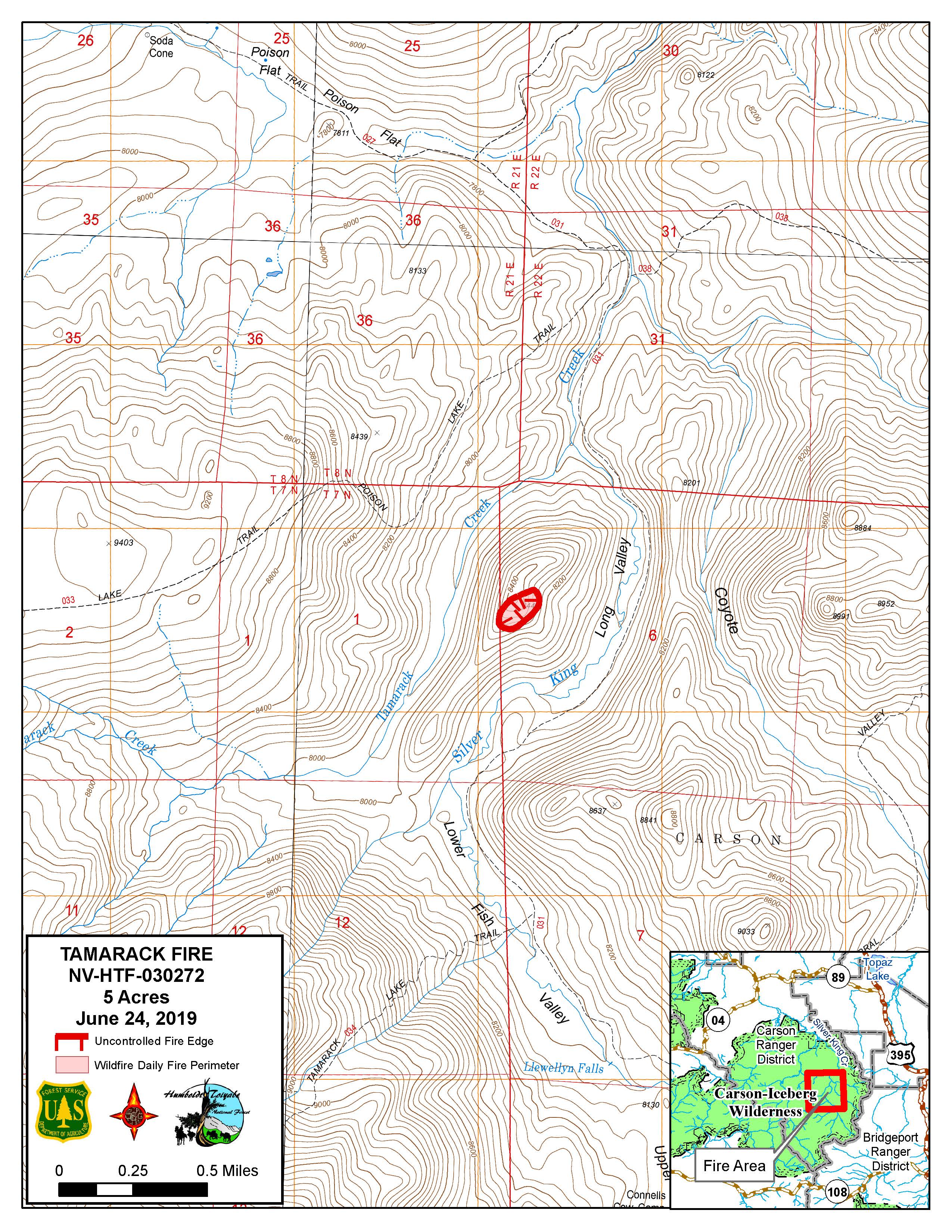
The Tamarack Fire, which ignited on July 4, 2021, near the town of Markleeville, California, rapidly grew into a major wildfire, burning over 68,000 acres. Fire maps played a critical role in managing this event, providing real-time updates on the fire’s progress, containment lines, and evacuation zones.
Key Features of Tamarack Fire Maps:
- Perimeter: The maps clearly outlined the fire’s perimeter, showing its expansion over time and helping to identify areas at risk.
- Containment lines: Fire maps depicted the containment lines established by firefighters, illustrating their efforts to control the fire’s spread.
- Evacuation zones: Maps highlighted areas under evacuation orders, guiding residents to safety.
- Fire intensity: Some maps displayed fire intensity, indicating areas of active burning and helping firefighters prioritize resources.
- Historical data: Fire maps also provided historical data, allowing for comparisons of fire progression over different time periods.
Accessing Fire Maps:
Several resources provide access to real-time and historical fire maps:
- InciWeb: The Incident Information System (InciWeb) is a comprehensive platform maintained by the National Interagency Fire Center (NIFC). It offers detailed information on active fires, including maps, updates, and incident reports.
- Cal Fire: The California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection (Cal Fire) provides fire maps and updates specific to wildfires within California.
- USFS: The United States Forest Service (USFS) offers maps and information for wildfires occurring on federal lands.
- Google Maps: Google Maps integrates real-time fire information, allowing users to visualize active fires and potential smoke impacts.
- Local news sources: Local news organizations often provide live updates and maps for significant wildfires in their coverage areas.
Interpreting Fire Maps:
Understanding the symbols and data presented on fire maps is essential for effective use. Common symbols include:
- Fire perimeter: Typically depicted as a solid line, indicating the outer boundary of the fire.
- Containment lines: Usually represented by dashed lines, showing areas where firefighters have established control.
- Evacuation zones: Often highlighted with distinct colors or symbols, indicating areas under evacuation orders.
- Fire intensity: May be represented by color gradients, with darker colors indicating higher intensity.
Benefits of Fire Maps:
- Improved fire management: Fire maps provide critical information for firefighters, enabling them to make informed decisions about resource allocation, suppression strategies, and safety protocols.
- Enhanced public safety: Maps inform the public about fire locations, evacuation orders, and potential hazards, promoting safety and preparedness.
- Environmental monitoring: Fire maps contribute to understanding fire behavior, smoke impacts, and the overall effects of wildfires on ecosystems.
- Research and analysis: Historical fire maps provide valuable data for researchers studying fire patterns, climate change, and the impact of wildfires on landscapes.
FAQs about Fire Maps:
-
What data sources are used to create fire maps?
- Fire maps utilize a combination of data sources, including satellite imagery, aerial reconnaissance, ground observations, and reports from firefighters.
-
How often are fire maps updated?
- The frequency of updates varies depending on the fire’s intensity and the resources available. Some maps are updated hourly, while others may be updated less frequently.
-
Can I contribute to fire mapping?
- Citizen scientists can contribute to fire mapping efforts by reporting fire observations, sharing photos, and using apps like FireMapper to provide real-time information.
-
What are the limitations of fire maps?
- Fire maps are based on available data and may not always reflect the true extent of the fire due to factors like smoke, terrain, and weather conditions.
Tips for Using Fire Maps:
- Check multiple sources: Compare maps from different sources to get a comprehensive understanding of the fire situation.
- Pay attention to updates: Fire maps are dynamic and constantly changing; check for updates regularly.
- Understand the symbols: Familiarize yourself with the symbols used on fire maps to interpret the information accurately.
- Use maps alongside other resources: Combine fire maps with news reports, evacuation orders, and official websites for a complete picture.
Conclusion:
Fire maps are essential tools for understanding, managing, and responding to wildfires. They provide a visual representation of fire progression, containment efforts, and potential hazards, enabling informed decision-making for firefighters, emergency responders, and the public. By utilizing available resources and understanding the information presented on fire maps, individuals can play a vital role in promoting safety, preparedness, and effective wildfire management.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Tamarack Fire: A Comprehensive Guide to Fire Maps and Resources. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!