Unveiling Ireland’s Landscape: A Journey Through the Topographic Map
Related Articles: Unveiling Ireland’s Landscape: A Journey Through the Topographic Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Ireland’s Landscape: A Journey Through the Topographic Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling Ireland’s Landscape: A Journey Through the Topographic Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling Ireland’s Landscape: A Journey Through the Topographic Map
- 3.1 Understanding the Topography of Ireland
- 3.2 The Importance of the Topographic Map
- 3.3 Exploring the Benefits of the Topographic Map
- 3.4 FAQs About the Topographic Map of Ireland
- 3.5 Tips for Using a Topographic Map of Ireland
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling Ireland’s Landscape: A Journey Through the Topographic Map
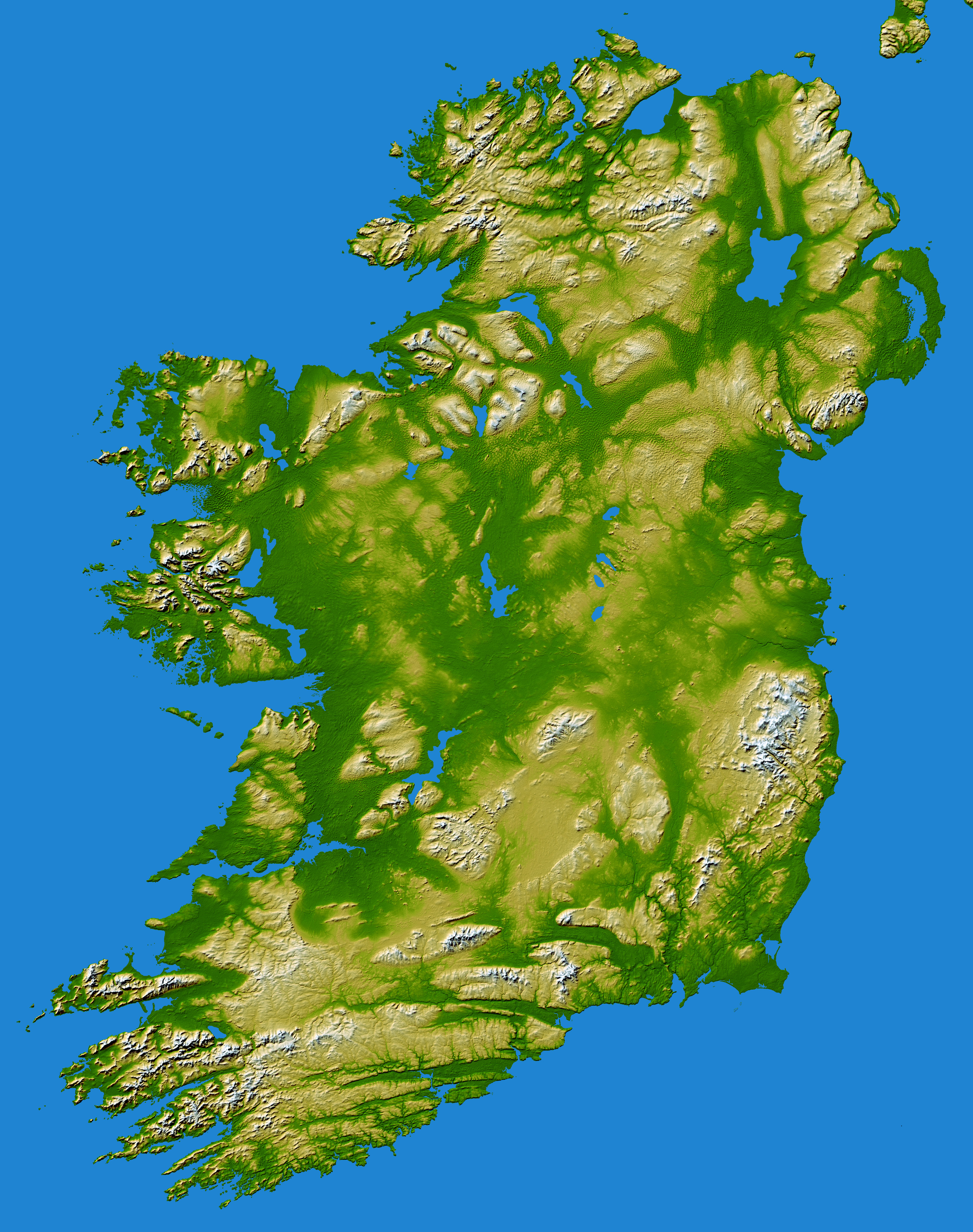
Ireland, the Emerald Isle, is renowned for its captivating landscapes, from rugged coastlines to rolling hills and verdant valleys. Understanding the intricate interplay of these features is crucial for appreciating the country’s natural beauty and understanding its unique character. This is where the topographic map of Ireland becomes an invaluable tool, providing a visual representation of the island’s terrain and its diverse geological formations.
Understanding the Topography of Ireland
A topographic map, unlike a traditional map, goes beyond simply outlining geographical boundaries. It utilizes contour lines, elevation markings, and symbols to depict the three-dimensional nature of the land. These lines connect points of equal elevation, allowing viewers to visualize the rise and fall of the terrain. This visual representation reveals the island’s dramatic landscapes, from the towering peaks of the Wicklow Mountains to the gentle slopes of the Burren in County Clare.
Key Features of the Irish Topographic Map:
- Mountains and Uplands: The map highlights the presence of mountain ranges like the Wicklow Mountains, the Mourne Mountains, and the Macgillycuddy’s Reeks, Ireland’s highest mountain range. These elevated areas often exhibit steep slopes and rugged terrain.
- Lowlands and Plains: The map also showcases extensive lowlands and plains, such as the Central Plain of Ireland, which is characterized by gentle slopes and fertile land. This region has historically been important for agriculture and settlement.
- Rivers and Lakes: Ireland’s intricate network of rivers and lakes is clearly depicted, showcasing the influence of water on the landscape. The River Shannon, the longest river in Ireland, meanders through the country, while numerous lakes dot the landscape, including Lough Neagh, Ireland’s largest lake.
- Coastal Features: The map accurately represents Ireland’s extensive coastline, including its numerous bays, inlets, and peninsulas. This intricate coastline provides a diverse range of habitats for marine life and offers stunning views for visitors.
- Geological Formations: The map provides insights into the geological history of Ireland, revealing the presence of various rock formations, including limestone, granite, and sandstone. These formations contribute to the unique character of different regions, influencing the soil type, vegetation, and overall landscape.
The Importance of the Topographic Map
The topographic map serves as a valuable resource for a wide range of purposes, including:
- Navigation and Exploration: For hikers, cyclists, and outdoor enthusiasts, the map provides crucial information about elevation changes, terrain features, and potential hazards. It enables them to plan routes, assess difficulty levels, and navigate safely.
- Environmental Studies: Scientists and researchers utilize the topographic map to study the impact of climate change on the landscape, analyze erosion patterns, and understand the distribution of flora and fauna.
- Land Management and Development: Planners and developers rely on the map to assess the suitability of land for various uses, considering factors like terrain, drainage, and access.
- Educational Purposes: The topographic map serves as an effective educational tool for students learning about geography, geology, and environmental science. It provides a visual representation of the country’s landscape and fosters a deeper understanding of its natural processes.
Exploring the Benefits of the Topographic Map
Beyond its practical applications, the topographic map offers a unique perspective on Ireland’s landscape, highlighting its beauty and complexity. It allows viewers to:
- Appreciate the Scale and Diversity of the Landscape: By visualizing the elevation changes and topographic features, one can better grasp the scale and diversity of Ireland’s landscape, from the majestic mountains to the gentle lowlands.
- Gain a Deeper Understanding of the Relationship Between Land and Water: The map reveals the intricate connection between Ireland’s rivers, lakes, and coastline, showcasing the influence of water on shaping the landscape.
- Recognize the Impact of Geology on the Terrain: The map highlights the presence of different geological formations, revealing how they contribute to the diverse character of different regions.
- Develop a Sense of Place: By studying the topographic map, individuals can develop a deeper appreciation for the unique characteristics of specific regions and their place within the broader landscape.
FAQs About the Topographic Map of Ireland
1. Where can I find a topographic map of Ireland?
Topographic maps of Ireland are available from various sources, including:
- The Ordnance Survey of Ireland: The official government agency responsible for mapping Ireland provides detailed topographic maps both online and in print.
- Online Mapping Platforms: Websites like Google Maps and OpenStreetMap offer interactive topographic maps with varying levels of detail.
- Outdoor Stores and Bookstores: Specialized outdoor stores and bookstores often carry topographic maps specifically designed for hiking, cycling, or other outdoor activities.
2. What is the difference between a topographic map and a regular map?
A topographic map differs from a regular map by incorporating elevation data and using contour lines to depict the terrain. A regular map primarily focuses on geographical boundaries and political features, while a topographic map provides a more comprehensive representation of the land’s three-dimensional nature.
3. How can I interpret contour lines on a topographic map?
Contour lines connect points of equal elevation. The closer the lines are together, the steeper the slope. Conversely, widely spaced lines indicate a gentler slope. By following the direction of the contour lines, one can visualize the shape of the terrain.
4. Are there different scales of topographic maps available?
Yes, topographic maps are available in various scales, ranging from large-scale maps covering small areas with greater detail to smaller-scale maps covering larger areas with less detail. The scale of the map should be chosen based on the specific purpose and area of interest.
5. How can I use a topographic map for hiking or cycling?
A topographic map is essential for planning hiking or cycling routes. It helps identify elevation changes, potential hazards, and suitable trails. By studying the map, one can assess the difficulty level of the route and choose appropriate gear and equipment.
Tips for Using a Topographic Map of Ireland
- Understand the Map’s Scale and Legend: Before using the map, familiarize yourself with its scale and legend, which explains the symbols and markings used.
- Identify Key Features: Identify prominent features like mountains, rivers, lakes, and roads to orient yourself within the map.
- Plan Your Route Carefully: Consider elevation changes, terrain features, and potential hazards when planning your route.
- Use a Compass and GPS Device: A compass and GPS device can be helpful for navigating and ensuring you stay on course.
- Be Prepared for Changing Weather Conditions: Weather conditions can change quickly, so be prepared with appropriate clothing and gear.
Conclusion
The topographic map of Ireland serves as a powerful tool for understanding and appreciating the country’s diverse and captivating landscape. It provides a visual representation of the terrain, highlighting the intricate interplay of mountains, lowlands, rivers, lakes, and coastal features. By studying the map, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the island’s geological history, its natural processes, and the unique character of its various regions. Whether used for navigation, environmental studies, land management, or educational purposes, the topographic map of Ireland remains an invaluable resource for exploring and appreciating the beauty of the Emerald Isle.
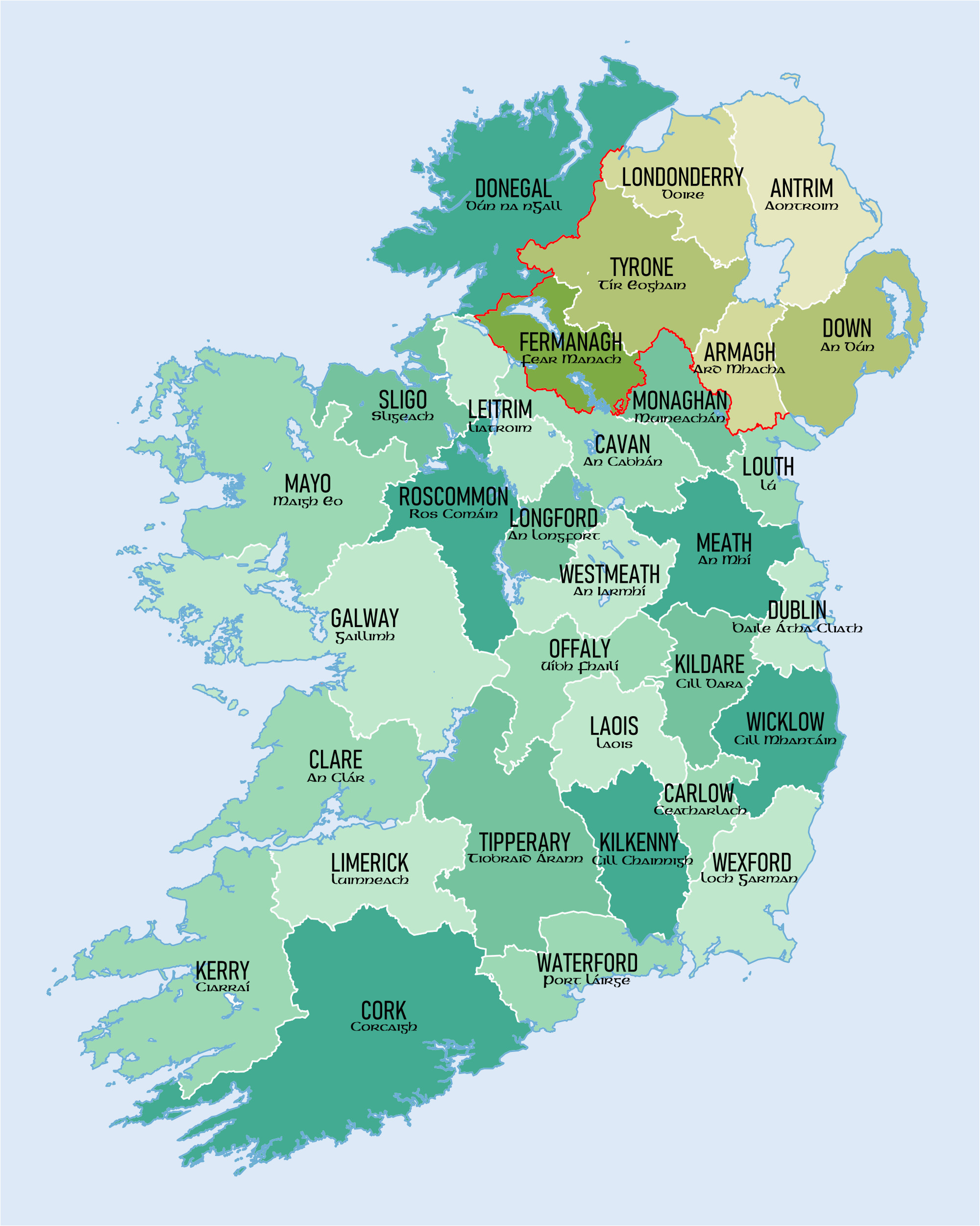
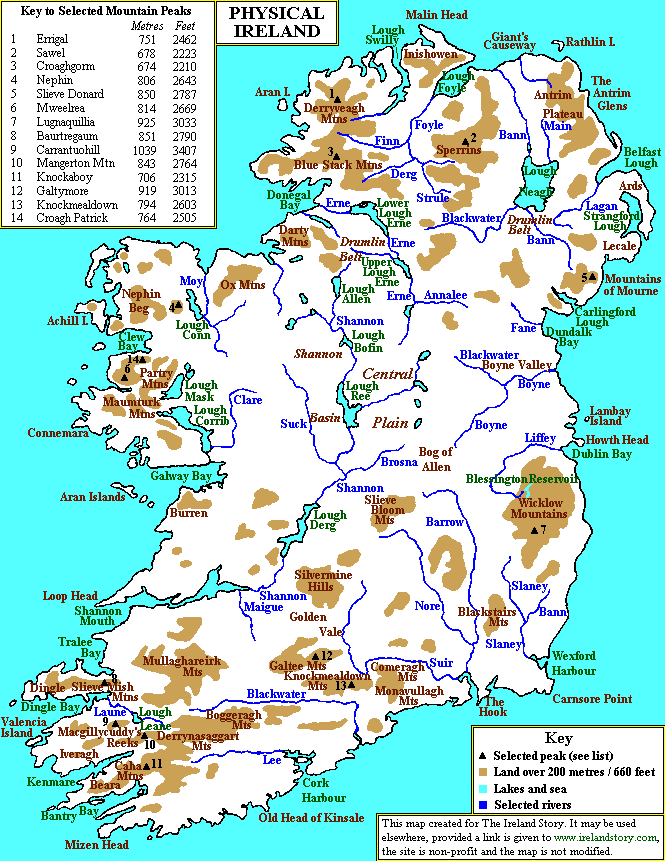


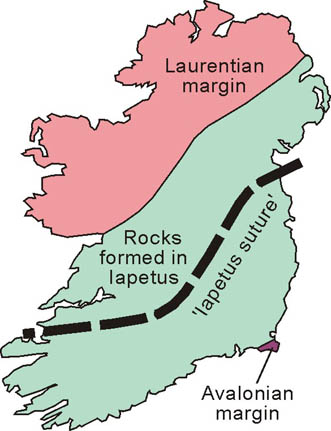



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Ireland’s Landscape: A Journey Through the Topographic Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!