Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Humidity: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the World’s Moisture Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Humidity: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the World’s Moisture Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Humidity: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the World’s Moisture Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Humidity: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the World’s Moisture Map

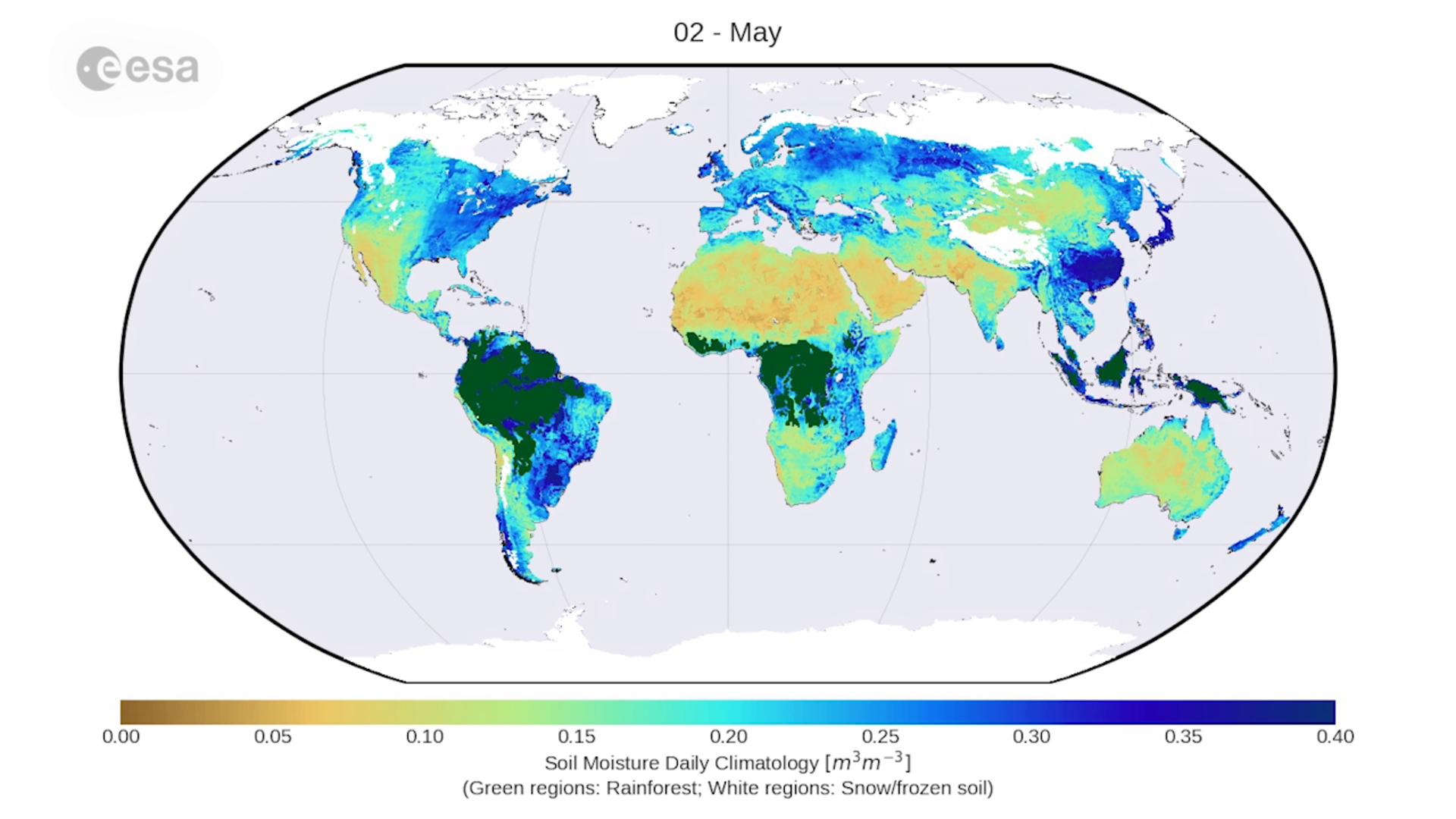
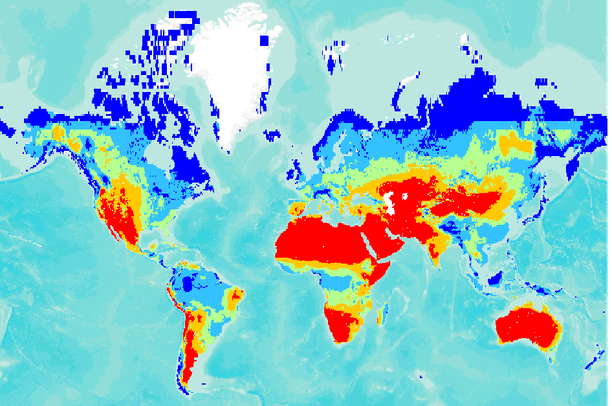
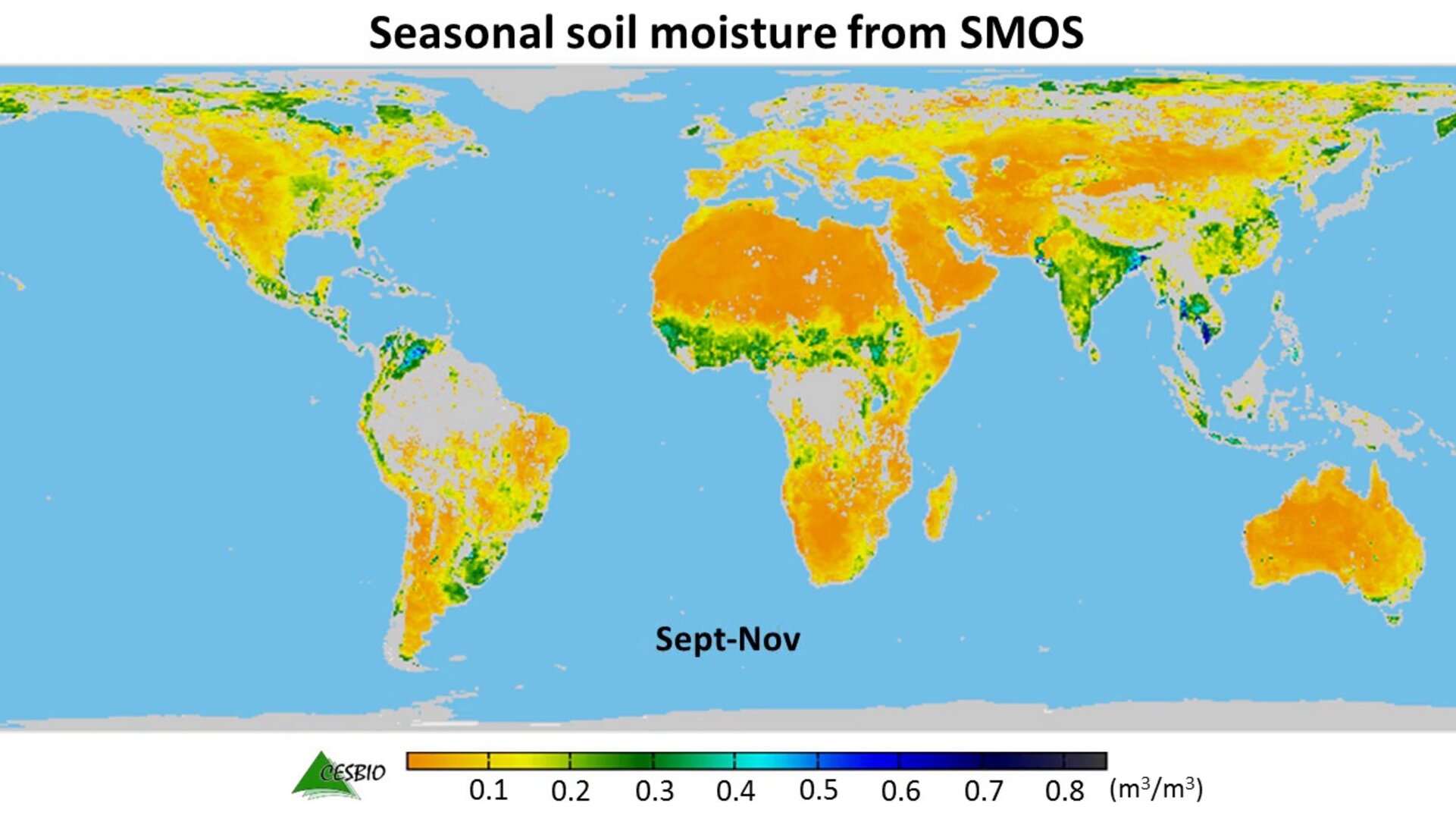
Humidity, the invisible force that shapes our weather, climate, and even our comfort, is a crucial element of Earth’s atmospheric system. It is the amount of moisture present in the air, expressed as a percentage of the maximum amount of moisture the air can hold at a given temperature. A humidity world map provides a visual representation of this invisible force, revealing the intricate patterns of moisture distribution across the globe.
Understanding the Humidity World Map: A Visual Guide to Global Moisture
The humidity world map, often depicted as a colorful globe or a series of shaded maps, illustrates the spatial variation of humidity levels across the Earth’s surface. Different colors represent varying levels of humidity, with darker shades indicating higher humidity and lighter shades indicating lower humidity. This visual representation offers a powerful tool for understanding the global distribution of moisture, its influencing factors, and its impact on various aspects of our planet.
Factors Influencing Global Humidity Distribution
The humidity world map reflects the interplay of numerous factors that influence the amount of moisture in the atmosphere. These factors include:
-
Proximity to Water Bodies: Regions near large bodies of water, such as oceans, seas, and lakes, tend to have higher humidity levels. This is because water evaporates readily, increasing the moisture content in the surrounding air.
-
Latitude: Humidity levels generally decrease with increasing latitude. This is because warmer temperatures near the equator allow the air to hold more moisture, leading to higher humidity. Conversely, colder temperatures at higher latitudes limit the air’s moisture-holding capacity, resulting in lower humidity.
-
Altitude: Humidity typically decreases with increasing altitude. This is because air pressure decreases at higher altitudes, leading to lower air density and a reduced ability to hold moisture.
-
Wind Patterns: Prevailing wind patterns play a significant role in transporting moisture across the globe. For instance, trade winds carry moisture from tropical regions towards the poles, influencing humidity levels in those areas.
-
Topography: Mountains and other elevated landforms can act as barriers to moisture flow, creating distinct patterns of humidity on either side. Windward sides, facing the prevailing winds, often experience higher humidity due to the forced ascent of moist air, while leeward sides experience lower humidity due to the descending dry air.
-
Seasonality: Humidity levels can vary significantly throughout the year, influenced by seasonal changes in temperature and precipitation patterns.
Interpreting the Humidity World Map: Unraveling the Patterns of Moisture
The humidity world map reveals fascinating patterns of moisture distribution across the globe. Some key observations include:
-
High Humidity Zones: Tropical regions near the equator, particularly those with abundant rainfall, exhibit high humidity levels throughout the year. These regions, often characterized by lush vegetation and dense rainforests, are influenced by the convergence of moist air masses and ample evaporation from warm water bodies.
-
Low Humidity Zones: Deserts and other arid regions typically exhibit low humidity levels. The lack of moisture sources, combined with high temperatures and low precipitation, contribute to the dry conditions in these areas.
-
Seasonal Variations: The humidity world map also highlights the seasonal variations in moisture distribution. During the summer months, humidity levels tend to be higher in temperate regions due to increased evaporation and precipitation. Conversely, during the winter months, humidity levels tend to be lower due to colder temperatures and reduced evaporation.
-
Regional Anomalies: The humidity world map also reveals regional anomalies, where specific locations deviate from the general patterns. For example, coastal areas may experience higher humidity levels than inland areas at the same latitude due to the proximity to large bodies of water.
The Importance of Humidity: A Vital Factor for Life and Climate
Humidity plays a crucial role in shaping our planet’s climate, ecosystems, and human well-being. Some key impacts include:
-
Climate Regulation: Humidity influences the Earth’s energy balance by affecting cloud formation, precipitation, and temperature. High humidity levels contribute to cloud formation and precipitation, which can cool the atmosphere. Conversely, low humidity levels can lead to dry conditions and extreme temperatures.
-
Ecosystem Functioning: Humidity is essential for the survival of many plants and animals. High humidity levels support lush vegetation in tropical rainforests, while low humidity levels characterize desert ecosystems.
-
Human Health: Humidity levels can significantly impact human health. High humidity can lead to heat stress and respiratory problems, while low humidity can contribute to dry skin and respiratory issues.
-
Agriculture: Humidity levels influence crop growth and yield. High humidity levels can promote plant growth but also increase the risk of fungal diseases. Low humidity levels can lead to drought conditions and crop failure.
FAQs About the Humidity World Map
1. What is the difference between relative humidity and absolute humidity?
Relative humidity is the amount of moisture in the air expressed as a percentage of the maximum amount the air can hold at a given temperature. Absolute humidity, on the other hand, is the actual amount of moisture present in the air, measured in grams per cubic meter.
2. How is humidity measured?
Humidity is typically measured using a hygrometer, which can be either a psychrometer or a hair hygrometer. A psychrometer measures the difference in temperature between a wet-bulb thermometer and a dry-bulb thermometer, while a hair hygrometer measures the expansion and contraction of human hair in response to changes in humidity.
3. How does humidity affect weather patterns?
Humidity plays a crucial role in weather patterns by influencing cloud formation, precipitation, and temperature. High humidity levels contribute to cloud formation and precipitation, which can cool the atmosphere. Conversely, low humidity levels can lead to dry conditions and extreme temperatures.
4. What are the health implications of high and low humidity?
High humidity levels can lead to heat stress and respiratory problems, while low humidity levels can contribute to dry skin and respiratory issues.
5. How does humidity affect agriculture?
Humidity levels influence crop growth and yield. High humidity levels can promote plant growth but also increase the risk of fungal diseases. Low humidity levels can lead to drought conditions and crop failure.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing the Humidity World Map
-
Explore the map interactively: Utilize online interactive maps that allow you to zoom in and out, view different time periods, and compare data from different regions.
-
Consider the context: When interpreting the humidity world map, consider the geographical location, season, and other factors that might influence humidity levels.
-
Relate humidity to other climate variables: Analyze the humidity map in conjunction with other climate variables, such as temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the global climate system.
-
Apply the information to real-world scenarios: Utilize the humidity world map to understand the impact of humidity on various aspects of life, such as agriculture, health, and climate change.
Conclusion
The humidity world map provides a powerful visual tool for understanding the global distribution of moisture, its influencing factors, and its impact on various aspects of our planet. By revealing the intricate patterns of moisture distribution, the humidity world map underscores the importance of humidity as a crucial factor shaping our weather, climate, and even our comfort. As we continue to grapple with the challenges of climate change, understanding and utilizing the information provided by the humidity world map becomes increasingly important for mitigating its impacts and ensuring a sustainable future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Humidity: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the World’s Moisture Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!