Unveiling the Power of 3D Map Software: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of 3D Map Software: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of 3D Map Software: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of 3D Map Software: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Power of 3D Map Software: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Defining 3D Map Software: Beyond Flat Representations
- 3.2 Key Features of 3D Map Software: A Deeper Dive
- 3.3 Benefits of 3D Map Software: Unveiling the Potential
- 3.4 Applications of 3D Map Software: A Diverse Landscape
- 3.5 FAQs about 3D Map Software: Addressing Common Concerns
- 3.6 Tips for Using 3D Map Software Effectively: Maximizing Potential
- 3.7 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of 3D Map Software
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Power of 3D Map Software: A Comprehensive Guide
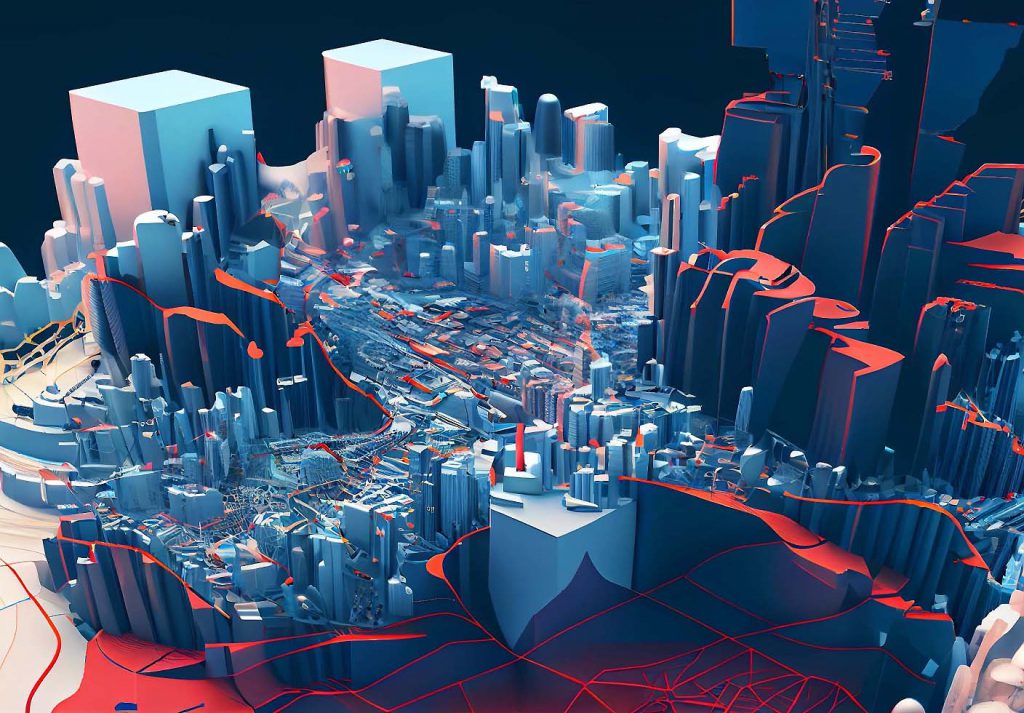
In the contemporary digital landscape, the ability to visualize and interact with data in a three-dimensional space is paramount. This is where 3D map software emerges as a powerful tool, revolutionizing how we understand, analyze, and communicate spatial information. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of this technology, exploring its features, benefits, applications, and future prospects.
Defining 3D Map Software: Beyond Flat Representations
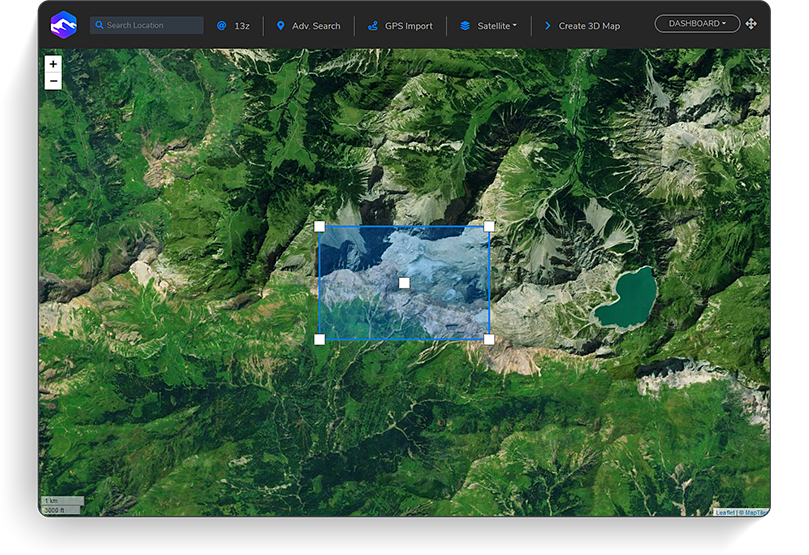
3D map software transcends the limitations of traditional, two-dimensional maps. It utilizes advanced algorithms and rendering techniques to create immersive, interactive representations of real-world environments. These digital twins capture the complexities of topography, infrastructure, buildings, and even the flow of people and vehicles. This enhanced visualization allows for a deeper understanding of spatial relationships, facilitating informed decision-making across various domains.
Key Features of 3D Map Software: A Deeper Dive
-
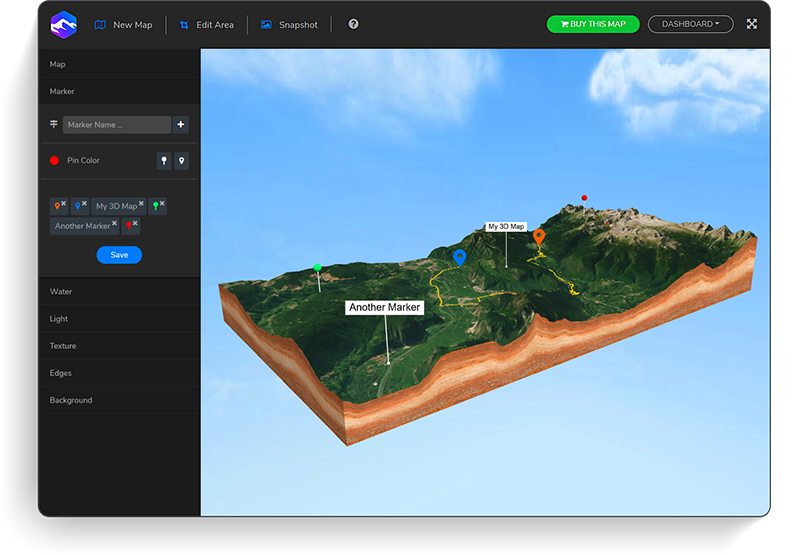
3D Modeling and Rendering: The foundation of 3D map software lies in its ability to create realistic representations of landscapes, buildings, and other objects. This involves converting data from various sources, such as aerial imagery, LiDAR scans, and CAD models, into a 3D digital model. Advanced rendering techniques, employing shaders and textures, enhance the visual fidelity, bringing the virtual world to life.
-
Interactive Exploration: Unlike static maps, 3D map software enables users to explore the virtual environment freely. Users can pan, zoom, rotate, and even fly through the 3D space, gaining a comprehensive perspective. This interactivity allows for a more engaging and intuitive understanding of spatial relationships.
-
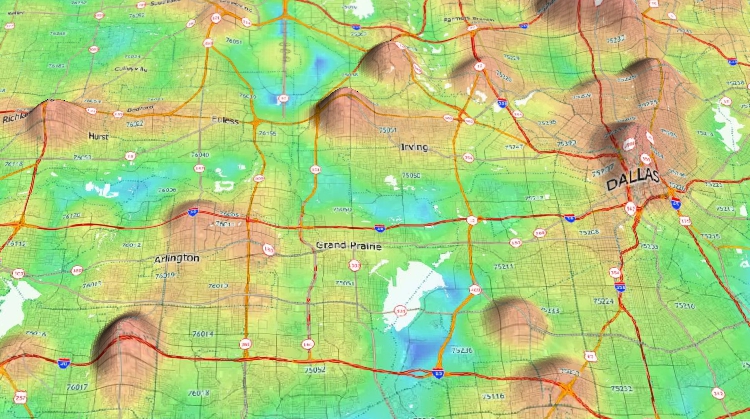
Data Visualization and Analysis: 3D map software goes beyond mere visualization, offering powerful tools for data analysis. Users can overlay various data layers, such as population density, crime rates, or traffic flow, onto the 3D model. This data integration facilitates spatial analysis, enabling the identification of patterns and trends, and informing decision-making.
-
Collaboration and Sharing: Many 3D map software platforms offer collaborative features, allowing multiple users to work on projects simultaneously. They also provide tools for sharing and publishing 3D maps, facilitating communication and knowledge dissemination. This collaborative aspect enables stakeholders to visualize and discuss complex projects, fostering better understanding and alignment.
-
Integration with Other Systems: 3D map software seamlessly integrates with other systems, such as GIS platforms, CAD software, and BIM models. This integration allows for a holistic view of data from different sources, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of the project or environment.
Benefits of 3D Map Software: Unveiling the Potential
-
Enhanced Visualization and Understanding: 3D map software provides a more intuitive and engaging way to visualize spatial information, leading to a deeper understanding of the environment. This enhanced understanding can facilitate better decision-making in various fields.
-
Improved Communication and Collaboration: The interactive nature of 3D maps fosters better communication and collaboration among stakeholders. By visualizing complex projects in a shared 3D space, teams can achieve greater alignment and understanding, leading to improved outcomes.
-
Data-Driven Insights and Analytics: The integration of data layers with 3D models allows for powerful spatial analysis. This data-driven approach enables the identification of patterns, trends, and insights that might be missed in traditional 2D maps, leading to more informed decision-making.
-
Increased Efficiency and Productivity: 3D map software can streamline workflows by providing a centralized platform for data visualization, analysis, and collaboration. This efficiency translates into faster project completion and reduced costs.
-
Innovation and New Possibilities: 3D map software paves the way for innovative applications and solutions in various sectors. From urban planning and disaster management to environmental monitoring and virtual reality experiences, the possibilities are vast and continuously evolving.
Applications of 3D Map Software: A Diverse Landscape
-
Urban Planning and Development: 3D map software plays a crucial role in urban planning, enabling planners to visualize proposed developments, assess their impact on the surrounding environment, and optimize infrastructure. This technology facilitates the creation of sustainable and livable cities.
-
Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC): 3D map software is widely used in the AEC industry for building information modeling (BIM), enabling architects, engineers, and contractors to design, visualize, and manage complex projects. This technology promotes collaboration, reduces errors, and optimizes project efficiency.
-
Environmental Monitoring and Management: 3D map software aids in environmental monitoring and management by visualizing land use patterns, pollution levels, and other environmental data. This information can inform decision-making for conservation efforts, pollution control, and sustainable resource management.
-
Disaster Management and Emergency Response: 3D map software facilitates disaster planning and response by visualizing evacuation routes, identifying vulnerable areas, and tracking the spread of natural hazards. This technology enables faster and more effective disaster response, saving lives and minimizing damage.
-
Education and Training: 3D map software provides interactive and engaging learning experiences in various fields, such as geography, history, and environmental science. These virtual environments allow students to explore different locations and concepts in an immersive and interactive way.
-
Tourism and Entertainment: 3D map software is used to create virtual tours of historical sites, landmarks, and natural wonders, enhancing the tourism experience. It is also employed in the entertainment industry for creating immersive virtual reality experiences.
FAQs about 3D Map Software: Addressing Common Concerns
1. What are the different types of 3D map software available?
The market offers a wide range of 3D map software, catering to specific needs and budgets. Some prominent categories include:
- Desktop Software: These are standalone applications that are installed on a computer. Examples include ArcGIS Pro, Autodesk Revit, and Trimble SketchUp.
- Web-Based Platforms: These are cloud-based platforms accessible through a web browser. Examples include Google Earth Pro, Cesium, and Mapbox.
- Mobile Applications: These are apps designed for smartphones and tablets, offering on-the-go access to 3D maps. Examples include Google Maps, Citymapper, and Wikitude.
2. What are the key factors to consider when choosing 3D map software?
Choosing the right 3D map software depends on specific needs and requirements. Consider factors such as:
- Features and Functionality: Assess the software’s capabilities in terms of 3D modeling, data visualization, analysis, and collaboration.
- Data Sources and Formats: Determine the software’s compatibility with various data sources, including aerial imagery, LiDAR scans, and CAD models.
- User Interface and Ease of Use: Evaluate the software’s user interface and how intuitive it is for users of varying technical expertise.
- Pricing and Licensing: Consider the cost of the software, including licensing fees, subscription models, and maintenance costs.
- Support and Documentation: Assess the availability of technical support, online documentation, and community resources.
3. What are the limitations of 3D map software?
While 3D map software offers significant advantages, it also has certain limitations:
- Data Availability and Accuracy: The quality and accuracy of 3D models depend on the availability and accuracy of source data. Incomplete or inaccurate data can lead to inaccuracies in the 3D representation.
- Computational Requirements: Rendering and manipulating complex 3D models can require significant computational resources, potentially limiting accessibility for users with limited hardware.
- Security and Privacy: When using cloud-based platforms, data security and privacy become crucial considerations. Ensure that the chosen platform adheres to industry standards and best practices.
- Cost and Complexity: Implementing and using 3D map software can be expensive and complex, requiring specialized skills and knowledge.
4. How can I learn more about 3D map software?
Numerous resources are available for learning about 3D map software:
- Online Courses and Tutorials: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Skillshare offer courses and tutorials on 3D mapping and related technologies.
- Vendor Documentation and Support: Software vendors typically provide comprehensive documentation, online tutorials, and technical support.
- Industry Conferences and Events: Attending industry events and conferences provides opportunities to learn from experts and network with professionals in the field.
Tips for Using 3D Map Software Effectively: Maximizing Potential
-
Define Clear Objectives: Before using 3D map software, clearly define the project’s goals and objectives. This will help you choose the right software and features for your specific needs.
-
Ensure Data Quality and Accuracy: The quality of your 3D model depends heavily on the accuracy and completeness of the source data. Ensure that the data used for 3D modeling is reliable and up-to-date.
-
Optimize for Performance: Rendering and manipulating complex 3D models can be computationally demanding. Optimize your workflow and settings to ensure smooth performance and avoid bottlenecks.
-
Collaborate Effectively: Leverage the collaborative features of 3D map software to facilitate communication and knowledge sharing among stakeholders. This will ensure everyone is on the same page and working towards common goals.
-
Stay Updated with Industry Trends: The field of 3D mapping is constantly evolving. Stay informed about new technologies, software updates, and best practices to remain competitive and leverage the latest advancements.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of 3D Map Software
3D map software has emerged as a powerful tool for visualizing, analyzing, and communicating spatial information. Its versatility, data-driven insights, and collaborative capabilities are transforming various industries, from urban planning and architecture to environmental monitoring and disaster management. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications and solutions powered by 3D map software, further enhancing our understanding and interaction with the world around us.
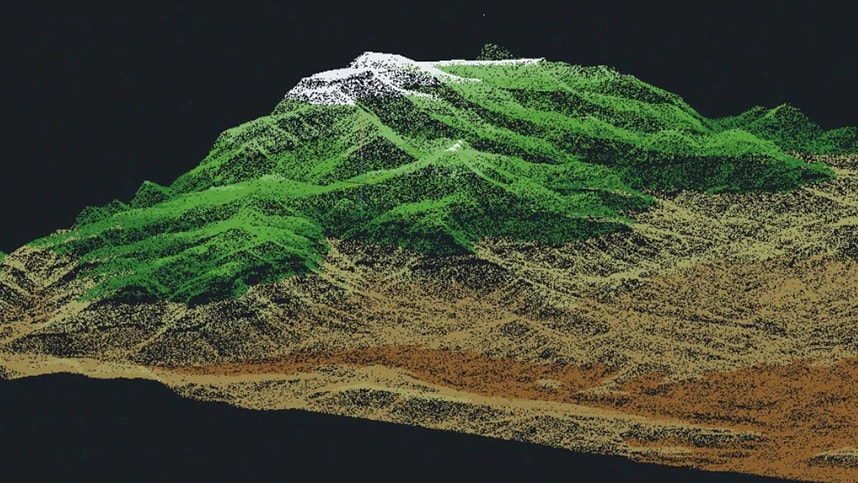

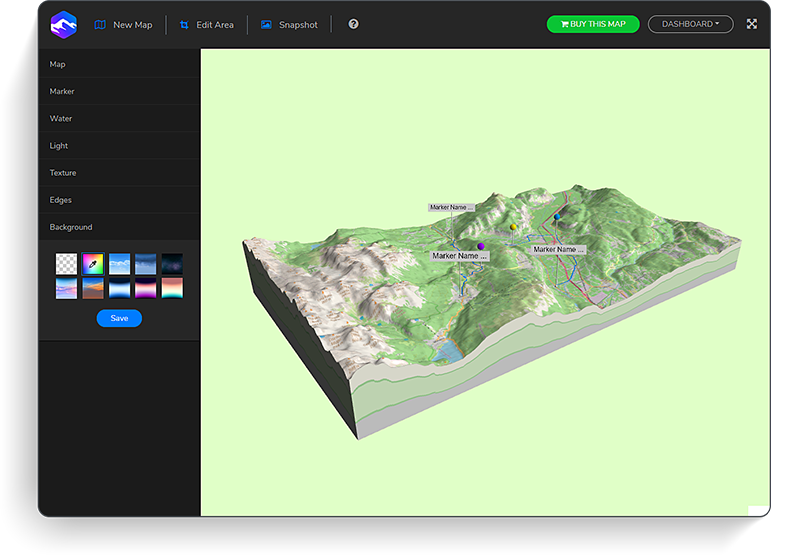
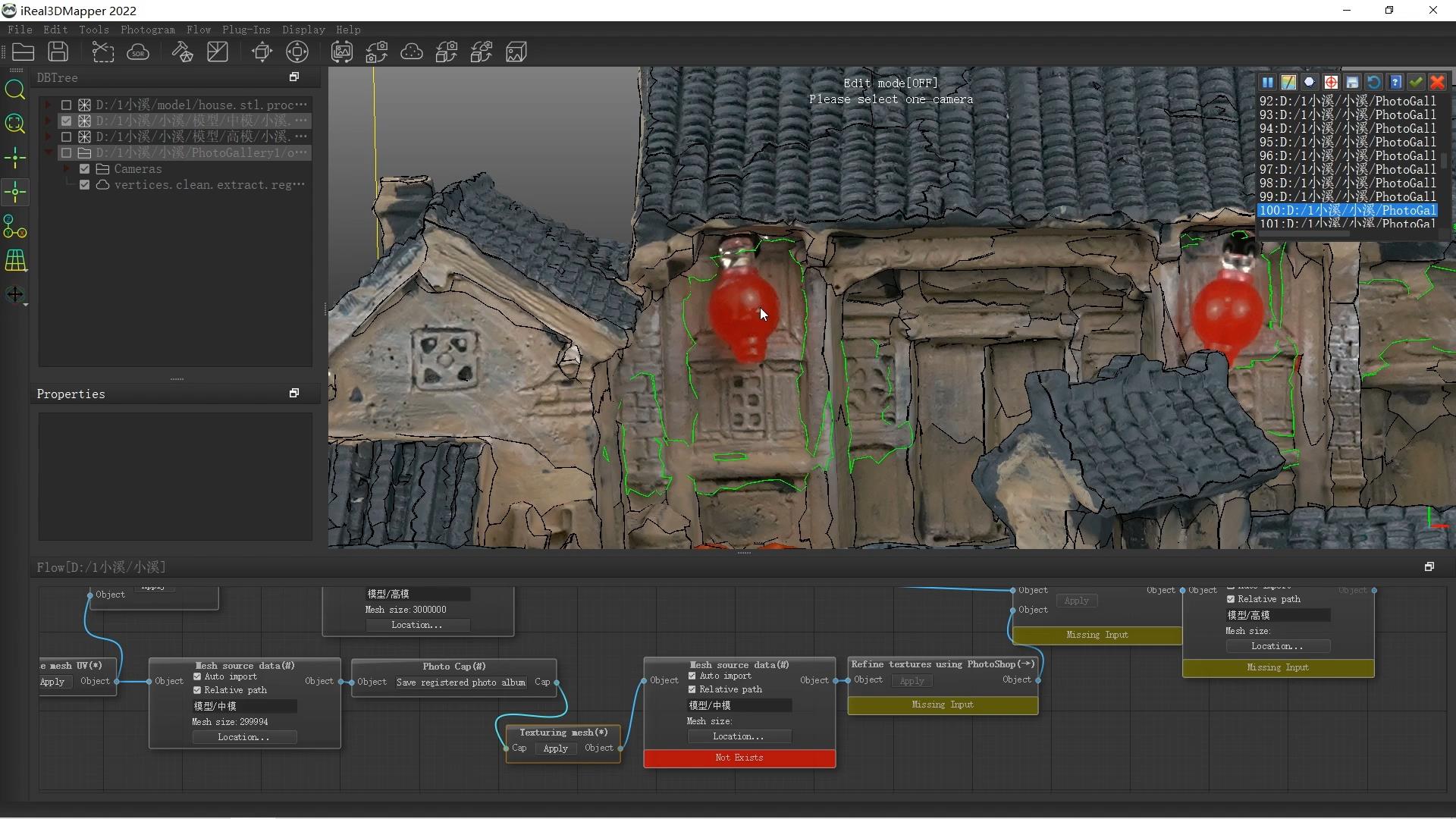
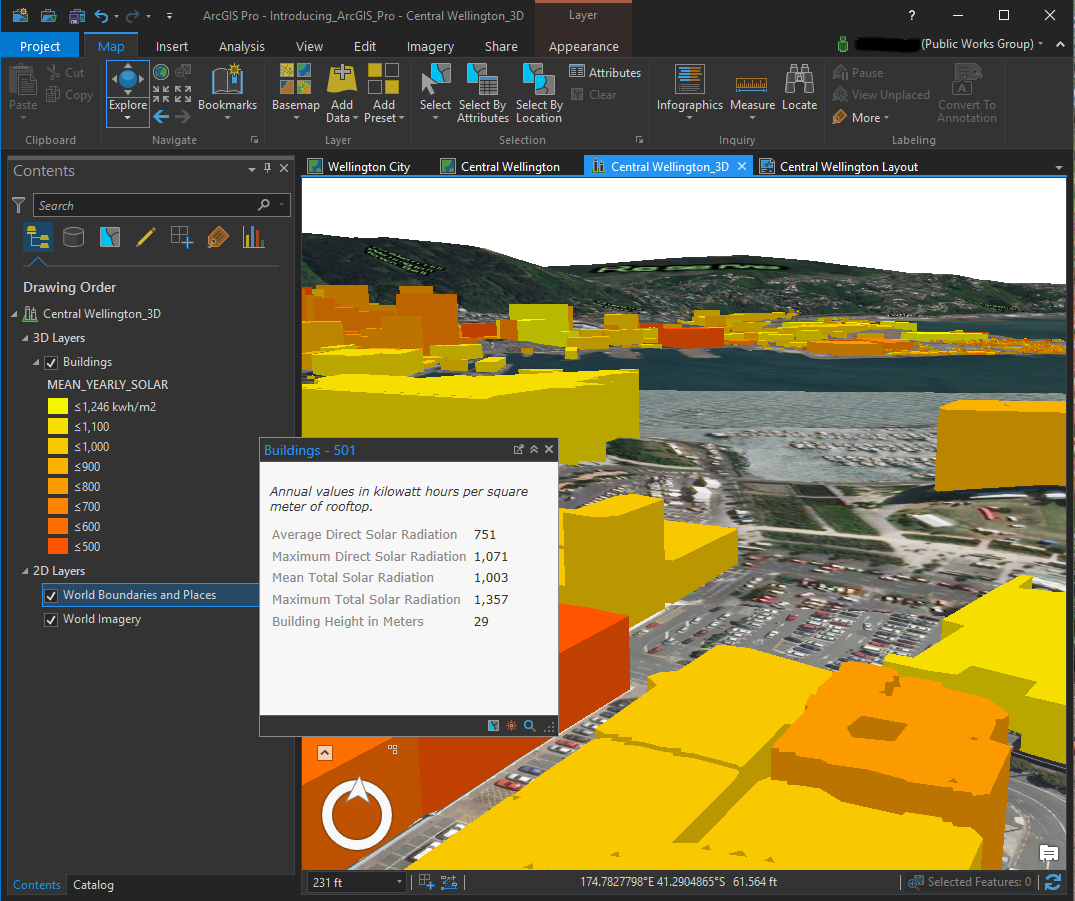

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of 3D Map Software: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!